Resilience in Amazon SQS
The Amazon global infrastructure is built around Amazon Regions and Availability Zones.
Amazon Regions provide multiple physically separated and isolated Availability Zones, which
are connected with low-latency, high throughput, and highly redundant networking. With
Availability Zones, you can design and operate applications and databases that automatically
fail over between zones without interruption. Availability Zones are more highly available,
fault tolerant, and scalable than traditional single or multiple data center
infrastructures. For more information about Amazon Regions and Availability Zones, see Amazon Global
Infrastructure
In addition to the Amazon global infrastructure, Amazon SQS offers distributed queues.
Distributed queues
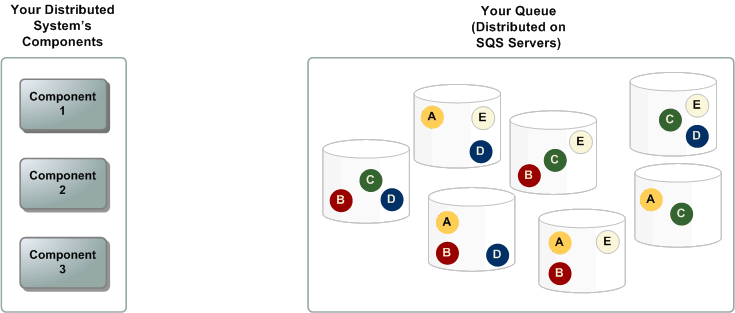
There are three main parts in a distributed messaging system: the components of your distributed system, your queue (distributed on Amazon SQS servers), and the messages in the queue.
In the following scenario, your system has several producers (components that send messages to the queue) and consumers (components that receive messages from the queue). The queue (which holds messages A through E) redundantly stores the messages across multiple Amazon SQS servers.