The confused deputy problem
The confused deputy problem is a security issue where an entity that doesn't have permission to perform an action can coerce a more-privileged entity to perform the action. To prevent this, Amazon provides tools that help you protect your account if you provide third parties (known as cross-account) or other Amazon services (known as cross-service) access to resources in your account.
At times, you might need to give a third party access to your Amazon resources (delegate access). For example, you decide to hire a third-party company called Example Corp to monitor your Amazon Web Services account and help optimize costs. In order to track your daily spending, Example Corp needs to access your Amazon resources. Example Corp also monitors many other Amazon Web Services accounts for other customers. You can use an IAM role to establish a trusted relationship between your Amazon Web Services account and the Example Corp account. One important aspect of this scenario is the external ID, an optional identifier that you can use in an IAM role trust policy to designate who can assume the role. The primary function of the external ID is to address and prevent the confused deputy problem.
Some Amazon services (calling services) use their Amazon service principal to access Amazon
resources from other Amazon services (called services). In some of these service interactions
you can configure calling services to communicate with the resources from a called service
in a different Amazon Web Services account. An example of this is configuring Amazon CloudTrail to write to a
central Amazon S3 bucket which is located in a different Amazon Web Services account. The calling service, CloudTrail
is granted access to your S3 bucket using the S3 bucket’s policy by adding an allow
statement for cloudtrail.amazonaws.com.cn.
When an Amazon service principal from a calling service is accessing a resource from a called service, the resource policy from the called service is only authorizing the Amazon service principal, and not the actor who configured the calling service. For example, an S3 bucket that trusts the CloudTrail service principal with no conditions could receive CloudTrail logs from the Amazon Web Services accounts that a trusted admin configures, but also CloudTrail logs from an unauthorized actor in their Amazon Web Services account, if they know the name of the S3 bucket.
The confused deputy problem arises when an actor uses the trust of an Amazon service’s service principal to gain access to resources that they are not intended to have access to.
Cross-account confused deputy prevention
The following diagram illustrates the cross-account confused deputy problem.
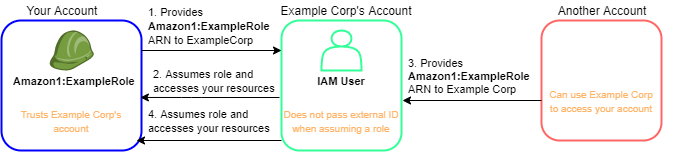
This scenario assumes the following:
-
Amazon1 is your Amazon Web Services account.
-
Amazon1:ExampleRole is a role in your account. This role's trust policy trusts Example Corp by specifying Example Corp's Amazon account as the one that can assume the role.
Here's what happens:
-
When you start using Example Corp's service, you provide the ARN of Amazon1:ExampleRole to Example Corp.
-
Example Corp uses that role ARN to obtain temporary security credentials to access resources in your Amazon Web Services account. In this way, you are trusting Example Corp as a "deputy" that can act on your behalf.
-
Another Amazon customer also starts using Example Corp's service, and this customer also provides the ARN of Amazon1:ExampleRole for Example Corp to use. Presumably the other customer learned or guessed the Amazon1:ExampleRole, which isn't a secret.
-
When the other customer asks Example Corp to access Amazon resources in (what it claims to be) its account, Example Corp uses Amazon1:ExampleRole to access resources in your account.
This is how the other customer could gain unauthorized access to your resources. Because this other customer was able to trick Example Corp into unwittingly acting on your resources, Example Corp is now a "confused deputy."
Example Corp can address the confused deputy problem by requiring that you include the
ExternalId condition check in the role's trust policy. Example Corp
generates a unique ExternalId value for each customer and uses that value
in its request to assume the role. The ExternalId value must be unique
among Example Corp's customers and controlled by Example Corp, not its customers. This
is why you get it from Example Corp and you don't come up with it on your own. This
prevents Example Corp from being a confused deputy and granting access to another
account's Amazon resources.
In our scenario, imagine Example Corp's unique identifier for you is 12345, and its identifier for the other customer is 67890. These identifiers are simplified for this scenario. Generally, these identifiers are GUIDs. Assuming that these identifiers are unique among Example Corp's customers, they are sensible values to use for the external ID.
Example Corp gives the external ID value of 12345 to you. You must then add a
Condition element to the role's trust policy that requires the sts:ExternalId value to be 12345, like this:
The Condition element in this policy allows Example Corp to assume the role only when the AssumeRole API call includes the external ID value of 12345. Example Corp makes sure that whenever it assumes a role on behalf of a customer, it always includes that customer's external ID value in the AssumeRole call. Even if another customer supplies Example Corp with your ARN, it cannot control the external ID that Example Corp includes in its request to Amazon. This helps prevent an unauthorized customer from gaining access to your resources.
