Prepare for Amazon Fargate task retirement on Amazon ECS
In order to prepare for task retirement, perform the following operations:
-
Set the task retirement wait period or use Amazon EC2 event windows.
-
Capture task retirement notifications to notify team members.
-
You can ensure all your services' tasks run on the latest platform revision by updating the service with the force-deployment option. This step is optional.
Step 1: Set the task wait time or use Amazon EC2 event windows
You have two account settings options to configure the time that Fargate starts
task retirements: fargateTaskRetirementWaitPeriod and fargateEventWindows.
Using fargateTaskRetirementWaitPeriod account setting
You can configure the time that Fargate starts the task retirement.
The default wait period is 7 days. For workloads
that require immediate application of the updates, choose the immediate setting (0). If you need more time,
configure the 7, or 14 day option.
We recommend that you choose a shorter waiting period in order to pick up newer platform versions revisions sooner.
Configure the wait period by running
put-account-setting-default or put-account-setting as the root user or an administrative user. Use the
fargateTaskRetirementWaitPeriod option for the name and the value option set to one of the following values:
-
0- Amazon sends the notification, and immediately starts to retire the affected tasks. -
7- Amazon sends the notification, and waits 7 calendar days before starting to retire the affected tasks. This is the default. -
14- Amazon sends the notification, and waits 14 calendar days before starting to retire the affected tasks.
For more information, see, put-account-setting-default and put-account-setting in the Amazon Elastic Container Service API Reference.
Using fargateEventWindows account setting
As of 12/18/2025, Amazon ECS enables you to configure Amazon EC2 event windows for your Fargate tasks. If you need precise control over the exact timing of task retirements, for example, scheduling them over weekends to avoid disruption during business hours, you can configure Amazon EC2 event windows for your tasks, services, or clusters.
When you use event windows, Fargate ensures that your tasks run for at least 3 days before they are retired within the next available window, unless stopped by user-initiated actions or critical health events such as degradation of the underlying hardware.
Set the fargateEventWindows account setting to enabled. You can use one of the following APIs:
put-account-setting-default or put-account-setting as the root user or an administrative user.
Each Amazon EC2 event window must be open for at least 4 hours per week, and each time range must be at least 2 hours long. For large clusters and services we recommend configuring event windows with either long durations (8 hours or more) or more frequent time ranges that occur at least once every 3 days. You can further review considerations for Amazon EC2 event windows in the user guide Amazon Fargate ensures that your tasks run for at least 3 days before they are retired, unless stopped by user-initiated actions or critical health events such as degradation of the underlying hardware.
Important
Replacement of tasks within event window is best effort. If you notice tasks being retired outside of your event windows, consider expanding the duration (8 hours or more) or increasing frequency (at least once every 3 days).
To apply Amazon EC2 event windows to your Fargate task retirements:
-
Set the
fargateEventWindowsaccount setting toenabled. You can use one of the following APIs:put-account-setting-defaultorput-account-settingas the root user or an administrative user. Note that this is a one-time enablement for usage of the Amazon EC2 event windows feature for your Fargate tasks. -
Create an Amazon EC2 event window through the AWS console or the AWS CLI. To create an event window using CLI, use EC2
create-instance-event-windowAPI with time ranges or cron expressions. Take note of theInstanceEventWindowIdfrom the response.aws ec2 create-instance-event-window \ --time-range StartWeekDay=monday,StartHour=2,EndWeekDay=wednesday,EndHour=8\ --tag-specifications "ResourceType=instance-event-window,Tags=[{Key=K1,Value=V1" \ --namemyEventWindowNameAlternatively, you can use cron expressions when creating EC2 event windows.
aws ec2 create-instance-event-window \ --cron-expression"* 21-23 * * 2,3"\ --tag-specifications "ResourceType=instance-event-window,Tags=[{Key=K1,Value=V1" \ --namemyEventWindowName -
You can then associate the event window with specific services, clusters or all tasks in your account using EC2
associate-instance-event-windowAPI.-
For ECS service tasks
aws ec2 associate-instance-event-window \ --instance-event-window-idiew-0abcdef1234567890\ --association-target "InstanceTags=[{Key=aws:ecs:serviceArn,Value=your-service-arn}]" -
For ECS clusters
aws ec2 associate-instance-event-window \ --instance-event-window-idiew-0abcdef1234567890\ --association-target "InstanceTags=[{Key=aws:ecs:clusterArn,Value=your-cluster-arn}]" -
To associate an event window with all tasks in the account
aws ec2 associate-instance-event-window \ --instance-event-window-idiew-0abcdef1234567890\ --association-target "InstanceTags=[{Key=aws:ecs:fargateTask,Value=true}]"
-
You can use more than one key-value pair to associate an event window with multiple services or clusters.
Fargate will choose the event window for each task in the following order:
-
If there is an event window associated with the task's service, it will be used. This is not applicable for standalone or unmanaged tasks.
