CloudWatch solution: NGINX workload on Amazon EC2
This solution helps you configure out-of-the-box metric collection using CloudWatch agents for NGINX application running on EC2 instances. For general information about all CloudWatch observability solutions, see CloudWatch observability solutions.
Topics
Requirements
This solution is relevant for the following conditions:
-
Supported versions: NGINX version 1.24
-
Compute: Amazon EC2
-
Supports up to 500 EC2 instances across all NGINX workloads in a given Amazon Web Services Region
-
Latest version of CloudWatch agent
-
Prometheus Exporter: nginxinc/nginx-prometheus-exporter (Apache 2.0 license)
-
SSM agent installed on EC2 instance
Note
Amazon Systems Manager (SSM agent) is pre-installed on some Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) provided by Amazon and trusted third-parties. If the agent isn't installed, you can install it manually using the procedure for your operating system type.
Benefits
The solution delivers NGINX monitoring, providing valuable insights for the following use cases:
-
Review connection metrics to identify potential bottlenecks, connection issues, or unexpected usage.
-
Analyze HTTP request volume to understand overall traffic load on the NGINX.
Below are the key advantages of the solution:
-
Automates metric collection for NGINX using CloudWatch agent configuration, eliminating manual instrumentation.
-
Provides a pre-configured, consolidated CloudWatch dashboard for NGINX metrics. The dashboard will automatically handle metrics from new NGINX EC2 instances configured using the solution, even if those metrics don't exist when you first create the dashboard.
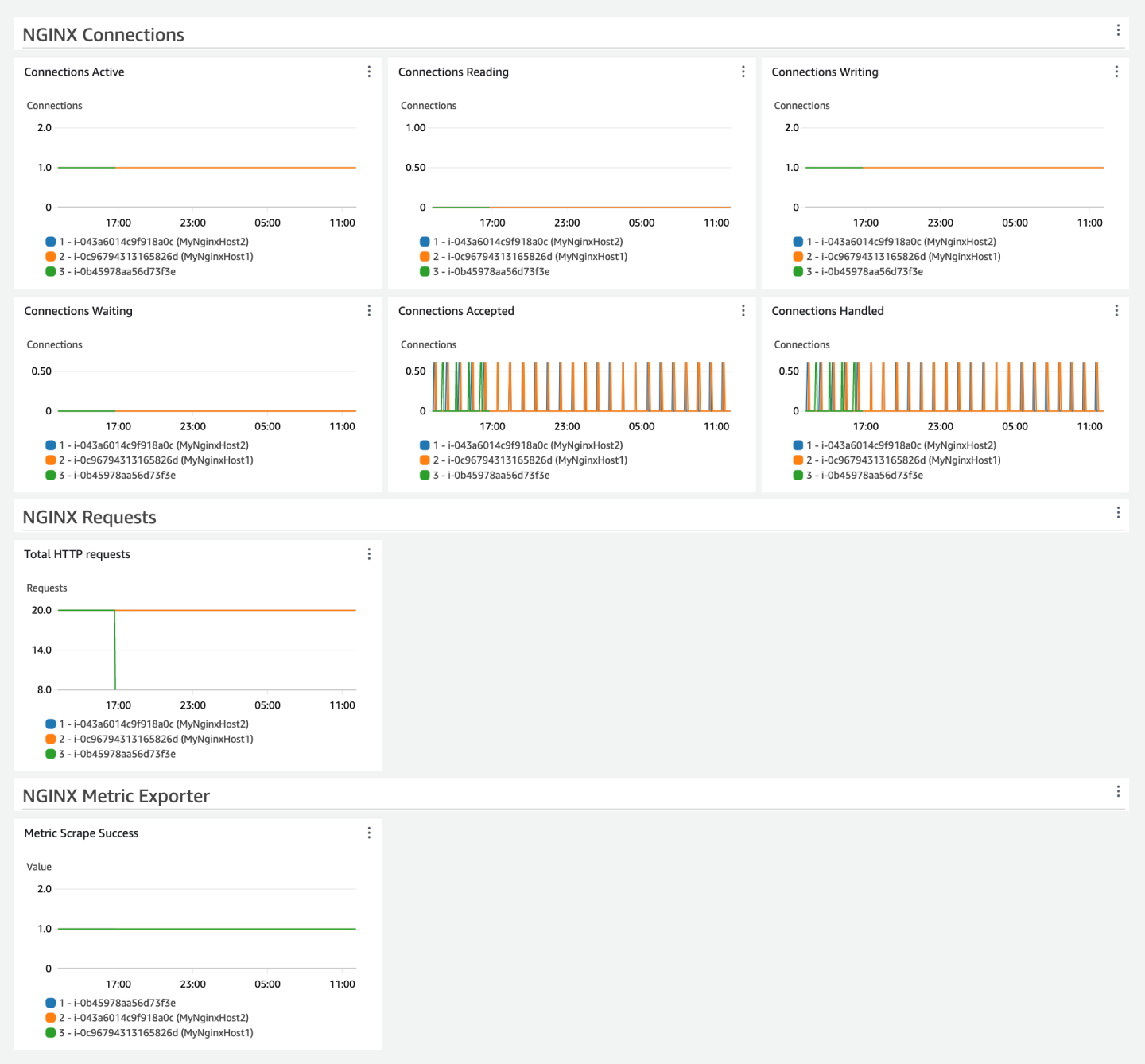
The following image is an example of the dashboard for this solution.
Costs
This solution creates and uses resources in your account. You are charged for standard usage, including the following:
-
All metrics collected by the CloudWatch agent for this solution are published to CloudWatch Logs using the Embedded Metric Format (EMF). These CloudWatch logs are charged based on their volume and retention period. Therefore, you will not be billed for any PutMetricData API calls for this solution. The metrics extracted and ingested from your logs are charged as custom metrics. The number of metrics used by this solution depends on the number of EC2 hosts.
-
Each NGINX EC2 host configured for the solution publishes a total of eight metrics.
-
-
One custom dashboard.
For more information about CloudWatch pricing, see Amazon CloudWatch Pricing
The pricing calculator can help you estimate approximate monthly costs for using this solution.
To use the pricing calculator to estimate your monthly solution costs
-
Open the Amazon CloudWatch pricing calculator
. -
For Choose a Region, select the Amazon Web Services Region where you would like to deploy the solution.