The following diagram illustrates this.
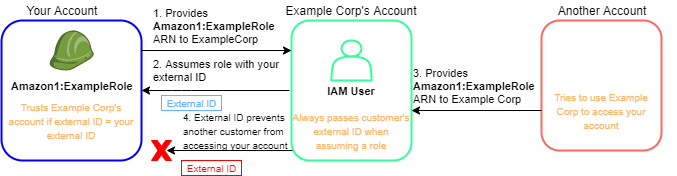
-
As before, when you start using Example Corp's service, you provide the ARN of Amazon1:ExampleRole to Example Corp.
-
When Example Corp uses that role ARN to assume the role Amazon1:ExampleRole, Example Corp includes your external ID (12345) in the AssumeRole API call. The external ID matches the role's trust policy, so the AssumeRole API call succeeds and Example Corp obtains temporary security credentials to access resources in your Amazon Web Services account.
-
Another Amazon customer also starts using Example Corp's service, and as before, this customer also provides the ARN of Amazon1:ExampleRole for Example Corp to use.
-
But this time, when Example Corp attempts to assume the role Amazon1:ExampleRole, it provides the external ID associated with the other customer (67890). The other customer has no way to change this. Example Corp does this because the request to use the role came from the other customer, so 67890 indicates the circumstance in which Example Corp is acting. Because you added a condition with your own external ID (12345) to the trust policy of Amazon1:ExampleRole, the AssumeRole API call fails. The other customer is prevented from gaining unauthorized access to resources in your account (indicated by the red "X" in the diagram).
The external ID helps prevent any other customer from tricking Example Corp into unwittingly accessing your resources.
Cross-service confused deputy prevention
The following diagram demonstrates the cross-service confused deputy problem using the CloudTrail and Amazon S3 interaction example, where an unauthorized actor writes CloudTrail logs to an Amazon S3 bucket they are not authorized to have access to.
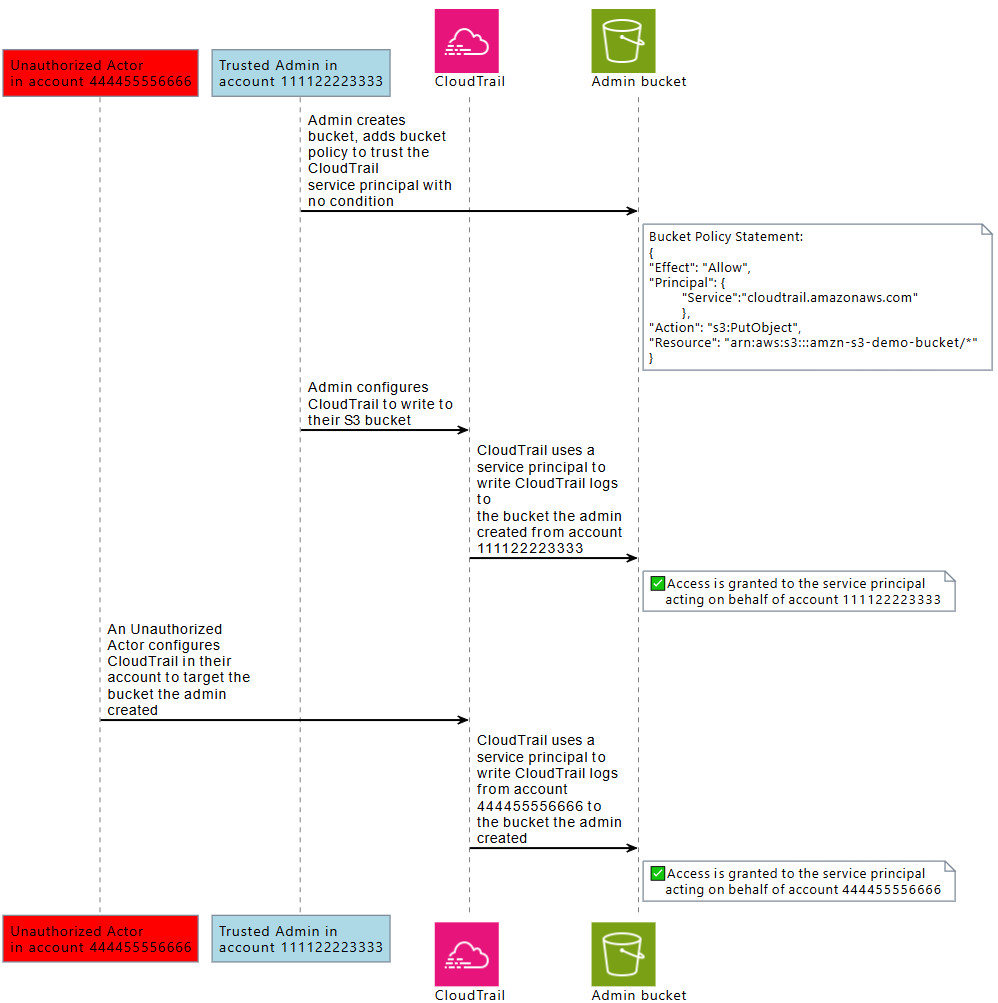
To help protect against an unauthorized actor from using the trust of an Amazon principal to gain access to your resources, Amazon service principals include information about the Amazon resource, Amazon Web Services account, and Amazon organization they’re acting on behalf of.
