Browser-Based Uploads Using POST (Amazon Signature Version 4)
This section discusses how to upload files directly to Amazon S3 through a browser using HTTP POST requests. It also contains information about how to use the Amazon Amplify JavaScript library for browser-based file uploads to Amazon S3.
Topics
Browser-Based Uploads Using HTTP POST
Amazon S3 supports HTTP POST requests so that users can upload content directly to Amazon S3. By using POST, end users can authenticate requests without having to pass data through a secure intermediary node that protects your credentials. Thus, HTTP POST has the potential to reduce latency.
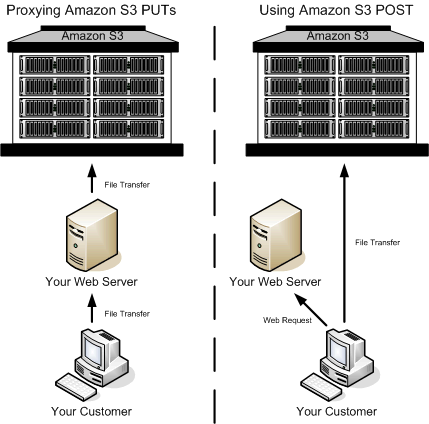
The following figure shows an Amazon S3 upload using a POST request.
-
The user accesses your page from a web browser.
-
Your webpage contains an HTML form that contains all the information necessary for the user to upload content to Amazon S3.
-
The user uploads content to Amazon S3 through the web browser.
The process for sending browser-based POST requests is as follows:
-
Create a security policy specifying conditions that restrict what you want to allow in the request, such as the bucket name where objects can be uploaded, and key name prefixes that you want to allow for the object that is being created.
-
Create a signature that is based on the policy. For authenticated requests, the form must include a valid signature and the policy.
-
Create an HTML form that your users can access in order to upload objects to your Amazon S3 bucket.
The following section describes how to create a signature to authenticate a request. For information about creating forms and security policies, see Creating an HTML Form (Using Amazon Signature Version 4).
Calculating a Signature
For authenticated requests, the HTML form must include fields for a security policy and a signature.
-
A security policy (see POST Policy) controls what is allowed in the request.
-
The security policy is the
StringToSign(see Introduction to Signing Requests) in your signature calculation.
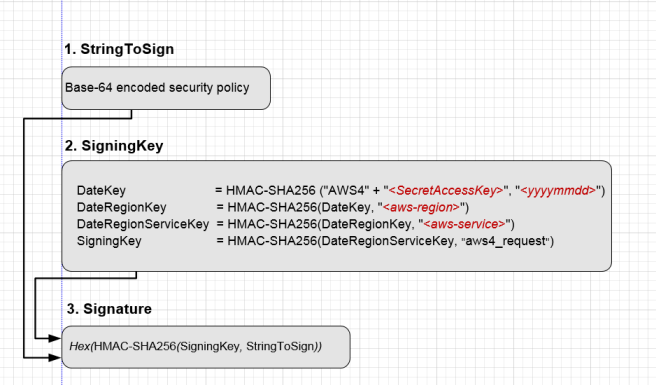
To Calculate a signature
-
Create a policy using UTF-8 encoding.
-
Convert the UTF-8-encoded policy bytes to base64. The result is the
StringToSign. -
Create a signing key.
-
Use the signing key to sign the
StringToSignusing HMAC-SHA256 signing algorithm.
For more information about creating HTML forms, security policies, and an example, see the following: