Map Amazon ECS container ports to the EC2 instance network interface
The host network mode is only supported for Amazon ECS tasks hosted on Amazon EC2
instances. It's not supported when using Amazon ECS on Fargate.
The host network mode is the most basic network mode that's supported in
Amazon ECS. Using host mode, the networking of the container is tied directly to the
underlying host that's running the container.
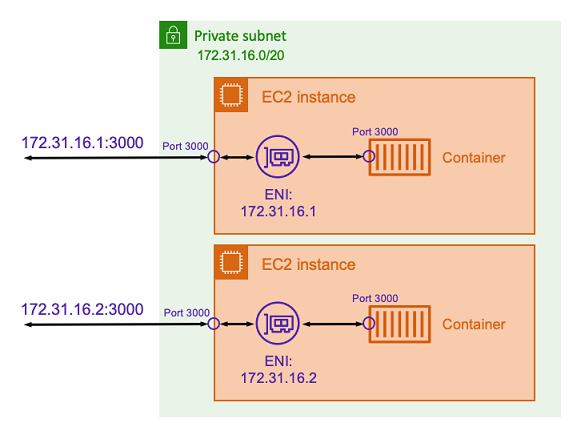
Assume that you're running a Node.js container with an Express application that
listens on port 3000 similar to the one illustrated in the preceding
diagram. When the host network mode is used, the container receives traffic
on port 3000 using the IP address of the underlying host Amazon EC2 instance. We do not
recommend using this mode.
There are significant drawbacks to using this network mode. You can’t run more than a
single instantiation of a task on each host. This is because only the first task can
bind to its required port on the Amazon EC2 instance. There's also no way to remap a
container port when it's using host network mode. For example, if an
application needs to listen on a particular port number, you can't remap the port number
directly. Instead, you must manage any port conflicts through changing the application
configuration.
There are also security implications when using the host network mode.
This mode allows containers to impersonate the host, and it allows containers to connect
to private loopback network services on the host.