Managing clusters in ElastiCache
A cluster is a collection of one or more cache nodes, all of which run an instance of the Valkey, Memcached, and Redis OSS engine software. When you create a cluster, you specify the engine and version for all of the nodes to use.
Valkey and Redis OSS clusters
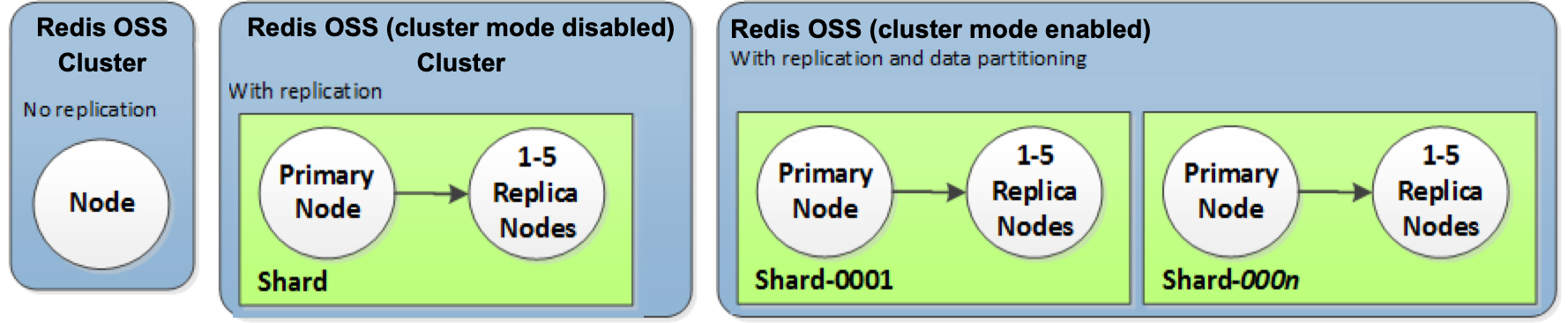
The following diagram illustrates a typical Valkey or Redis OSS cluster. These clusters can contain a single node or up to six nodes inside a shard (API/CLI: node group), A single-node Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster has no shard, and a multi-node Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster has a single shard. Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) clusters can have up to 500 shards, with your data partitioned across the shards. The node or shard limit can be increased to a maximum of 500 per cluster if the engine version is Valkey 7.2 and higher or Redis OSS 5.0.6 and higher. For example, you can choose to configure a 500 node cluster that ranges between 83 shards (one primary and 5 replicas per shard) and 500 shards (single primary and no replicas). Make sure there are enough available IP addresses to accommodate the increase. Common pitfalls include the subnets in the subnet group have too small a CIDR range or the subnets are shared and heavily used by other clusters. For more information, see Creating a subnet group. For versions below 5.0.6, the limit is 250 per cluster.
To request a limit increase, see
Amazon Service Limits
When you have multiple nodes in a Valkey or Redis OSS shard, one of the nodes is a read/write primary node. All other nodes in the shard are read-only replicas.
Typical Valkey or Redis OSS clusters look as follows.
Memcached clusters
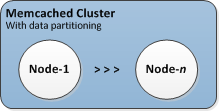
Typical Memcached clusters look as follows. Memcached clusters contain from 1 to 60 nodes, across which you horizontally partition your data.
Elasticache operations for Valkey, Memcached, and Redis OSS
Most ElastiCache operations are performed at the cluster level. You can set up a cluster with a specific number of nodes and a parameter group that controls the properties for each node. All nodes within a cluster are designed to be of the same node type and have the same parameter and security group settings.
Every cluster must have a cluster identifier. The cluster identifier is a customer-supplied name for the cluster. This identifier specifies a particular cluster when interacting with the ElastiCache API and Amazon CLI commands. The cluster identifier must be unique for that customer in an Amazon Region.
ElastiCache supports multiple engine versions. Unless you have specific reasons, we recommend using the latest version.
ElastiCache clusters are designed to be accessed using an Amazon EC2 instance. If you launch your cluster in a virtual private cloud (VPC) based on the Amazon VPC service, you can access it from outside Amazon. For more information, see Accessing ElastiCache resources from outside Amazon.
For a list of supported versions, see Supported engines and versions, Supported Redis OSS engine versions, and Supported ElastiCache for Memcached versions.