Get the status of a Spot Instance request
To help you track your Spot Instance requests and plan your use of Spot Instances, use the request status provided by Amazon EC2. For example, the request status can provide the reason why your Spot request isn't fulfilled yet, or list the constraints that are preventing the fulfillment of your Spot request.
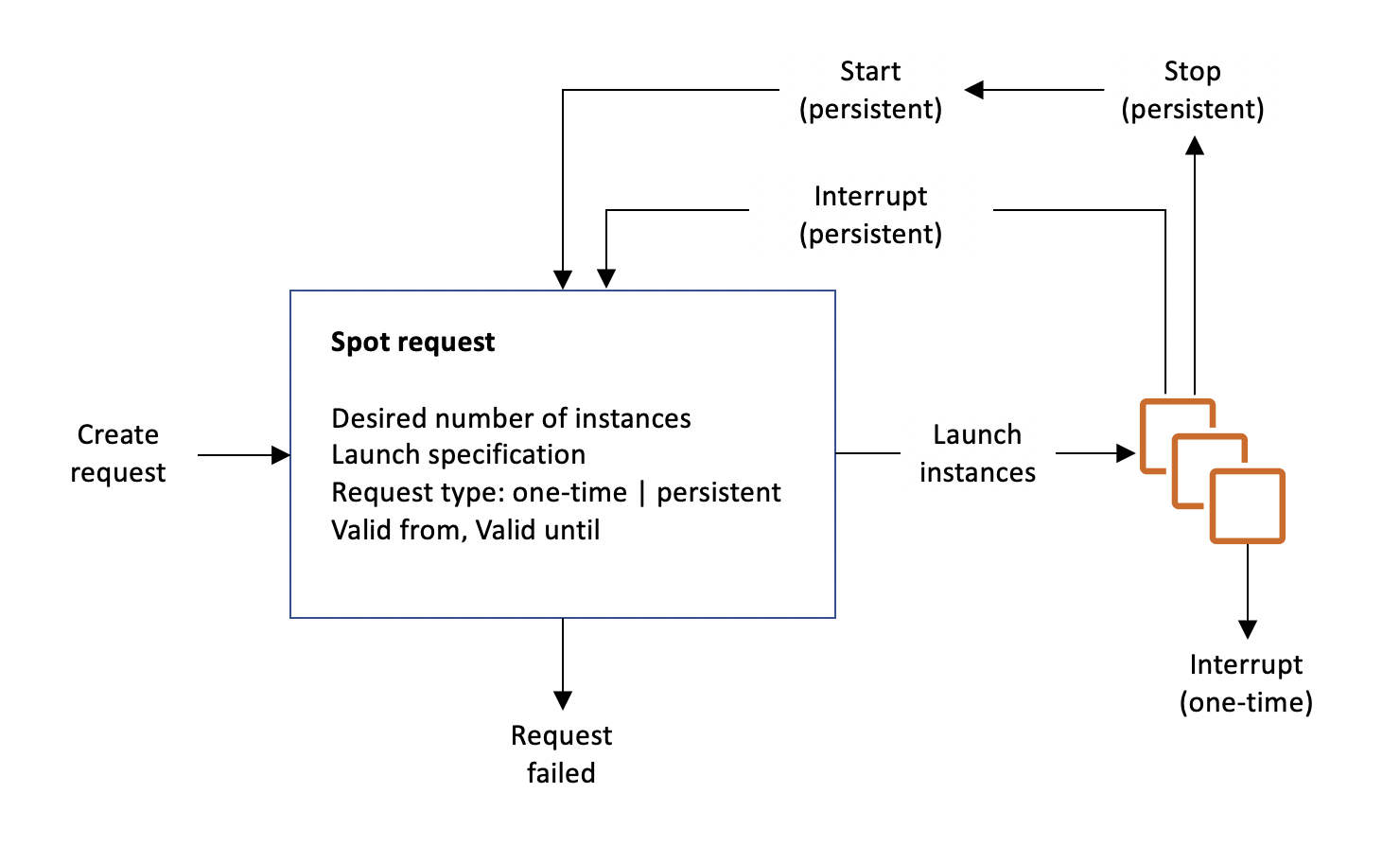
At each step of the process—also called the Spot request lifecycle—specific events determine successive request states.
