用于排查无法访问的 Windows 实例问题的常见屏幕截图
可以根据服务返回的屏幕截图,利用以下信息帮助对无法访问的 Windows 实例进行故障排除。
登录屏幕 (Ctrl+Alt+Delete)
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。
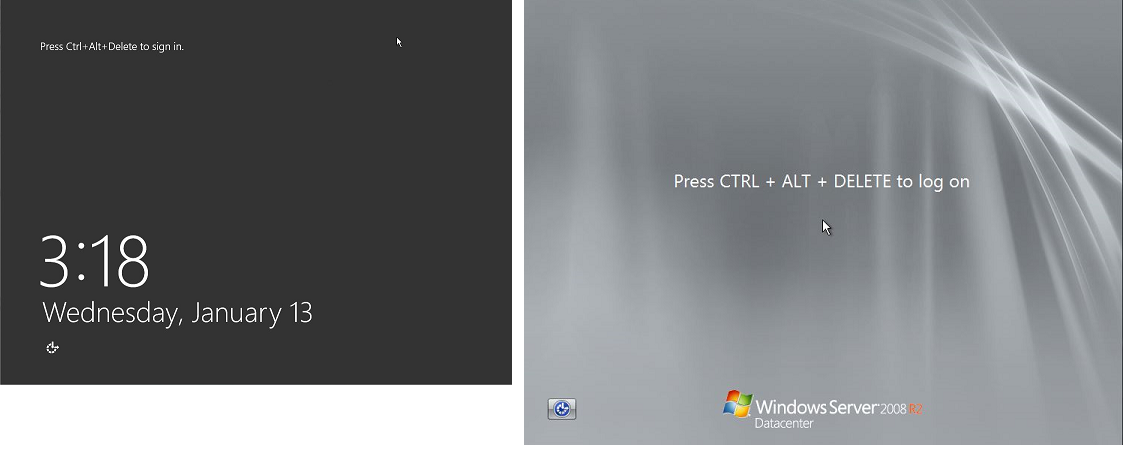
如果实例在登录时无法访问,可能是因为网络配置或 Windows 远程桌面服务存在问题。如果某个进程占用了大量 CPU,实例也可能没有响应。
网络配置
使用以下信息验证您的 Amazon、Microsoft Windows 和本地(或内部部署)网络配置是否阻止了对实例的访问。
| 配置 | 验证 |
|---|---|
| 安全组配置 | 验证端口 3389 是否向您的安全组开放。验证您是否连接到正确的公有 IP 地址。如果实例未与弹性 IP 关联,公有 IP 就会在实例停止或启动后发生更改。有关更多信息,请参阅远程桌面无法连接到远程计算机。 |
| VPC 配置 (网络 ACL) | 验证您的 Amazon VPC 的访问控制列表 (ACL) 是否阻止访问。有关信息,请参阅 Amazon VPC 用户指南 中的网络 ACL。 |
| VPN 配置 | 如果您使用虚拟专用网络(VPN)连接您的 VPC,请验证 VPN 隧道的连通性。有关更多信息,请参阅 Troubleshooting Amazon Client VPN: Tunnel connectivity issues to a VPC。 |
| 配置 | 验证 |
|---|---|
| Windows 防火墙 | 验证 Windows 防火墙是否阻止与您的实例建立连接。按照远程桌面故障排除部分第 7 项的说明禁用 Windows 防火墙:远程桌面无法连接到远程计算机。 |
| 高级 TCP/IP 配置 (使用静态 IP) | 实例可能因您配置了静态 IP 地址而没有响应。对于 VPC,请创建网络接口并将其连接到实例。 |
本地或内部部署网络配置
验证本地网络配置是否阻止访问。尝试连接无法访问的实例所在 VPC 中的其他实例。如果您无法访问其他实例,请联系本地网络管理员确定是否有本地策略限制了访问。
