Understanding the Event API WebSocket protocol
Amazon AppSync Events' WebSocket API allows a client to subscribe and receive events in real-time. After the client is connected, the client can also publish to channels. Establishing a valid connection and subscribing to receive events is a simple multi-step process.
First, a client establishes a WebSocket connection with the Amazon real-time endpoint, sends a connection initialization message, and waits for acknowledgment.
After a successful connection is established, the client registers subscriptions by sending a “subscribe” message with a unique ID and a channel path of interest. Amazon AppSync confirms successful subscriptions with acknowledgment messages. The client then listens for subscription events, which are triggered when a publisher publishes events that are broadcast by the service. To maintain the connection, Amazon AppSync sends periodic keep-alive messages.
When finished, the client unsubscribes by sending “unsubscribe” messages. This system supports multiple subscriptions on a single WebSocket connection and accommodates various authorization modes, including API keys, Amazon Cognito user pools, IAM, and Lambda.
The following diagram demonstrates the WebSocket protocol message flow between the WebSocket client and the real-time endpoint.
WebSocket protocol overview
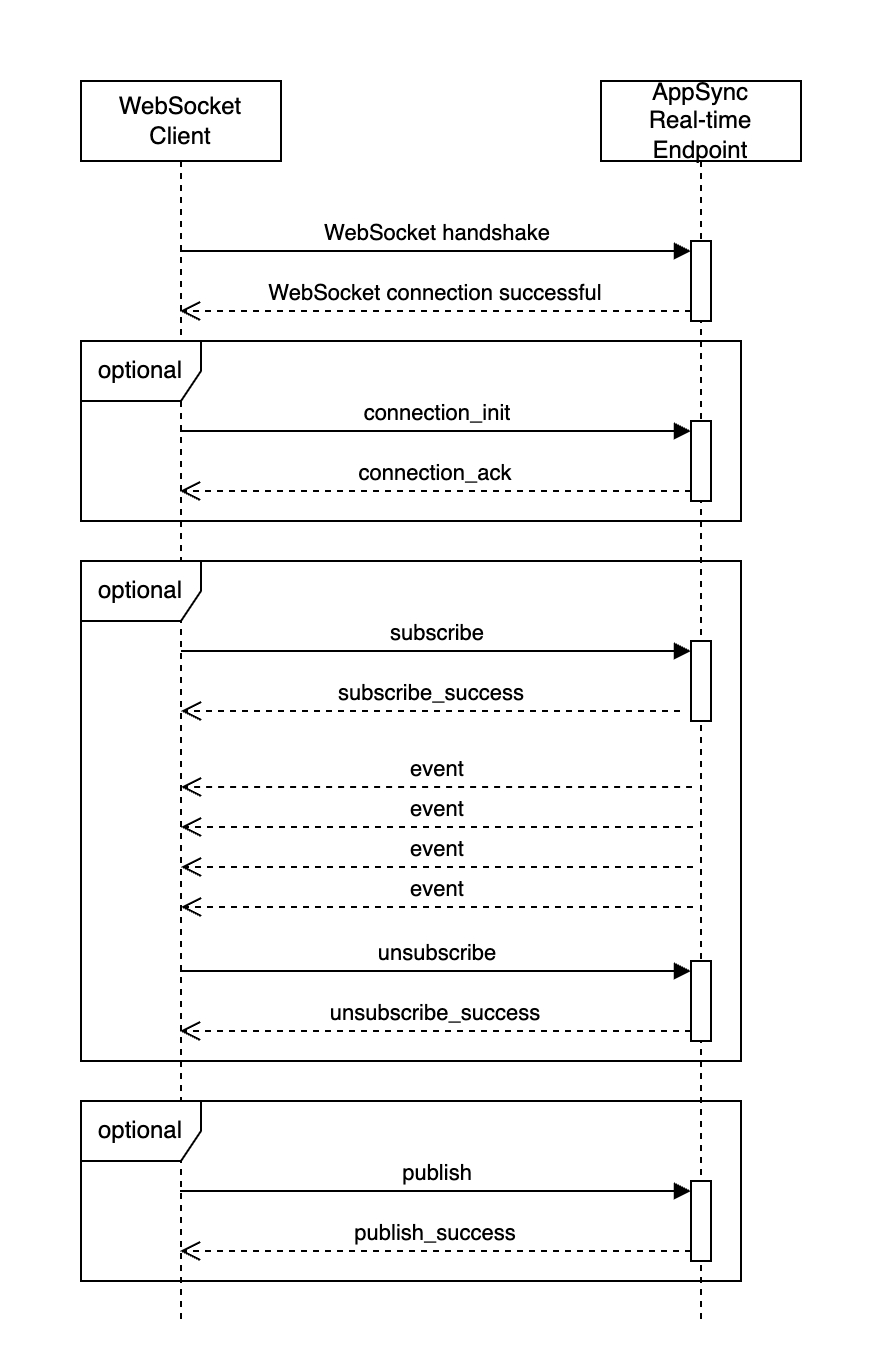
In the preceeding diagram, the following WebSocket steps occur in the message flow.
-
A client establishes a WebSocket connection with the Amazon AppSync real-time endpoint. If there is a network error, the client should do a jittered exponential backoff. For more information, see Exponential backoff and jitter
on the Amazon Architecture Blog.
-
After successfully establishing the WebSocket connection, the client can optionally send a
connection_initmessage.-
The client waits for a
connection_ackmessage from Amazon AppSync. This message includes aconnectionTimeoutMsparameter, which is the maximum wait time in milliseconds for a "ka" (keep-alive) message.
-
-
Amazon AppSync sends "ka" messages periodically. The client keeps track of the time that it received each "ka" message. If the client doesn't receive a "ka" message within
connectionTimeoutMsmilliseconds, the client should close the connection.
-
The client registers the subscription by sending a subscribe message. A single WebSocket connection supports multiple subscriptions, even if they are in different authorization modes.
-
The client waits for Amazon AppSync to send
subscribe_successmessages to confirm successful subscriptions.
-
The client listens for subscription events, which are sent after events are published to the channel of interest.
-
The client unregisters the subscription by sending an
unsubscribesubscription message. -
At any time after connection, the client can publish a message by sending a
publishmessage. Subscribing to a channel is not required before publishing. -
The client receives a
publish_successacknowledgement.
-
After unregistering all subscriptions and checking that there are no messages transferring through the WebSocket, the client can disconnect from the WebSocket connection.
Handshake details to establish the WebSocket connection
All interactions with the Amazon AppSync real-time endpoint begin with establishing a WebSocket connection. The connection remains open as long as the client remains connected, up to a maximum of 24 hours. Connecting is an operation that requires authorization credentials to complete the handshake. To connect and initiate a successful handshake with Amazon AppSync, a WebSocket client needs the following information:
-
The Amazon AppSync Events realtime and HTTP endpoints
-
The authorization details
To authorize your WebSocket connection establishment, send the authorization information as a WebSocket subprotocol. To do this, a client must wrap the appropriate authorization credentials in a JSON object, encode the object in Base64URL format, and append the encoded header string in the list of subprotocols.
The following JavaScript example converts an authorization object into a base64URL encoded string.
/** * Encodes an object into Base64 URL format * @param {*} authorization - an object with the required authorization properties **/ function getBase64URLEncoded(authorization) { return btoa(JSON.stringify(authorization)) .replace(/\+/g, '-') // Convert '+' to '-' .replace(/\//g, '_') // Convert '/' to '_' .replace(/=+$/, '') // Remove padding `=` }
Next, this example creates the required subprotocol value.
function getAuthProtocol(authorization) { const header = getBase64URLEncoded(authorization) return `header-${header}` }
The following example uses bash to create a header, and then uses wscat to connect. You
must specify aws-appsync-event-ws as one of the subprotocols.
$ REALTIME_DOMAIN='example1234567890000.appsync-realtime-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com' $ HTTP_DOMAIN='example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com' $ API_KEY='da2-12345678901234567890123456' $ header="{\"host\":\"$HTTP_DOMAIN\", \"x-api-key\":\"$API_KEY\"}" $ header=`echo "$header" | base64 | tr '+/' '-_' | tr -d '\n='` $ wscat -p 13 -s "header-$header" -s "aws-appsync-event-ws" -c "wss://$REALTIME_DOMAIN/event/realtime" Connected (press CTRL+C to quit)
Discovering the real-time endpoint from the Event API endpoint
Amazon AppSync Event APIs are configured with two endpoints: a realtime endpoint and an HTTP
endpoint. You can retrieve your endpoint information by visiting your API’s
Settings page in the Amazon Web Services Management Console or by running the Amazon CLI command
aws appsync get-api.
- Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint
-
https://example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/event
- Amazon AppSync Events real-time endpoint
-
wss://example1234567890000.appsync-realtime-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/event/realtime
Applications can connect to the HTTP endpoint (https://) using any HTTP client, and can connect to the real-time endpoint (wss://) using any WebSocket client.
With custom domain names, you can interact with both endpoints using a single domain. For example, if you configure api.example.com as your custom domain, you can interact with your HTTP and real-time endpoints using the following URLs.
- Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint
-
https://api.example.com/event
- Amazon AppSync Events real-time endpoint
-
wss://api.example.com/event/realtime
Authorization formatting based on the Amazon AppSync API authorization mode
The format of the authorization subprotocol varies depending on the Amazon AppSync authorization mode. Amazon AppSync supports API key, Amazon Cognito user pools, OpenID Connect (OIDC), Amazon Lambda, and IAM authorization modes. The host field in the object refers to the Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint, which is used to validate the connection even if the wss:// call is made against the real-time endpoint.
Use the following sections to learn how to format the authorization subprotocol for the supported authorization modes.
API key subprotocol format
Header content
-
"host": <string>: The host for the Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint or your custom domain name. Only required for connection authorization. -
"x-api-key": <string>: The API key configured for the Amazon AppSync Event API.
Example
{ "host":"example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com", "x-api-key":"da2-12345678901234567890123456" }
Amazon Cognito user pools and OpenID Connect (OIDC) subprotocol format
Header content
-
"host": <string>: The host for the Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint or your custom domain name. Only required for connection authorization. -
"Authorization": <string>: A JWT ID token. The header can use a Bearer scheme.
Example
{ "Authorization":"eyEXAMPLEiJjbG5xb3A5eW5MK09QYXIrMTJHWEFLSXBieU5WNHhsQjEXAMPLEnM2WldvPSIsImFsZyI6IlEXAMPLEn0.eyEXAMPLEiJhNmNmMjcwNy0xNjgxLTQ1NDItOWYxOC1lNjY0MTg2NjlkMzYiLCJldmVudF9pZCI6ImVkMzM5MmNkLWNjYTMtNGM2OC1hNDYyLTJlZGI3ZTNmY2FjZiIsInRva2VuX3VzZSI6ImFjY2VzcyIsInNjb3BlIjoiYXdzLmNvZ25pdG8uc2lnbmluLnVzZXIuYWRtaW4iLCJhdXRoX3RpbWUiOjE1Njk0NTc3MTgsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOlwvXC9jb2duaXRvLWlkcC5hcC1zb3V0aGVhc3QtMi5hbWF6b25hd3MuY29tXC9hcC1zb3V0aGVhc3QtMl83OHY0SVZibVAiLCJleHAiOjE1Njk0NjEzMjAsImlhdCI6MTU2OTQ1NzcyMCwianRpIjoiNTgzZjhmYmMtMzk2MS00YzA4LWJhZTAtYzQyY2IxMTM5NDY5IiwiY2xpZW50X2lkIjoiM3FlajVlMXZmMzd1N3RoZWw0dG91dDJkMWwiLCJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ImVsb3EXAMPLEn0.B4EXAMPLEFNpJ6ikVp7e6DRee95V6Qi-zEE2DJH7sHOl2zxYi7f-SmEGoh2AD8emxQRYajByz-rE4Jh0QOymN2Ys-ZIkMpVBTPgu-TMWDyOHhDUmUj2OP82yeZ3wlZAtr_gM4LzjXUXmI_K2yGjuXfXTaa1mvQEBG0mQfVd7SfwXB-jcv4RYVi6j25qgow9Ew52ufurPqaK-3WAKG32KpV8J4-Wejq8t0c-yA7sb8EnB551b7TU93uKRiVVK3E55Nk5ADPoam_WYE45i3s5qVAP_-InW75NUoOCGTsS8YWMfb6ecHYJ-1j-bzA27zaT9VjctXn9byNFZmEXAMPLExw", "host":"example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com" }
Amazon Lambda subprotocol format
Header content
-
"host": <string>: The host for the Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint or your custom domain name. Only required for connection authorization. -
"Authorization": <string>: A custom authorization token of your design.
