Using SQL Server Agent
With Amazon RDS, you can use SQL Server Agent on a DB instance running Microsoft SQL Server Enterprise Edition, Standard Edition, or Web Edition. SQL Server Agent is a Microsoft Windows service that runs scheduled administrative tasks that are called jobs. You can use SQL Server Agent to run T-SQL jobs to rebuild indexes, run corruption checks, and aggregate data in a SQL Server DB instance.
When you create a SQL Server DB instance, the master user is enrolled in the SQLAgentUserRole role.
SQL Server Agent can run a job on a schedule, in response to a specific event, or on demand. For more information, see SQL Server Agent
Note
Avoid scheduling jobs to run during the maintenance and backup windows for your DB instance. The maintenance and backup processes that are launched by Amazon could interrupt a job or cause it to be canceled.
In Multi-AZ deployments, SQL Server Agent jobs are replicated from the primary host to the secondary host when the job replication feature is turned on. For more information, see Turning on SQL Server Agent job replication.
Multi-AZ deployments have a limit of 10,000 SQL Server Agent jobs. If you need a higher limit, request an increase by
contacting Amazon Web Services Support. Open the Amazon Web Services Support Center
To view the history of an individual SQL Server Agent job in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), open Object Explorer, right-click the job, and then choose View History.
Because SQL Server Agent is running on a managed host in a DB instance, some actions aren't supported:
-
Running replication jobs and running command-line scripts by using ActiveX, Windows command shell, or Windows PowerShell aren't supported.
-
You can't manually start, stop, or restart SQL Server Agent.
-
Email notifications through SQL Server Agent aren't available from a DB instance.
-
SQL Server Agent alerts and operators aren't supported.
-
Using SQL Server Agent to create backups isn't supported. Use Amazon RDS to back up your DB instance.
Turning on SQL Server Agent job replication
You can turn on SQL Server Agent job replication by using the following stored procedure:
EXECUTE msdb.dbo.rds_set_system_database_sync_objects @object_types = 'SQLAgentJob';
You can run the stored procedure on all SQL Server versions supported by Amazon RDS for SQL Server. Jobs in the following categories are replicated:
-
[Uncategorized (Local)]
-
[Uncategorized (Multi-Server)]
-
[Uncategorized]
-
Data Collector
-
Database Engine Tuning Advisor
-
Database Maintenance
-
Full-Text
Only jobs that use T-SQL job steps are replicated. Jobs with step types such as SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS), Replication, and PowerShell aren't replicated. Jobs that use Database Mail and server-level objects aren't replicated.
Important
The primary host is the source of truth for replication. Before turning on job replication, make sure that your SQL Server Agent jobs are on the primary. If you don't do this, it could lead to the deletion of your SQL Server Agent jobs if you turn on the feature when newer jobs are on the secondary host.
You can use the following function to confirm whether replication is turned on.
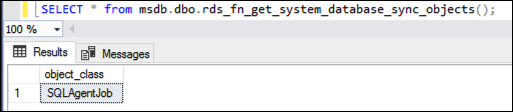
SELECT * from msdb.dbo.rds_fn_get_system_database_sync_objects();
The T-SQL query returns the following if SQL Server Agent jobs are replicating. If they're not replicating, it
returns nothing for object_class.
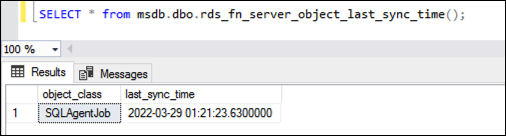
You can use the following function to find the last time objects were synchronized in UTC time.
SELECT * from msdb.dbo.rds_fn_server_object_last_sync_time();
For example, suppose that you modify a SQL Server Agent job at 01:00. You expect the most recent synchronization time to be after 01:00, indicating that synchronization has taken place.
After synchronization, the values returned for date_created and date_modified on the secondary node are expected to match.
If you are also using tempdb replication, you can enable replication for both SQL Agent jobs and the tempdb
configuration by providing them in the @object_type parameter:
EXECUTE msdb.dbo.rds_set_system_database_sync_objects @object_types = 'SQLAgentJob,TempDbFile';
For more information on tempdb replication, see TempDB configuration for Multi-AZ deployments.
Adding a user to the SQLAgentUser role
To allow an additional login or user to use SQL Server Agent, log in as the master user and do the following:
-
Create another server-level login by using the
CREATE LOGINcommand. -
Create a user in
msdbusingCREATE USERcommand, and then link this user to the login that you created in the previous step. -
Add the user to the
SQLAgentUserRoleusing thesp_addrolemembersystem stored procedure.
For example, suppose that your master user name is admin
and you want to give access to SQL Server Agent to a user named
theirname with a password
theirpassword. In that case, you can use the following
procedure.
To add a user to the SQLAgentUser role
-
Log in as the master user.
-
Run the following commands:
--Initially set context to master database USE [master]; GO --Create a server-level login named theirname with password theirpassword CREATE LOGIN [theirname] WITH PASSWORD = 'theirpassword'; GO --Set context to msdb database USE [msdb]; GO --Create a database user named theirname and link it to server-level login theirname CREATE USER [theirname] FOR LOGIN [theirname]; GO --Added database user theirname in msdb to SQLAgentUserRole in msdb EXEC sp_addrolemember [SQLAgentUserRole], [theirname];
Deleting a SQL Server Agent job
You use the sp_delete_job stored procedure to delete SQL Server Agent jobs on Amazon RDS for Microsoft SQL Server.
You can't use SSMS to delete SQL Server Agent jobs. If you try to do so, you get an error message similar to the following:
The EXECUTE permission was denied on the object 'xp_regread', database 'mssqlsystemresource', schema 'sys'.
As a managed service, RDS is restricted from running procedures that access the Windows registry. When you use SSMS, it
tries to run a process (xp_regread) for which RDS isn't authorized.
Note
On RDS for SQL Server, only members of the sysadmin role are allowed to update or delete jobs owned by a different login.
To delete a SQL Server Agent job
-
Run the following T-SQL statement:
EXEC msdb..sp_delete_job @job_name = 'job_name';