Step 7: Run the Amazon DMS Task
After you create your Amazon Database Migration Service (Amazon DMS) task, do a test run to identify the full load run time and ongoing replication performance. You can validate that initial configurations work as expected. You can do this by monitoring and documenting resource utilization on the source database, replication instance, and target database. These details make up the initial baseline and help determine if you need further optimization.
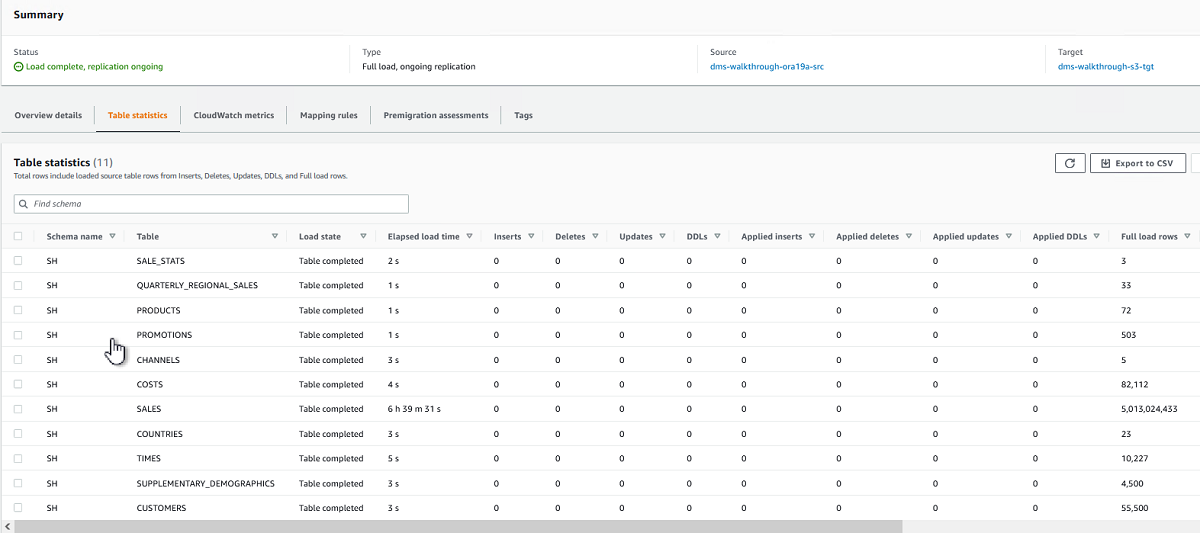
After you started the task, the full load operation starts loading tables. You can see the table load completion status in the Table Statistics section and the corresponding target files in the Amazon S3 bucket.
The following image shows table statistics with c5.12xlarge replication instance with parallel-load ranges option. The full load completed in 6.5 hours. This means that we achieved our goal of completing full load in less than 8 hours.
We also monitored the CloudWatch metrics such as compute, memory, network to identify the resource usage of Amazon DMS instances. You have to identify the resource constraint and scale-up to the Amazon DMS instance class that serves your workloads better. You could also scale-down the Amazon DMS instance to a t3 or r5 instance class based on the transaction volume for your ongoing replication task.
Because we turned on the parallel-load option, the I/O load on the replication instance is expected to increase. We described in Step 1: Create an Amazon DMS Replication Instance that you should monitor the Write IOPS and Read IOPS metrics in CloudWatch to make sure that the total IOPS (write + read IOPS) doesn’t exceed the total IOPS available for your replication instance. If it does, make sure that you allocate more storage to scale for better I/O performance. For more information, see Monitoring replication tasks using Amazon CloudWatch.
We covered most prerequisites that help avoid errors related to configuration. If you observe issues when running the task, then see Troubleshooting migration tasks in Database Migration Service, Best practices for Database Migration Service, or reach out to Amazon Support for further assistance.
Optionally, you could choose to validate the successful completion of the data migration by querying the Amazon S3 data through Athena console. You can run count or aggregation queries on key metric columns and compare with the source database to validate the migration task. Amazon DMS also provides data validation features to verify successful migration of the data. For more information, see Data validation.
After you completed the migration, validate that your data migrated successfully and delete the cloud resources that you created.