Example
{ "Authorization":"M0UzQzM1MkQtMkI0Ni00OTZCLUI1NkQtMUM0MTQ0QjVBRTczCkI1REEzRTIxLTk5NzItNDJENi1BQjMwLTFCNjRFNzQ2NzlCNQo=", "host":"example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com" }
Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) subprotocol format
Header content
-
"accept": "application/json, text/javascript": A constant string parameter. -
"content-encoding": "amz-1.0": A constant string parameter. -
"content-type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8": A constant string parameter. -
"host": <string>: This is the host for the Amazon AppSync Events HTTP endpoint. -
"x-amz-date": <string>: The timestamp must be in UTC and in the following ISO 8601 format: YYYYMMDD'T'HHMMSS'Z'. For example, 20150830T123600Z is a valid timestamp. Don't include milliseconds in the timestamp. For more information, see Elements of an Amazon API request signature in the IAM User Guide. -
"X-Amz-Security-Token": <string>: The Amazon session token, which is required when using temporary security credentials. For more information, see Use temporary credentials with Amazon resources in the IAM User Guide. -
"Authorization": <string>: Signature Version 4 (SigV4) signing information for the Amazon AppSync endpoint. For more information on the signing process, see Create a signed Amazon API request in the IAM User Guide.
The SigV4 signing HTTP request includes a canonical URL, which is the AWS AppSync
HTTP endpoint with /event appended. The service endpoint Amazon Web Services Region is
the same Region where you're using the Amazon AppSync API, and the service name is
'appsync'.
The HTTP request to sign to connect is the following.
{ url: "https://example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/event", data: "{}", method: "POST", headers: { "accept": "application/json, text/javascript", "content-encoding": "amz-1.0", "content-type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8", "host": "example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com", } }
The following is the request to sign when sending a subscribe message. The channel name is specified in the request.
{ url: "https://example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/event", body: "{\"channel\":\"/your/channel/*\"}", method: "POST", headers: { "accept": "application/json, text/javascript", "content-encoding": "amz-1.0", "content-type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8", "host": "example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com", } }
The following is the request to sign when publishing over WebSocket. The channel name and event payload are specified in the request.
{ url: "https://example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/event", body: "{\"channel\":\"/your/channel/*\",\"events\":[{\"event_1\":\"data_1\"},{\"event_2\":\"data_2\"}]}", method: "POST", headers: { "accept": "application/json, text/javascript", "content-encoding": "amz-1.0", "content-type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8", "host": "example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com", } }
Authorization header example