远程桌面服务问题
如果实例在登录时无法访问,可能是因为实例存在远程桌面服务 (RDS) 问题。
提示
您可以使用 AWSSupport-TroubleshootRDP 运行手册检查和修改可能影响远程桌面协议 (RDP) 连接的各种设置。有关更多信息,请参阅 Amazon Systems Manager Automation 运行手册参考中的 AWSSupport-TroubleshootRDP。
| 配置 | 验证 |
|---|---|
| RDS 正在运行 | 验证实例上的 RDS 是否在运行。使用 Microsoft 管理控制台 (MMC) 的服务管理单元 (services.msc) 连接实例。在服务列表中,验证Remote Desktop Services (远程桌面服务) 是否处于正在运行状态。如果不是,请将其开启,然后将启动类型设置为 Automatic。如果使用服务管理单元无法连接到实例,请将根卷从该实例分离并为其创建快照或 AMI,将原始卷作为辅助卷附加到同一个可用区中的其他实例,并修改 Start |
| RDS 已启用 |
即使该服务已启动,它也有可能被禁用。将根卷从实例分离并为其创建快照或 AMI,将原始卷作为辅助卷挂载到同一个可用区中的其他实例,然后按照 在具有远程注册表的 EC2 实例上启用远程桌面中的说明,通过修改 Terminal Server (终端服务器) 注册表项来启用该服务。 完成后,请重新将根卷附加到原始实例。 |
较高的 CPU 使用率
使用 Amazon CloudWatch 检查您实例上的 CPUUtilization (Maximum) 指标。如果 CPUUtilization (Maximum) 的值比较大,请等待 CPU 使用率下降后尝试重新连接。CPU 使用率高可能由以下原因导致:
-
Windows 更新
-
安全软件扫描
-
自定义启动脚本
-
任务计划程序
有关更多信息,请参阅 Amazon CloudWatch 用户指南 中的获取特定资源的统计信息。有关其他故障排除提示,请参阅 Windows 启动后,CPU 使用率短时增高(仅限 Windows 实例)。
恢复控制台屏幕