The following illustration shows how Spot Instance requests work. Notice that the request type (one-time or persistent) determines whether the request is opened again when Amazon EC2 interrupts a Spot Instance or if you stop a Spot Instance. If the request is persistent, the request is opened again after your Spot Instance is interrupted. If the request is persistent and you stop your Spot Instance, the request only opens after you start your Spot Instance.
Contents
Get request status information
You can get status information for your Spot Instance request.
Spot request status codes
Spot request status information is composed of a status code, the update time, and a status message. Together, these help you determine the disposition of your Spot request.
The following are the Spot request status codes:
az-group-constraint-
Amazon EC2 cannot launch all the instances you requested in the same Availability Zone.
bad-parameters-
One or more parameters for your Spot request are not valid (for example, the AMI you specified does not exist). The status message indicates which parameter is not valid.
canceled-before-fulfillment-
The user canceled the Spot request before it was fulfilled.
capacity-not-available-
There is not enough capacity available for the instances that you requested.
constraint-not-fulfillable-
The Spot request can't be fulfilled because one or more constraints are not valid (for example, the Availability Zone does not exist). The status message indicates which constraint is not valid.
fulfilled-
The Spot request is
active, and Amazon EC2 is launching your Spot Instances. instance-stopped-by-price-
Your instance was stopped because the Spot price exceeded your maximum price.
instance-stopped-by-user-
Your instance was stopped because a user stopped the instance or ran the shutdown command from the instance.
instance-stopped-no-capacity-
Your instance was stopped due to EC2 capacity management needs.
instance-terminated-by-price-
Your instance was terminated because the Spot price exceeded your maximum price. If your request is persistent, the process restarts, so your request is pending evaluation.
instance-terminated-by-schedule-
Your Spot Instance was terminated at the end of its scheduled duration.
instance-terminated-by-service-
Your instance was terminated from a stopped state.
instance-terminated-by-userorspot-instance-terminated-by-user-
You terminated a Spot Instance that had been fulfilled, so the request state is
closed(unless it's a persistent request) and the instance state isterminated. instance-terminated-launch-group-constraint-
One or more of the instances in your launch group was terminated, so the launch group constraint is no longer fulfilled.
instance-terminated-no-capacity-
Your instance was terminated due to standard capacity management processes.
launch-group-constraint-
Amazon EC2 cannot launch all the instances that you requested at the same time. All instances in a launch group are started and terminated together.
limit-exceeded-
The limit on the number of EBS volumes or total volume storage was exceeded. For more information, see Quotas for Amazon EBS in the Amazon EBS User Guide.
marked-for-stop-
The Spot Instance is marked for stopping.
marked-for-termination-
The Spot Instance is marked for termination.
not-scheduled-yet-
The Spot request is not evaluated until the scheduled date.
pending-evaluation-
After you make a Spot Instance request, it goes into the
pending-evaluationstate while the system evaluates the parameters of your request. pending-fulfillment-
Amazon EC2 is trying to provision your Spot Instances.
placement-group-constraint-
The Spot request can't be fulfilled yet because a Spot Instance can't be added to the placement group at this time.
price-too-low-
The request can't be fulfilled yet because your maximum price is below the Spot price. In this case, no instance is launched and your request remains
open. request-canceled-and-instance-running-
You canceled the Spot request while the Spot Instances are still running. The request is
cancelled, but the instances remainrunning. schedule-expired-
The Spot request expired because it was not fulfilled before the specified date.
system-error-
There was an unexpected system error. If this is a recurring issue, please contact Amazon Web Services Support for assistance.
EC2 Spot Instance Request Fulfillment event
When a Spot Instance request is fulfilled, Amazon EC2 sends an EC2 Spot Instance Request Fulfillment event to Amazon EventBridge. You can create a rule to take an action whenever this event occurs, such as invoking a Lambda function or notifying an Amazon SNS topic.
The following is example data for this event.
{
"version": "0",
"id": "01234567-1234-0123-1234-012345678901",
"detail-type": "EC2 Spot Instance Request Fulfillment",
"source": "aws.ec2",
"account": "123456789012",
"time": "yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ssZ",
"region": "us-west-2",
"resources": ["arn:aws-cn:ec2:us-west-2:123456789012:instance/i-1234567890abcdef0"],
"detail": {
"spot-instance-request-id": "sir-0e54a519c9EXAMPLE",
"instance-id": "i-1234567890abcdef0"
}
}For more information, see the Amazon EventBridge User Guide.