Create tables based on encrypted datasets in Amazon S3
Athena can read and write to tables whose underlying datasets are SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, or CSE-KMS encrypted. Depending on the encryption option used for the table data and the type of queries ran, you will possibly have to specify some additional table properties in order to read and write encrypted data.
Reading SSE-S3/SSE-KMS encrypted tables
No additional table properties need to be specified on table creation in order to read SSE-S3/SSE-KMS encrypted datasets. Amazon S3 handles decrypting the SSE objects automatically.
Reading CSE-KMS encrypted tables
There are two different sets of table properties that can be specified in order for Athena to read CSE-KMS encrypted datasets,
-
Using the
encryption_optionandkms_keytable properties (Recommended) -
Using the
has_encrypted_datatable property
Important
If you use Amazon EMR along with EMRFS to upload CSE-KMS encrypted Parquet files, you must
disable multipart uploads by setting
fs.s3n.multipart.uploads.enabled to false. If you
don't do this, Athena is unable to determine the Parquet file length and a
HIVE_CANNOT_OPEN_SPLIT error occurs. For
more information, see Configure
multipart upload for Amazon S3 in the
Amazon EMR Management Guide.
Using encryption_option and kms_key table properties
In a CREATE TABLE statement, use a
TBLPROPERTIES clause that specifies encryption_option='CSE_KMS' and
kms_key='aws_kms_key_arn', as in the following example.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE 'my_encrypted_data' ( `n_nationkey` int, `n_name` string, `n_regionkey` int, `n_comment` string) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.serde.ParquetHiveSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.MapredParquetInputFormat' LOCATION 's3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/folder_with_my_encrypted_data/' TBLPROPERTIES ( 'encryption_option' = 'CSE_KMS', 'kms_key' = 'arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:012345678901:key/my_kms_key')
When these properties are configured,
-
Athena can read CSE-KMS encrypted objects created by the V1, V2, or V3 Amazon S3 encryption clients.
-
Athena will use the Amazon KMS key in
kms_keyto decrypt the CSE-KMS data. If any objects were encrypted with a different Amazon KMS key, the query will fail. -
Athena can still read SSE-S3 and SSE-KMS encrypted objects, though mixing server-side and client-side encrypted objects is not recommended.
Using has_encrypted_data table property
In a CREATE TABLE statement, use a
TBLPROPERTIES clause that specifies
has_encrypted_data='true', as in the following example.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE 'my_encrypted_data' ( `n_nationkey` int, `n_name` string, `n_regionkey` int, `n_comment` string) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.serde.ParquetHiveSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.MapredParquetInputFormat' LOCATION 's3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/folder_with_my_encrypted_data/' TBLPROPERTIES ( 'has_encrypted_data' = 'true')
When the has_encrypted_data table property is specified,
-
Athena can only read CSE-KMS encrypted objects created by the V1 Amazon S3 encryption client.
-
Athena will infer the Amazon KMS key used to encrypt the CSE-KMS object from the object metadata and then use that key to decrypt the object.
-
Athena can still read SSE-S3 and SSE-KMS encrypted objects, though mixing server-side and client-side encrypted objects is not recommended.
Note
When encryption_option and kms_key are specified
alongside has_encrypted_data, the encryption_option
and kms_key table properties take precedence, and
has_encrypted_data is ignored.
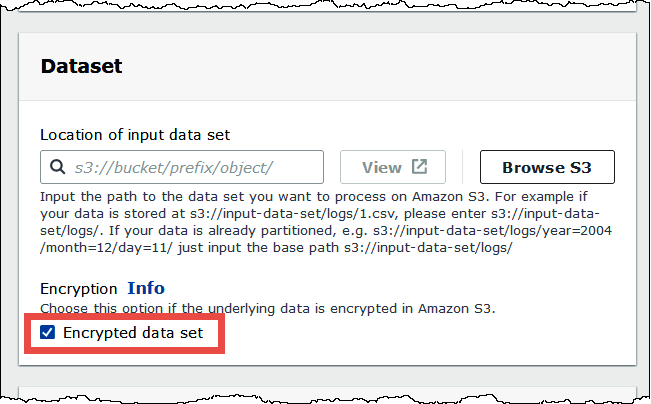
When you use the Athena console to create a table using a
form and specify the table location, select the
Encrypted data set option to add the
has_encrypted_data='true' property to the table.
In the Athena console list of tables, CSE-KMS encrypted tables with
has_encrypted_data='true' display a key-shaped icon.
Writing SSE-S3/SSE-KMS/CSE-KMS encrypted data
By default, newly inserted data files will be encrypted using the encryption configuration of the query results specified in the Athena workgroup. In order to write table data with a different encryption configuration than the encryption configuration of the query results, you will have to add some additional table properties.
In a CREATE TABLE statement, use a TBLPROPERTIES
clause that specifies encryption_option='SSE_S3 | SSE_KMS | CSE_KMS' and
kms_key='aws_kms_key_arn', as in the following example.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE 'my_encrypted_data' ( `n_nationkey` int, `n_name` string, `n_regionkey` int, `n_comment` string) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.serde.ParquetHiveSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.MapredParquetInputFormat' LOCATION 's3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/folder_with_my_encrypted_data/' TBLPROPERTIES ( 'encryption_option' = 'SSE_KMS', 'kms_key' = 'arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:012345678901:key/my_kms_key')
All newly inserted data will be encrypted using the encryption configuration specified by the table properties rather than using the encryption configuration of the query results in the workgroup.
Considerations and Limitations
When writing and reading encrypted datasets, consider the following points.
-
The
has_encrypted_data,encryption_option, andkms_keytable properties can only be used with Hive tables. -
When creating a table with CSE-KMS encrypted data, we recommend that you ensure that all data is encrypted with the same Amazon KMS key.
-
When creating a table with CSE-KMS encrypted data, we recommend that you ensure that all data is CSE-KMS encrypted and that there is not a mix of non-CSE-KMS and CSE-KMS encrypted objects.