Enabling RDS for SQL Server integration with S3
In the following section, you can find how to enable Amazon S3 integration with Amazon RDS for SQL
Server. To work with S3 integration, your DB instance must be associated with the IAM
role that you previously created before you use the S3_INTEGRATION
feature-name parameter.
Note
To add an IAM role to a DB instance, the status of the DB instance must be available.
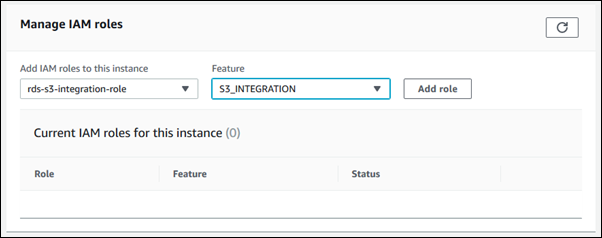
To associate your IAM role with your DB instance
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
Choose the RDS for SQL Server DB instance name to display its details.
-
On the Connectivity & security tab, in the Manage IAM roles section, choose the IAM role to add for Add IAM roles to this instance.
-
For Feature, choose S3_INTEGRATION.
-
Choose Add role.
To add the IAM role to the RDS for SQL Server DB instance
-
The following Amazon CLI command adds your IAM role to an RDS for SQL Server DB instance named
mydbinstanceExample
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds add-role-to-db-instance \ --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance\ --feature-name S3_INTEGRATION \ --role-arnyour-role-arnFor Windows:
aws rds add-role-to-db-instance ^ --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance^ --feature-name S3_INTEGRATION ^ --role-arnyour-role-arnReplace
your-role-arnS3_INTEGRATIONmust be specified for the--feature-nameoption.