{ "accept": "application/json, text/javascript", "content-encoding": "amz-1.0", "content-type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8", "host": "example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com", "x-amz-date": "20200401T001010Z", "X-Amz-Security-Token": "AgEXAMPLEZ2luX2VjEAoaDmFwLXNvdXRoZWFEXAMPLEcwRQIgAh97Cljq7wOPL8KsxP3YtDuyc/9hAj8PhJ7Fvf38SgoCIQDhJEXAMPLEPspioOztj++pEagWCveZUjKEn0zyUhBEXAMPLEjj//////////8BEXAMPLExODk2NDgyNzg1NSIMo1mWnpESWUoYw4BkKqEFSrm3DXuL8w+ZbVc4JKjDP4vUCKNR6Le9C9pZp9PsW0NoFy3vLBUdAXEXAMPLEOVG8feXfiEEA+1khgFK/wEtwR+9zF7NaMMMse07wN2gG2tH0eKMEXAMPLEQX+sMbytQo8iepP9PZOzlZsSFb/dP5Q8hk6YEXAMPLEYcKZsTkDAq2uKFQ8mYUVA9EtQnNRiFLEY83aKvG/tqLWNnGlSNVx7SMcfovkFDqQamm+88y1OwwAEYK7qcoceX6Z7GGcaYuIfGpaX2MCCELeQvZ+8WxEgOnIfz7GYvsYNjLZSaRnV4G+ILY1F0QNW64S9Nvj+BwDg3ht2CrNvpwjVYlj9U3nmxE0UG5ne83LL5hhqMpm25kmL7enVgw2kQzmU2id4IKu0C/WaoDRuO2F5zE63vJbxN8AYs7338+4B4HBb6BZ6OUgg96Q15RA41/gIqxaVPxyTpDfTU5GfSLxocdYeniqqpFMtZG2n9d0u7GsQNcFkNcG3qDZm4tDo8tZbuym0a2VcF2E5hFEgXBa+XLJCfXi/77OqAEjP0x7Qdk3B43p8KG/BaioP5RsV8zBGvH1zAgyPha2rN70/tT13yrmPd5QYEfwzexjKrV4mWIuRg8NTHYSZJUaeyCwTom80VFUJXG+GYTUyv5W22aBcnoRGiCiKEYTLOkgXecdKFTHmcIAejQ9Welr0a196Kq87w5KNMCkcCGFnwBNFLmfnbpNqT6rUBxxs3X5ntX9d8HVtSYINTsGXXMZCJ7fnbWajhg/aox0FtHX21eF6qIGT8j1z+l2opU+ggwUgkhUUgCH2TfqBj+MLMVVvpgqJsPKt582caFKArIFIvO+9QupxLnEH2hz04TMTfnU6bQC6z1buVe7h+tOLnh1YPFsLQ88anib/7TTC8k9DsBTq0ASe8R2GbSEsmO9qbbMwgEaYUhOKtGeyQsSJdhSk6XxXThrWL9EnwBCXDkICMqdntAxyyM9nWsZ4bL9JHqExgWUmfWChzPFAqn3F4y896UqHTZxlq3WGypn5HHcem2Hqf3IVxKH1inhqdVtkryEiTWrI7ZdjbqnqRbl+WgtPtKOOweDlCaRs3R2qXcbNgVhleMk4IWnF8D1695AenU1LwHjOJLkCjxgNFiWAFEPH9aEXAMPLExA==", "Authorization": "AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 Credential=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX/20200401/us-east-1/appsync/aws4_request, SignedHeaders=accept;content-encoding;content-type;host;x-amz-date;x-amz-security-token, Signature=83EXAMPLEbcc1fe3ee69f75cd5ebbf4cb4f150e4f99cec869f149c5EXAMPLEdc" }
Real-time WebSocket operations
After initiating a successful WebSocket handshake with Amazon AppSync, the client must send a subsequent message to connect to Amazon AppSync for different operations. The WebSocket API has the following properties.
WebSocket API message properties
- id
-
The client provided ID of the operation. This property is required and is used to correlate response error and success messages. For subscriptions, this property must be unique for all subscriptions within a connection. The property is a string and is limited to a maximum of 128 alphanumeric and special character
(_,+,-)characters:/^[a-zA-Z0-9-_+]{1,128}$/. - type
-
The type of operation being performed. Supported client operations are subscribe, unsubscribe, publish. The property is a string and must be one of the message types defined in the next section, Configuring message details.
- channel
-
The channel to subscribe to, or to publish events to. The property is a string made up of one to five segments separated by a slash. Each segment is limited to 50 alphanumeric + dash characters. The property is case sensitive. For example:
channelNamespaceNameorchannelNamespaceName/sub-segment-1/subSegment-2/^\/?[A-Za-z0-9](?:[A-Za-z0-9-]{0,48}[A-Za-z0-9])?(?:\/[A-Za-z0-9](?:[A-Za-z0-9-]{0,48}[A-Za-z0-9])?){0,4}\/?$/ - events
-
An array of events to be published. You can publish up to five events in a batch. Each specified event in your publish request must be a stringified valid JSON value.
- authorization
-
The authorization headers necessary to authorize the operation. For example, ApiKey will contain
x-api-key, while Amazon Cognito, OIDC, and Lambda will containauthorization. IAM will containhost,x-amz-date,x-amz-security-token, andauthorization. Thehostheader is required for IAM only.
Configuring message details
This section provides information about the syntax to use to configure the details for various message types.
