Use Docker's virtual network for Amazon ECS Linux tasks
The bridge network mode is only supported for Amazon ECS tasks hosted on Amazon EC2
instances.
With bridge mode, you're using a virtual network bridge to create a layer
between the host and the networking of the container. This way, you can create port
mappings that remap a host port to a container port. The mappings can be either static
or dynamic.
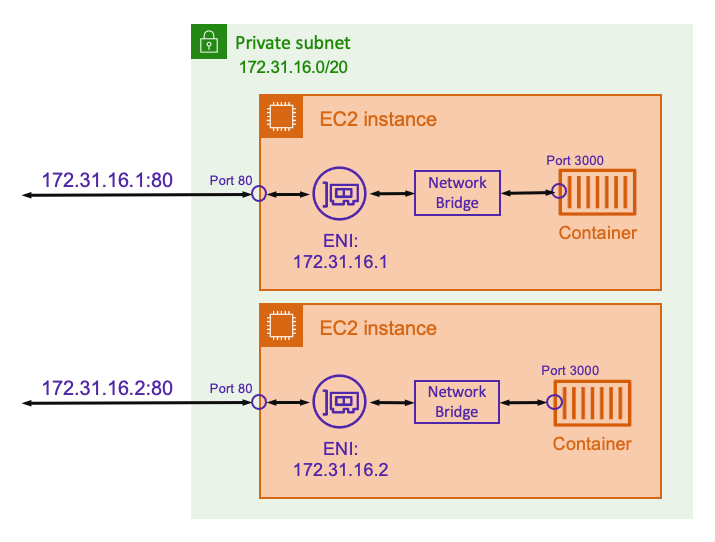
With a static port mapping, you can explicitly define which host port you want to map
to a container port. Using the example above, port 80 on the host is being
mapped to port 3000 on the container. To communicate to the containerized
application, you send traffic to port 80 to the Amazon EC2 instance's IP
address. From the containerized application’s perspective it sees that inbound traffic
on port 3000.
If you only want to change the traffic port, then static port mappings is suitable.
However, this still has the same disadvantage as using the host network
mode. You can't run more than a single instantiation of a task on each host. This is
because a static port mapping only allows a single container to be mapped to port
80.
To solve this problem, consider using the bridge network mode with a
dynamic port mapping as shown in the following diagram.
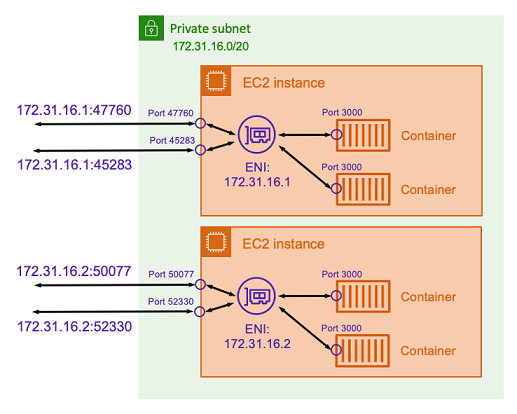
By not specifying a host port in the port mapping, you can have Docker
choose a random, unused port from the ephemeral port range and assign it as the public
host port for the container. For example, the Node.js application listening on port
3000 on the container might be assigned a random high number port such
as 47760 on the Amazon EC2 host. Doing this means that you can run multiple
copies of that container on the host. Moreover, each container can be assigned its own
port on the host. Each copy of the container receives traffic on port 3000.
However, clients that send traffic to these containers use the randomly assigned host
ports.
Amazon ECS helps you to keep track of the randomly assigned ports for each task. It does
this by automatically updating load balancer target groups and Amazon Cloud Map service discovery
to have the list of task IP addresses and ports. This makes it easier to use services
operating using bridge mode with dynamic ports.
However, one disadvantage of using the bridge network mode is that it's
difficult to lock down service to service communications. Because services might be
assigned to any random, unused port, it's necessary to open broad port ranges between
hosts. However, it's not easy to create specific rules so that a particular service can
only communicate to one other specific service. The services have no specific ports to
use for security group networking rules.
Configuring bridge networking mode for IPv6-only workloads
To configure bridge mode for communication over IPv6, you must update
Docker daemon settings. Update
/etc/docker/daemon.json with the following:
{ "ipv6": true, "fixed-cidr-v6": "2001:db8:1::/64", "ip6tables": true, "experimental": true }
After updating Docker daemon settings, you will need to restart the daemon.
Note
When you update and restart the daemon, Docker enables IPv6 forwarding on the instance, which can result in the loss of default routes on instances that use an Amazon Linux 2 AMI. To avoid this, use the following command to add a default route via the subnet's IPv6 gateway.
ip route add default via FE80:EC2::1 dev eth0 metric 100