This information is available in global condition key values that can be used in a resource policy, or resource control policy for requests made by Amazon service principals. We recommend using aws:SourceArn, aws:SourceAccount, aws:SourceOrgID, or aws:SourceOrgPaths in your resource policies wherever an Amazon service principal is granted permission to access one of your resources. These condition keys allow you to test in your resource policies, or resource control policies that Amazon service principals accessing your resources are doing so on behalf of Amazon resources, Amazon Web Services accounts, or Amazon Organizations you expect.
-
Use
aws:SourceArnto allow an Amazon service principal to access your resources on behalf of a specific resource, such as a specific Amazon CloudTrail trail or AppStream fleet. -
Use
aws:SourceAccountto allow an Amazon service principal to access your resources on behalf of a specific Amazon Web Services account. -
Use
aws:SourceOrgIDto allow an Amazon service principal to access your resources on behalf of specific Amazon Organizations. -
Use
aws:SourceOrgPathsto allow Amazon service principal to access your resources on behalf of a specific Amazon Organizations path.
The following diagram demonstrates the cross-service confused deputy scenario when a
resource is configured with the aws:SourceAccount global condition context
key, and an unauthorized actor from another account tries to access Amazon resources they
are not intended to have access to.
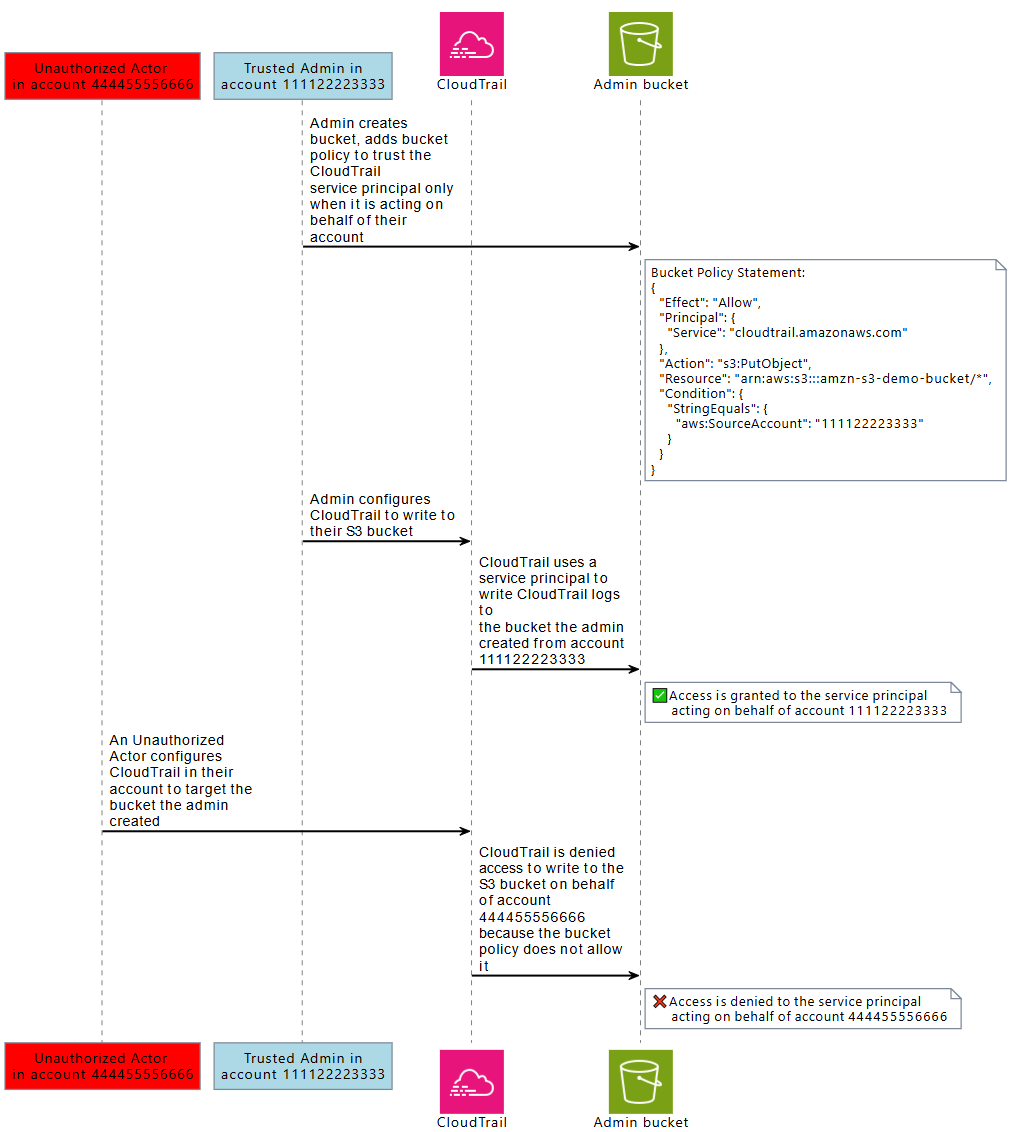
Using aws:SourceArn, aws:SourceAccount,
aws:SourceOrgID, and aws:SourceOrgPaths global condition
keys in a policy help you ensure service principals are accessing your resources on your
behalf. We recommend using these condition keys whenever access to one of your resources
is granted to an Amazon service principal.
Note
Some Amazon Web Services service interactions have additional controls to help protect against cross-service confused deputy issues that test user access to a resource. For example, when a KMS key grant is issued to an Amazon Web Services service, Amazon KMS uses the encryption context associated with the resource, and the key grant to help protect against cross-service confused deputy issues.
Please see the documentation of the services you use for more information about
service-specific mechanisms that can help avoid cross-service confused deputy risks,