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。
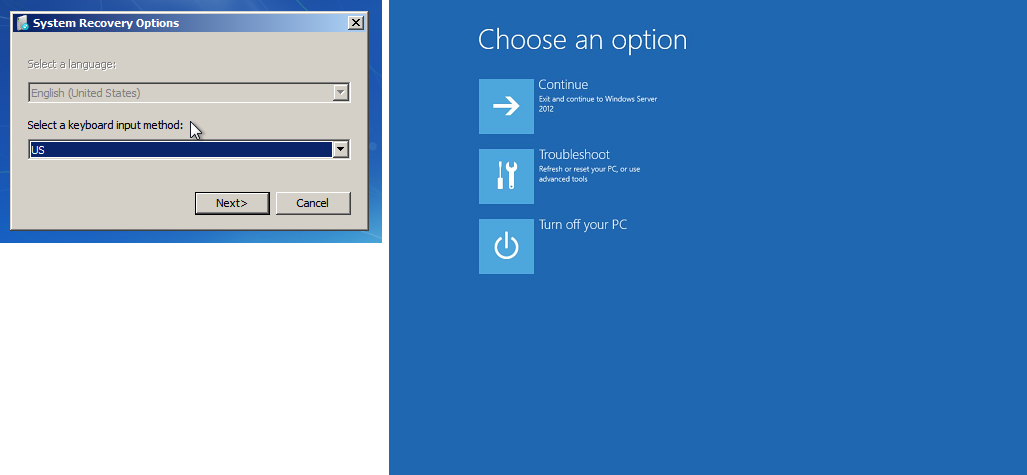
如果 bootstatuspolicy 未设置为 ignoreallfailures,操作系统可能启动至“Recovery”(恢复)控制台,并停滞在这一状态。请按照以下步骤将 bootstatuspolicy 配置更改为 ignoreallfailures。
默认情况下,Amazon 提供的公有 Windows AMI 的策略配置设置为 ignoreallfailures。
-
停止无法访问的实例。
-
创建根卷的快照。根卷是作为
/dev/sda1附加到实例的。将根卷从无法访问的实例分离并为其创建快照或 AMI,然后将根卷作为辅助卷附加到同一个可用区中的其他实例。
警告
如果您的临时实例和原始实例是使用相同的 AMI 启动的,则您必须完成额外步骤,否则在您恢复原始实例的根卷之后,由于磁盘签名冲突,您将无法启动该原始实例。如果您必须使用相同的 AMI 创建临时实例,为了避免磁盘签名冲突,请完成 磁盘签名冲突 中的步骤。
或者,可以为临时实例选择不同的 AMI。例如,如果原始实例使用适用于 Windows Server 2016 的 AMI,则使用适用于 Windows Server 2019 的 AMI 来启动临时实例。
-
登录实例并从命令提示符运行以下命令,以将
bootstatuspolicy配置更改为ignoreallfailures。bcdedit /storeDrive Letter:\boot\bcd /set {default} bootstatuspolicy ignoreallfailures -
重新将卷附加到无法访问的实例并重新启动实例。
Windows 引导管理器屏幕
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。
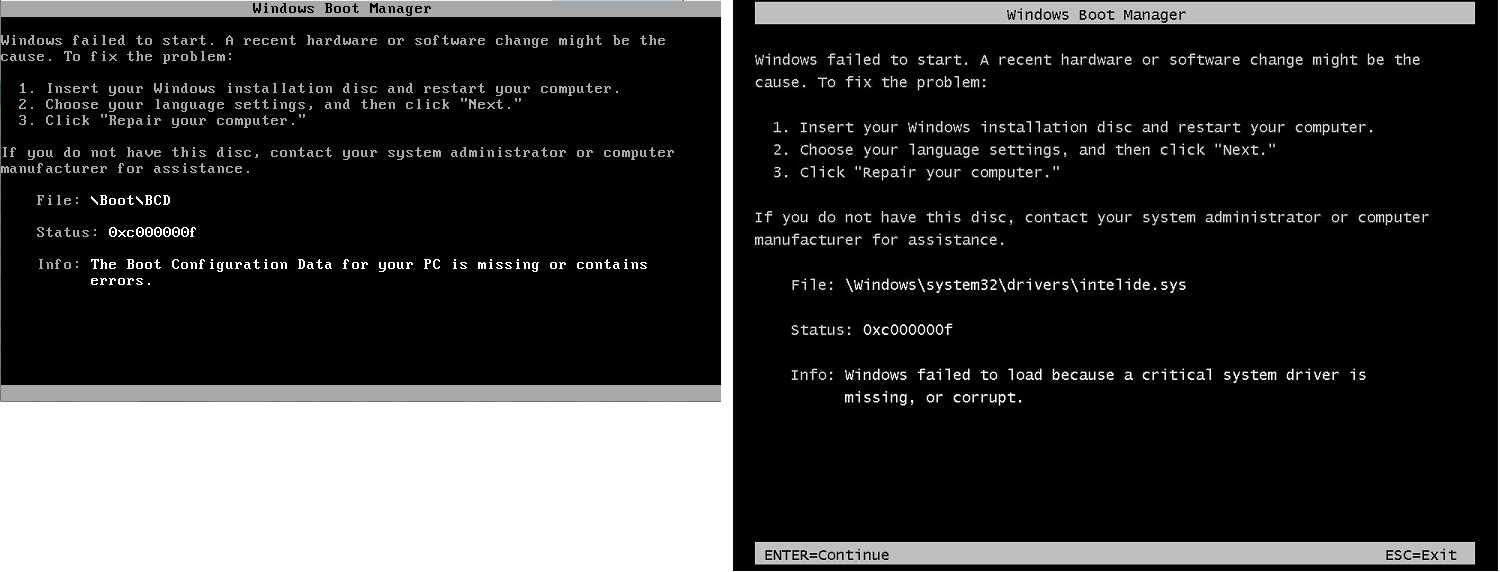
操作系统的系统文件和/或注册表遭到严重损坏。当实例停滞在这一状态时,您应该从最近备份的 AMI 恢复实例或启动一个替代实例。如果您需要访问实例上的数据,请将所有根卷从无法访问的实例上分离并为这些卷创建快照或 AMI,然后将其作为辅助卷附加到同一个可用区中的其他实例。