-
In the Metrics section, for Number of metrics, enter
8 * number of EC2 instances configured for this solution. -
In the Logs section, for Standard Logs: Data Ingested, enter the estimated daily log volume generated by the CloudWatch Agent across all EC2 hosts. For example, five EC2 instances produce less than 1000 bytes per day. Once set up, you can check your byte usage using the
IncomingBytesmetric, vended by CloudWatch Logs. Be sure to select the appropriate log group. -
In the Logs section, for Log Storage/Archival (Standard and Vended Logs), select
Yes to Store Logs: Assuming 1 month retention. Modify this value if you decide to make custom changes to the retention period. -
In the Dashboards and Alarms section, for Number of Dashboards, enter
1. -
You can see your monthly estimated costs at the bottom of the pricing calculator.
CloudWatch agent configuration for this solution
The CloudWatch agent is software that runs continuously and autonomously on your servers and in containerized environments. It collects metrics, logs, and traces from your infrastructure and applications and sends them to CloudWatch and X-Ray.
For more information about the CloudWatch agent, see Collect metrics, logs, and traces using the CloudWatch agent.
The agent configuration in this solution collects a set of metrics to help you get started monitoring
and observing your NGINX workload. The CloudWatch agent can be configured to collect more NGINX
metrics than the dashboard displays by default. For a list of all NGINX metrics that you can
collect, see Metrics
for NGINX OSS
Before configuring the CloudWatch agent, you must first configure NGINX to expose its metrics. Secondly, you must install and configure the third party Prometheus metric exporter.
Expose NGINX metrics
Note
The following commands are for Linux. Check NGINX for Windows page
You must first enable the stub_status module. Add a new location block in
your NGINX configuration file. Add the following lines in the server block of your nginx.conf
to enable NGINX's stub_status module:
location /nginx_status { stub_status on; allow 127.0.0.1; # Allow only localhost to access deny all; # Deny all other IPs }
Before reloading NGINX, validate your NGINX configuration:
sudo nginx -t
This validation command helps to prevent any unforeseen errors, which can cause your website to gown down. The following example demonstrates a successful response:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Once you've successfully validated the updated configuration, reload NGINX (no output is expected):
sudo systemctl reload nginx
This command instructs the NGINX process to reload the configuration. Reloads are more graceful compared to a full restart. A reload starts the new worker process with a new configuration, gracefully shutting down old worker processes.
