How S3 Versioning works
You can use S3 Versioning to keep multiple versions of an object in one bucket so that you can restore objects that are accidentally deleted or overwritten. For example, if you apply S3 Versioning to a bucket, the following changes occur:
-
If you delete an object, instead of removing the object permanently, Amazon S3 inserts a delete marker, which becomes the current object version. You can then restore the previous version. For more information, see Deleting object versions from a versioning-enabled bucket.
-
If you overwrite an object, Amazon S3 adds a new object version in the bucket. The previous version remains in the bucket and becomes a noncurrent version. You can restore the previous version.
Note
Normal Amazon S3 rates apply for every version of an object that is stored and transferred. Each version of an object is the entire object; it is not a diff from the previous version. Thus, if you have three versions of an object stored, you are charged for three objects.
Each S3 bucket that you create has a versioning subresource associated with it. (For more information, see General purpose buckets configuration options.) By default, your bucket is unversioned, and the versioning subresource stores the empty versioning configuration, as follows.
<VersioningConfiguration xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/"> </VersioningConfiguration>
To enable versioning, you can send a request to Amazon S3 with a versioning configuration that
includes an Enabled status.
<VersioningConfiguration xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/"> <Status>Enabled</Status> </VersioningConfiguration>
To suspend versioning, you set the status value to Suspended.
Note
When you enable versioning on a bucket for the first time, it might take a short
amount of time for the change to be fully propagated. While this change is propagating,
you may encounter intermittent HTTP 404 NoSuchKey errors for requests to
objects created or updated after enabling versioning. We recommend that you wait for 15
minutes after enabling versioning before issuing write operations (PUT or
DELETE) on objects in the bucket.
The bucket owner and all authorized Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) users can enable versioning. The bucket owner is the Amazon Web Services account that created the bucket. For more information about permissions, see Identity and Access Management for Amazon S3.
For more information about enabling and disabling S3 Versioning by using the Amazon Web Services Management Console, Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI), or REST API, see Enabling versioning on buckets.
Version IDs
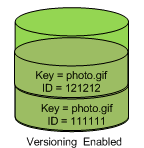
If you enable versioning for a bucket, Amazon S3 automatically generates a unique version
ID for the object that is being stored. For example, in one bucket you can have two
objects with the same key (object name) but different version IDs, such as
photo.gif (version 111111) and photo.gif
(version 121212).
Each object has a version ID, whether or not S3 Versioning is enabled. If S3 Versioning
is not enabled, Amazon S3 sets the value of the version ID to null. If you
enable S3 Versioning, Amazon S3 assigns a version ID value for the object. This value
distinguishes that object from other versions of the same key.
When you enable S3 Versioning on an existing bucket, objects that are already stored in
the bucket are unchanged. Their version IDs (null), contents, and
permissions remain the same. After you enable S3 Versioning, each object that is added to
the bucket gets a version ID, which distinguishes it from other versions of the same
key.
Only Amazon S3 generates version IDs, and they cannot be edited. Version IDs are Unicode, UTF-8 encoded, URL-ready, opaque strings that are no more than 1,024 bytes long. The following is an example:
3sL4kqtJlcpXroDTDmJ+rmSpXd3dIbrHY+MTRCxf3vjVBH40Nr8X8gdRQBpUMLUo
Note
For simplicity, the other examples in this topic use much shorter IDs.
Versioning workflows
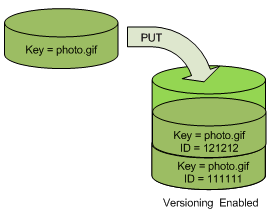
When you PUT an object in a versioning-enabled bucket, the noncurrent
version is not overwritten. As shown in the following figure, when a new version of
photo.gif is PUT into a bucket that already
contains an object with the same name, the following behavior occurs:
-
The original object (ID = 111111) remains in the bucket.
-
Amazon S3 generates a new version ID (121212), and adds this newer version of the object to the bucket.
With this functionality, you can retrieve a previous version of an object if an object has been accidentally overwritten or deleted.
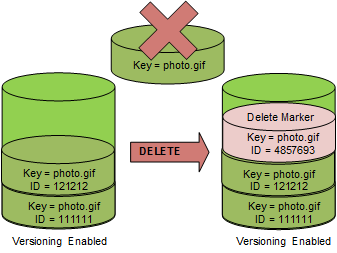
When you DELETE an object, all versions remain in the bucket, and Amazon S3
inserts a delete marker, as shown in the following figure.
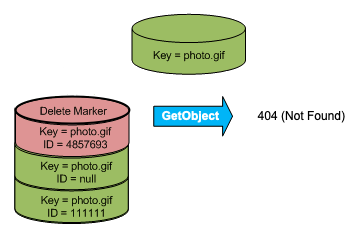
The delete marker becomes the current version of the object. By default,
GET requests retrieve the most recently stored version. Performing a
GET Object request when the current version is a delete marker returns
a 404 Not Found error, as shown in the following figure.
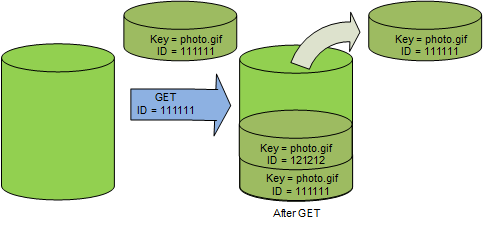
However, you can GET a noncurrent version of an object by specifying its
version ID. In the following figure, you GET a specific object version,
111111. Amazon S3 returns that object version even though it's not the current
version.
For more information, see Retrieving object versions from a versioning-enabled bucket.
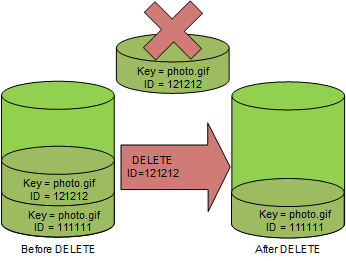
You can permanently delete an object by specifying the version that you want to
delete. Only the owner of an Amazon S3 bucket or an authorized IAM user can permanently
delete a version. If your DELETE operation specifies the
versionId, that object version is permanently deleted, and Amazon S3 doesn't
insert a delete marker.
You can add more security by configuring a bucket to enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) delete. When you enable MFA delete for a bucket, the bucket owner must include two forms of authentication in any request to delete a version or change the versioning state of the bucket. For more information, see Configuring MFA delete.
When are new versions created for an object?
New versions of objects are created only when you PUT a new object.
Be aware that certain actions, such as CopyObject, work by implementing a
PUT operation.
Some actions that modify the current object don't create a new
version because they don't PUT a new object. This includes actions such
as changing the tags on an object.
Important
If you notice a significant increase in the number of HTTP 503 (Service
Unavailable) responses received for Amazon S3 PUT or DELETE
object requests to a bucket that has S3 Versioning enabled, you might have one or
more objects in the bucket for which there are millions of versions. For more
information, see the S3 Versioning section of Troubleshooting versioning.