-
If there is an event window associated with the task's cluster, it will be used.
-
If there is an event window set for all Fargate tasks, it will be used.
-
The
fargateTaskRetirementWaitPeriodsetting will be used if none of the event windows match with the task.
Configuring event windows for Fargate task maintenance
Consider a case when you are running multiple ECS services on Fargate with different availability requirements. You want precise control over task retirements. You can configure multiple event windows as follows:
-
Default maintenance for all Fargate tasks: Create an event window for routine maintenance during off-peak hours (12AM to 4AM daily) and associate it with all Fargate tasks using the
aws:ecs:fargateTasktag. -
Weekend-only maintenance for development cluster: For a development cluster with services that can tolerate disruption on weekends, create a 24-hour weekend window (Saturday and Sunday, all day) and associate it with the cluster using the
aws:ecs:clusterArntag with your cluster ARN. -
Restricted window for mission-critical service: For a mission-critical payment processing service that requires high uptime during weekdays, restrict maintenance to weekend early morning hours (Saturday and Sunday, 12AM to 4AM) and associate it with the specific service using the
aws:ecs:serviceArntag with your service ARN.
With this configuration, the payment service uses its specific weekend-only window, the development cluster services and tasks use the weekend 24-hour window, and all other Fargate tasks use the default daily maintenance window.
For more information, see, put-account-setting-default and put-account-setting in the Amazon Elastic Container Service API Reference.
Step 2: Capture task retirement notifications to alert teams and take actions
When there is an upcoming task retirement, Amazon sends a task retirement notification to the Amazon Health Dashboard, and to the primary email contact on the Amazon Web Services account. The Amazon Health Dashboard provides a number of integrations into other Amazon services, including Amazon EventBridge. You can use EventBridge to build automations from a task retirement notification, such as increasing the visibility of the upcoming retirement by forwarding the message to a ChatOps tool. Amazon Health Aware is a resource that shows the power of the Amazon Health Dashboard and how notifications can be distributed throughout an organization. You can forward a task retirement notification to a chat application, such as Slack.
The following illustration shows the solution overview.
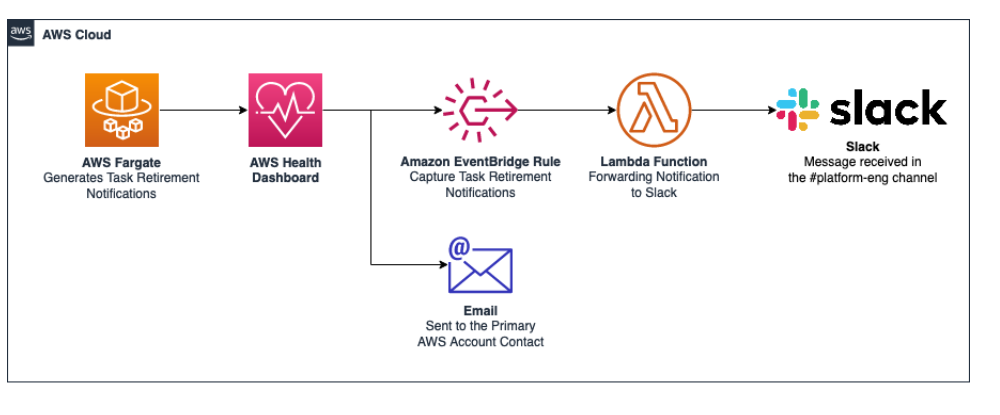
The following information provides details.
-
Fargate sends the task retirement notification to the Amazon Health Dashboard.
-
The Amazon Health Dashboard sends mail to the primary email contact on the Amazon Web Services account, and notifies EventBridge.
-
EventBridge has a rule that captures the retirement notification.
The rule looking for events with the Event Detail Type:
"AWS Health Event" and the Event Detail Type Code: "AWS_ECS_TASK_PATCHING_RETIREMENT" -
The rule triggers a Lambda function that forwards the information to Slack using a Slack Incoming Webhook. For more information, see Incoming Webhooks
.
For a code example, see Capturing Amazon Fargate Task Retirement Notifications
Step 3: Control the replacement of tasks
You can't control the exact timing of a task retirement, however, you can define a
wait time. If you want control over replacing tasks at your own schedule, you can
capture the task retirement notice to first understand the task retirement date. You can
then redeploy your service to launch replacement tasks, and likewise replace any
standalone tasks.For services that use rolling deployment, you update the service using
update-service with the force-deployment option before the
retirement start time.
The following update-service example uses the
force-deployment option.
aws ecs update-service —-serviceservice_name\ --clustercluster_name\ --force-new-deployment
For services that use the blue/green deployment, you need to create a new deployment in Amazon CodeDeploy. For information about how to create the deployment, see create-deployment in the Amazon Command Line Interface Reference.