and whether aws:SourceArn, aws:SourceAccount,
aws:SourceOrgID, and aws:SourceOrgPaths are
supported.
Cross-service confused deputy protection with resource-based policies
The following example policy grants the service principal
cloudtrail.amazonaws.com.cn access to the Amazon S3 bucket,
arn:aws-cn:s3:::amzn-s3-demo-bucket1, only when the service principal is acting on
behalf of Amazon Web Services account 111122223333.
This example bucket policy grants the service principal
appstream.amazonaws.com.cn access to the powershell script examplefile.psh
within the s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket2 only when it is acting on behalf of the specified
Amazon AppStream fleet, by specifying the fleet arn with aws:SourceArn.
Cross-service confused deputy protection with resource control policies
You can use resource control policies (RCP) to apply cross-service confused deputy
controls to resources of supported Amazon Web Services services. RCPs allow you to centrally apply
cross-service confused deputy controls on your resources. You can use condition keys
like aws:SourceOrgId and aws:SourceOrgPaths with RCPs attached
to your Amazon Organizations, organization units (OU) or Amazon Web Services accounts in your organization without
adding statements to specific resource-based policies. For more information about RCPs
and supported services, see Resource control
policies (RCPs) in the Amazon Organizations User Guide.
The following example RCP denies Amazon service principals access to Amazon S3 buckets in
your member accounts when aws:SourceOrgID is not equal to o-ExampleOrg. A
corresponding allow must be present in the resource-based policy of the S3 bucket to
allow Amazon Web Services service principals with a SourceOrgID equal to
o-ExampleOrg.
This policy applies the control only on requests by service principals ("Bool":
{"aws:PrincipalIsAWSService": "true"}) that have the
aws:SourceAccount key present ("Null": {"aws:SourceAccount":
"false"}), so that service integrations that don't require the use of the
condition key and calls by your principals aren't impacted. If the
aws:SourceAccount condition key is present in the request context, the
Null condition will evaluate to true, causing aws:SourceOrgID to be
enforced. We use aws:SourceAccount instead of aws:SourceOrgID
in the Null condition operator so that the control still applies if the request
originates from an account that doesn’t belong to an organization.