Test the NGINX status endpoint:
curl http://127.0.0.1/nginx_status
The following example demonstrates a successful response:
Active connections: 1 server accepts handled requests 6 6 6 Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
The following example demonstrates a failure response (review the previous steps before proceeding):
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en"> <head> <title>The page is not found</title> ...
Configure Prometheus metric exporter
Download the latest NGINX Prometheus exporter release from the official
GitHub repository
The following example demonstrates commands for AMD64:
cd /tmp wget https://github.com/nginxinc/nginx-prometheus-exporter/releases/download/v1.3.0/nginx-prometheus-exporter_1.3.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz tar -xzvf nginx-prometheus-exporter_1.3.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz sudo cp nginx-prometheus-exporter /usr/local/bin/ rm /tmp/nginx-prometheus-exporter*
Run the Prometheus exporter and point it to the NGINX stub status page:
nohup /usr/local/bin/nginx-prometheus-exporter -nginx.scrape-uri http://127.0.0.1/nginx_status &>/dev/null &
The following example demonstrates a response (background job ID and PID):
[1] 74699
Test the NGINX Prometheus endpoint
Validate that the NGINX Prometheus exporter has started to expose the relevant metrics:
curl http://localhost:port-number/metrics
The following example demonstrates a successful response:
# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles. # TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 0 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 0 ... # HELP nginx_connections_accepted Accepted client connections # TYPE nginx_connections_accepted counter nginx_connections_accepted 14 # HELP nginx_connections_active Active client connections # TYPE nginx_connections_active gauge nginx_connections_active 1 ... # TYPE promhttp_metric_handler_requests_total counter promhttp_metric_handler_requests_total{code="200"} 1 promhttp_metric_handler_requests_total{code="500"} 0 promhttp_metric_handler_requests_total{code="503"} 0
Agent configuration for this solution
The metrics collected by the agent are defined in the agent configuration. The solution provides agent configurations to collect the recommended metrics with suitable dimensions for the solution's dashboard.
The steps for deploying the solution are described later in Deploy the agent for your solution. The following information is intended to help you understand how to customize the agent configuration for your environment.
You must customize some parts of the agent and Prometheus configurations for your environment such as the port number used by the Prometheus exporter.
The port used by the Prometheus exporter can be verified using the following command:
sudo netstat -antp | grep nginx-prom
The following example demonstrates a response (see port value 9113):
tcp6 0 0 :::9113 :::* LISTEN 76398/nginx-prometh
Agent configuration for NGINX hosts
The CloudWatch agent with Prometheus monitoring needs two configurations to scrape the Prometheus metrics. Each configuration will be stored as a separate parameter in SSM's Parameter Store, as detailed later in Step 2: Store the recommended CloudWatch agent configuration file in Systems Manager Parameter Store.
The first configuration is for the Prometheus exporter, as documented in Prometheus'
scrape_config
Prometheus configuration
Replace port-number with the port of your server.
global: scrape_interval: 30s scrape_timeout: 10s scrape_configs: - job_name: 'nginx' metrics_path: /metrics static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:port-number'] ec2_sd_configs: - port:port-numberrelabel_configs: - source_labels: ['__meta_ec2_instance_id'] target_label: InstanceId metric_relabel_configs: - source_labels: ['__name__'] regex: 'nginx_up|nginx_http_requests_total|nginx_connections_.*' action: keep
CloudWatch agent configuration
As per the previous CloudWatch agent configuration, these metrics are published via CloudWatch
Logs using the embedded metric format (EMF) nginx. You can customize the log_group_name
with a different name that represents the CloudWatch logs.
If you are using Windows Server, set
prometheus_config_path in the following configuration to
C:\\ProgramData\\Amazon\\AmazonCloudWatchAgent\\prometheus.yaml.