Sysprep 屏幕
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。
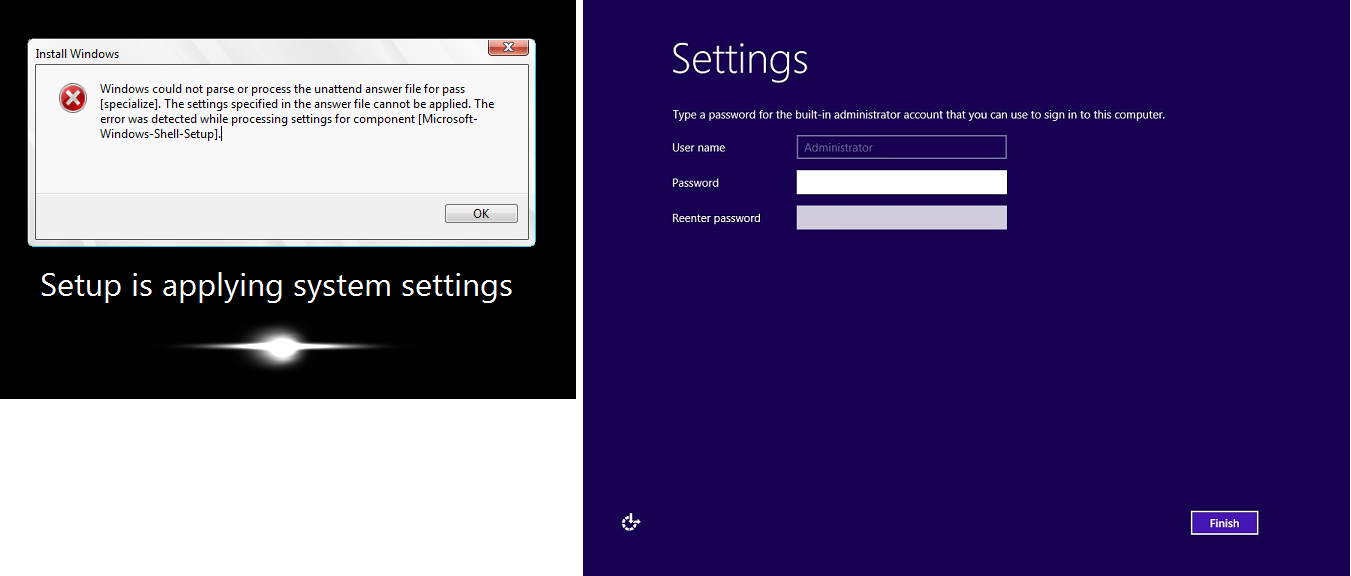
如果您没有使用 EC2Config 服务调用 Sysprep,或者操作系统在运行 Sysprep 时出现故障,您可能会看到此屏幕。您可以使用 EC2Rescue 重置密码。否则,请参阅使用 Windows Sysprep 创建 Amazon EC2 AMI。
Getting Ready 屏幕
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。
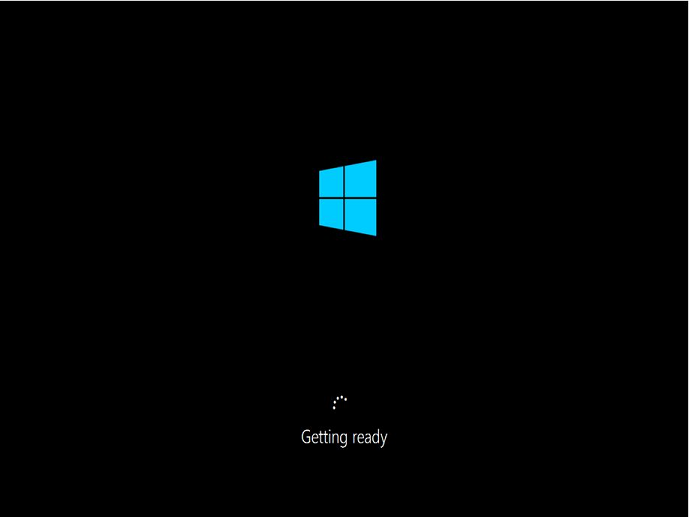
反复刷新实例控制台屏幕截图服务,验证环形进度条是否转动。如果环形进度条转动,请等待操作系统启动。您也可以使用 Amazon CloudWatch 查看您实例上的 CPUUtilization (Maximum) 指标,以确认操作系统是否处于活动状态。如果环形进度条不转,则实例可能停滞在启动过程。重启实例。如果重新启动无法解决问题,请从最近备份的 AMI 中恢复实例或启动一个替代实例。如果需要访问实例上的数据,请将根卷从无法访问的实例中分离,并为其创建快照或 AMI。然后,将根卷作为辅助卷附加到同一个可用区中的其他实例。
Windows Update 屏幕
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。

Windows 更新进程正在更新注册表。请等待更新完成。请勿在更新期间重新启动或停止实例,因为这可能会导致数据损坏。
注意
在更新时,Windows 更新进程会占用服务器上的资源。若您频繁遇到这一问题,可以考虑使用速度更快的实例类型和 EBS 卷。
Chkdsk
控制台屏幕截图服务返回以下截图。
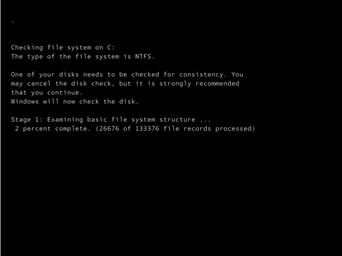
Windows 正在驱动器上运行 chkdsk 系统工具,以验证文件系统的完整性并修复逻辑文件系统错误。请等待该进程完成。