Connection init message
(Optional) After the client has established the WebSocket connection, the client sends an init message to initiate the connection session.
{ "type": "connection_init" }
Connection acknowledge message
Amazon AppSync responds with an “ack” message that contains a connection timeout value. If the client doesn’t receive a keep-alive message within the connection timeout period, the client should close the connection. The connection timeout period is 5 minutes.
{ "type": "connection_ack", "connectionTimeoutMs": 300000 }
Keep-alive message
Amazon AppSync periodically sends a keep-alive message to the client to maintain the connection. If the client doesn’t receive a keep-alive message within the connection timeout period, the client should close the connection. The keep-alive interval is 60 seconds. Clients do not need to acknowledge these messages.
{ "type": "ka" }
Subscribe message
After receiving a connection_ack message, the client can send a
subscription registration message to listen for events on a channel.
-
“id” is the ID of the subscription. This ID must be unique per client connection otherwise Amazon AppSync returns an error message indicating the subscription message is duplicated.
-
“channel” is the channel to which the subscribed client is listening. Any messages published to this channel will be delivered to the subscribed client.
-
“authorization” is an object containing the fields required for authorization. The authorization object follows the same rules as the headers for connecting to the WebSocket.
{ "type": "subscribe", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "channel": "/namespaceA/subB/subC", "authorization": { "x-api-key": "da2-12345678901234567890123456", "host": "example1234567890000.appsync-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com" } }
Subscription acknowledgment message
Amazon AppSync acknowledges with a success message. “id” is the ID of the corresponding subscribe operation that succeeded.
{ "type": "subscribe_success", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69" }
In case of an error, Amazon AppSync sends a subscribe_error response.
{ "type": "subscribe_error", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "errors": [ { "errorType": "SubscriptionProcessingError", "message": "There was an error processing the operation" } ] }
Data message
When an event is published to a channel the client is subscribed to, the event is broadcast and delivered in a data message. “id” is the ID of the corresponding subscription for the channel to which the message was published.
{ "type": "data", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "event": ["\"my event content\""] }
In case of an error, such as a broadcasting error, an error can be received at the client:
{ "type": "broadcast_error", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "errors": [ { "errorType": "MessageProcessingError", "message": "There was an error processing the message" } ] }
Unsubscribe message
When the client wants to stop listening to a subscribed channel, the client sends a message to unregister the subscription. “id” is the ID of the corresponding subscription to which the client wants to unregister.
{ "type": "unsubscribe", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69" }
Amazon AppSync acknowledges with a success message. “id” is the ID of the corresponding subscribe operation that succeeded.
{ "type": "unsubscribe_success", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69" }
If an error occurs, an error message is sent back to the client
{ "type": "unsubscribe_error", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "errors": [ { "errorType": "UnknownOperationError", "message": "Unknown operation id ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69" } ] }
Publish message
Once connected, the client can start publishing messages to channels. “id” is the ID of
the publish operation. “channel” is the channel to which the events are published. The
events will be delivered to all clients subscribed to the channel. “authorization” is an
object containing the fields required for authorization. The authorization object follows
the same rules as the headers for subscribing to the channel.
{ "type": "publish", "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "channel": "/namespaceA/subB/subC", "events": [ "{ \"msg\": \"Hello World!\" }" ], "authorization": { "x-api-key": "da2-12345678901234567890123456", } }
Publish success message
The server acknowledges with a success message. “id” is the ID of the corresponding
publish operation that succeeded. “failed” is the list of events which were marked in error
while executing the publish handler.
{ "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "type": "publish_success", "successful": [ { "identifier": "221b6b3f-46fd-4ac1-a327-bd2623b7402e", "index": 0 } ], "failed": [] }
If an error occurs, an error message is sent back to the client.
{ "id": "ee849ef0-cf23-4cb8-9fcb-152ae4fd1e69", "type": "publish_error", "errors": [ { "errorType": "An error type", "message": "A message" } ] }
Disconnecting the WebSocket
Before disconnecting the WebSocket, to avoid data loss, the client should have the necessary logic to check that no operation is currently in place through the WebSocket connection. All subscriptions should be unregistered before disconnecting from the WebSocket.