{ "agent": { "metrics_collection_interval": 60 }, "logs": { "metrics_collected": { "prometheus": { "log_group_name": "nginx", "prometheus_config_path": "/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/prometheus.yaml", "emf_processor": { "metric_declaration_dedup": true, "metric_namespace": "CWAgent", "metric_declaration":[ { "source_labels":["InstanceId"], "metric_selectors":["nginx_up", "nginx_http_requests_total", "nginx_connections*"], "dimensions": [["InstanceId"]] } ] } } } } }
Deploy the agent for your solution
There are several approaches for installing the CloudWatch agent, depending on the use case. We recommend using Systems Manager for this solution. It provides a console experience and makes it simpler to manage a fleet of managed servers within a single Amazon account. The instructions in this section use Systems Manager and are intended for when you don't have the CloudWatch agent running with existing configurations. You can check whether the CloudWatch agent is running by following the steps in Verify that the CloudWatch agent is running.
If you are already running the CloudWatch agent on the EC2 hosts where the workload is deployed and managing agent configurations, you can skip the instructions in this section and follow your existing deployment mechanism to update the configuration. Be sure to merge new CloudWatch agent and Prometheus configurations with your existing configurations, and then deploy the merged configurations. If you are using Systems Manager to store and manage the configuration for the CloudWatch agent, you can merge the configuration to the existing parameter value. For more information, see Managing CloudWatch agent configuration files.
Note
Using Systems Manager to deploy the following CloudWatch agent configurations will replace or overwrite any existing CloudWatch agent configuration on your EC2 instances. You can modify this configuration to suit your unique environment or use case. The metrics defined in configuration are the minimum required for the dashboard provided the solution.
The deployment process includes the following steps:
-
Step 1: Ensure that the target EC2 instances have the required IAM permissions.
-
Step 2: Store the recommended agent configuration file in the Systems Manager Parameter Store.
-
Step 3: Install the CloudWatch agent on one or more EC2 instances using an Amazon CloudFormation stack.
-
Step 4: Verify the agent setup is configured properly.
Step 1: Ensure the target EC2 instances have the required IAM permissions
You must grant permission for Systems Manager to install and configure the CloudWatch agent. You must
grant permission for the CloudWatch agent to publish telemetry from your EC2 instance to CloudWatch.
You must also grant the CloudWatch agent EC2 read access. EC2 read access is required for the
EC2 InstanceId to be added as a metric dimension. This additional requirement is driven by
prometheus.yaml as detailed above because it uses
__meta_ec2_instance_id via EC2 Service Discovery.
Make sure that the IAM role attached to the instance has the CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy, AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore, and AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess IAM policies attached.
-
After the role is created, attach the role to your EC2 instances. To attach a role to an EC2 instance, follow the steps in Attach an IAM role to an instance.
Step 2: Store the recommended CloudWatch agent configuration file in Systems Manager Parameter Store
Parameter Store simplifies the installation of the CloudWatch agent on an EC2 instance by securely storing and managing configuration parameters, eliminating the need for hard-coded values. This ensures a more secure and flexible deployment process, enabling centralized management and easier updates to configurations across multiple instances.
Use the following steps to store the recommended CloudWatch agent configuration file as a parameter in Parameter Store.
To create the CloudWatch agent configuration file as a parameter
Open the Amazon Systems Manager console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/systems-manager/
. -
Verify that the selected Region on the console is the Region where NGINX is running.
-
From the navigation pane, choose Application Management, Parameter Store
-
Follow these steps to create a new parameter for the configuration.
-
Choose Create parameter.
-
In the Name box, enter a name that you'll use to reference the CloudWatch agent configuration file in later steps. For example,
AmazonCloudWatch-NGINX-CloudWatchAgent-Configuration. -
(Optional) In the Description box, type a description for the parameter.
-
For Parameter tier, choose Standard.
-
For Type, choose String.
-
For Data type, choose text.
-
In the Value box, paste the corresponding JSON block that was listed in Agent configuration for NGINX hosts. Be sure to customize as required. For example, the relevant
log_group_name. -
Choose Create parameter.
