How Athena accesses data registered with Lake Formation
The access workflow described in this section applies when you run Athena queries on Amazon S3 locations, data catalogs, or metadata objects that are registered with Lake Formation. For more information, see Registering a data lake in the Amazon Lake Formation Developer Guide. In addition to registering data, the Lake Formation administrator applies Lake Formation permissions that grant or revoke access to metadata in the data catalog, Amazon Glue Data Catalog, or the data location in Amazon S3. For more information, see Security and access control to metadata and data in the Amazon Lake Formation Developer Guide.
Each time an Athena principal (user, group, or role) runs a query on data registered using Lake Formation, Lake Formation verifies that the principal has the appropriate Lake Formation permissions to the database, table, and data source location as appropriate for the query. If the principal has access, Lake Formation vends temporary credentials to Athena, and the query runs.
The following diagram shows how credential vending works in Athena on a query-by-query
basis for a hypothetical SELECT query on a table with an Amazon S3 location or
data catalog registered in Lake Formation:
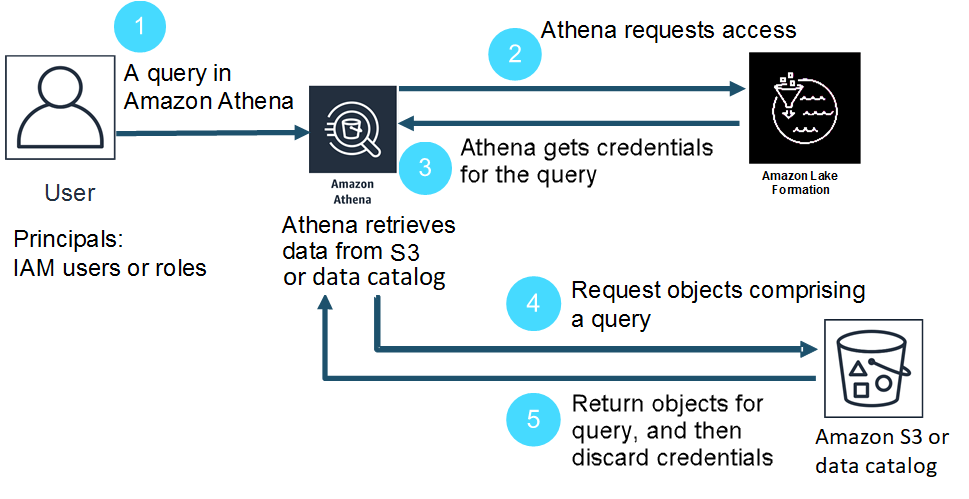
-
A principal runs a
SELECTquery in Athena. -
Athena analyzes the query and checks Lake Formation permissions to see if the principal has been granted access to the table and table columns.
-
If the principal has access, Athena requests credentials from Lake Formation. If the principal does not have access, Athena issues an access denied error.
-
Lake Formation issues credentials to Athena to use when reading data from Amazon S3 or catalog, along with the list of allowed columns.
-
Athena uses the Lake Formation temporary credentials to query the data from Amazon S3 or catalog. After the query completes, Athena discards the credentials.