-
To create the Prometheus configuration file as a parameter
Open the Amazon Systems Manager console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/systems-manager/
. -
From the navigation pane, choose Application Management, Parameter Store
-
Follow these steps to create a new parameter for the configuration.
-
Choose Create parameter.
-
In the Name box, enter a name that you'll use to reference the configuration file in later steps. For example,
AmazonCloudWatch-NGINX-Prometheus-Configuration. -
(Optional) In the Description box, type a description for the parameter.
-
For Parameter tier, choose Standard.
-
For Type, choose String.
-
For Data type, choose text.
-
In the Value box, paste the corresponding YAML block that was listed in the Agent configuration for NGINX hosts. Be sure to customize as required. For example, the relevant port number as per
targets. -
Choose Create parameter.
-
Step 3: Install the CloudWatch agent and apply the configuration using an Amazon CloudFormation template
You can use Amazon CloudFormation to install the agent and configure it to use the CloudWatch agent configuration that you created in the previous steps.
To install and configure the CloudWatch agent for this solution
-
Open the Amazon CloudFormation Quick create stack wizard using this link: https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?#/stacks/quickcreate?templateURL=https://aws-observability-solutions-prod-us-east-1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/CloudWatchAgent/CFN/v1.0.0/cw-agent-installation-template-with-prometheus-config-1.0.0.json
. -
Verify that the selected Region on the console is the Region where the NGINX workload is running.
-
For Stack name, enter a name to identity this stack, such as
CWAgentInstallationStack. -
In the Parameters section, specify the following:
-
For CloudWatchAgentConfigSSM, enter the name of the Amazon Systems Manager parameter for the agent configuration that you created earlier, such as
AmazonCloudWatch-NGINX-CloudWatchAgent-Configuration. -
For PrometheusConfigSSM, enter the name of the Amazon Systems Manager parameter for the agent configuration that you created earlier, such as
AmazonCloudWatch-NGINX-Prometheus-Configuration. -
To select the target instances, you have two options.
-
For InstanceIds, specify a comma-delimited list of instance IDs list of instance IDs where you want to install the CloudWatch agent with this configuration. You can list a single instance or several instances.
-
If you are deploying at scale, you can specify the TagKey and the corresponding TagValue to target all EC2 instances with this tag and value. If you specify a TagKey, you must specify a corresponding TagValue. (For an Auto Scaling group, specify
aws:autoscaling:groupNamefor the TagKey and specify the Auto Scaling group name for the TagValue to deploy to all instances within the Auto Scaling group.)
-
-
-
Review the settings, then choose Create stack.
If you want to edit the template file first to customize it, choose the Upload a template file option
under Create Stack Wizard to upload the edited template. For more information,
see Creating a stack on Amazon CloudFormation console.
You can use the following link to download the template:
https://aws-observability-solutions-prod-us-east-1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/CloudWatchAgent/CFN/v1.0.0/cw-agent-installation-template-with-prometheus-config-1.0.0.json
Note
After this step is completed, this Systems Manager parameter will be associated with the CloudWatch agents running in the targeted instances. This means that:
-
If the Systems Manager parameter is deleted, the agent will stop.
-
If the Systems Manager parameter is edited, the configuration changes will automatically apply to the agent at the scheduled frequency which is 30 days by default.
-
If you want to immediately apply changes to this Systems Manager parameter, you must run this step again. For more information about associations, see Working with associations in Systems Manager.
Step 4: Verify the agent setup is configured properly
You can verify whether the CloudWatch agent is installed by following the steps in Verify that the CloudWatch agent is running. If the CloudWatch agent is not installed and running, make sure you have set up everything correctly.
-
Be sure you have attached a role with correct permissions for the EC2 instance as described in Step 1: Ensure the target EC2 instances have the required IAM permissions.
-
Be sure you have correctly configured the JSON for the Systems Manager parameter. Follow the steps in .
If everything is set up correctly, then you should see the NGINX metrics being published to CloudWatch. You can check the CloudWatch console to verify they are being published.
To verify that NGINX metrics are being published to CloudWatch
Open the CloudWatch console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/cloudwatch/
. -
Choose Metrics, All metrics.
-
Make sure you've selected the Region where you deployed the solution, and choose Custom namespaces, CWAgent.
-
Search for metrics such as
nginx_http_requests_total. If you see results for these metrics, then the metrics are being published to CloudWatch.
Create the NGINX solution dashboard
The dashboard provided by this solution presents NGINX workload metrics by aggregating and presenting metrics across all instances. The dashboard shows a breakdown of the top contributors (top 10 per metric widget) for each metric. This helps you to quickly identify outliers or instances that significantly contribute to the observed metrics.
To create the dashboard, you can use the following options:
Use CloudWatch console to create the dashboard.
Use Amazon CloudFormation console to deploy the dashboard.
Download the Amazon CloudFormation infrastructure as code and integrate it as part of your continuous integration (CI) automation.
By using the CloudWatch console to create a dashboard, you can preview the dashboard before actually creating and being charged.
Note
The dashboard created with Amazon CloudFormation in this solution displays metrics from the Region where the solution is deployed. Be sure to create the Amazon CloudFormation stack in the Region where your NGINX metrics are published.
If you've specified a custom namespace other than CWAgent in the CloudWatch agent
configuration, you'll have to change the CloudFormation template
for the dashboard to replace CWAgent with the customized namespace you are using.
To create the dashboard via CloudWatch Console
-
Open the CloudWatch Console Create Dashboard using this link: https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/home?#dashboards?dashboardTemplate=NginxOnEc2&referrer=os-catalog
. -
Verify that the selected Region on the console is the Region where the NGINX workload is running.
-
Enter the name of the dashboard, then choose Create Dashboard.
To easily differentiate this dashboard from similar dashboards in other Regions, we recommend including the Region name in the dashboard name, such as
NGINXDashboard-us-east-1. -
Preview the dashboard and choose Save to create the dashboard.
To create the dashboard via Amazon CloudFormation
-
Open the Amazon CloudFormation Quick create stack wizard using this link: https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?#/stacks/quickcreate?templateURL=https://aws-observability-solutions-prod-us-east-1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/NGINX_EC2/CloudWatch/CFN/v1.0.0/dashboard-template-1.0.0.json
. -
Verify that the selected Region on the console is the Region where the NGINX workload is running.
-
For Stack name, enter a name to identity this stack, such as
NGINXDashboardStack. -
In the Parameters section, specify the name of the dashboard under the DashboardName parameter.
-
To easily differentiate this dashboard from similar dashboards in other Regions, we recommend including the Region name in the dashboard name, such as
NGINXDashboard-us-east-1. -
Acknowledge access capabilities for transforms under Capabilities and transforms. Note that CloudFormation doesn't add any IAM resources.
-
Review the settings, then choose Create stack.
-
After the stack status is CREATE_COMPLETE, choose the Resources tab under the created stack and then choose the link under Physical ID to go to the dashboard. You can also access the dashboard in the CloudWatch console by choosing Dashboards in the left navigation pane of the console, and finding the dashboard name under Custom Dashboards.
If you want to edit the template file first to customize it, choose the Upload a template file option
under Create Stack Wizard to upload the edited template. For more information,
see Creating a stack on Amazon CloudFormation console.
You can use the following link to download the template:
https://aws-observability-solutions-prod-us-east-1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/NGINX_EC2/CloudWatch/CFN/v1.0.0/dashboard-template-1.0.0.json
Get started with the NGINX dashboard
Here are a few tasks that you can try out with the new NGINX dashboard. These tasks allow you to validate that the dashboard is working correctly and provide you some hands-on experience using it to monitor a NGINX workload. As you try these out, you'll get familiar with navigating the dashboard and interpreting the visualized metrics.
Review connection metrics
In the Connections section, you can find several key metrics that provide insights into the client connection handling of your NGINX server. Monitoring these connection metrics can help you identify potential bottlenecks, connection issues, or unexpected connection patterns.
-
Accepted client connections
-
Active client connections
-
Handled client connections
-
Connections reading requests
-
Idle client connections
-
Connections writing responses
Analyze HTTP request volume
The request metric in the HTTP Requests section shows the total number of HTTP
requests handled by the NGINX server.
Tracking this metric over time can help you understand the overall traffic load on
your NGINX infrastructure and plan for resource allocation
and scaling accordingly.