Services or capabilities described in Amazon Web Services documentation might vary by Region. To see the differences applicable to the China Regions,
see Getting Started with Amazon Web Services in China
(PDF).
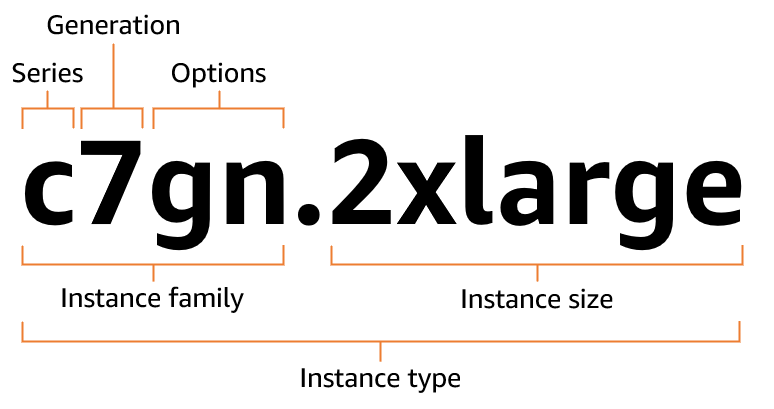
Amazon EC2 instance type naming conventions
Amazon EC2 provides a variety of instance types so you can choose the type that best meets your
requirements. Instance types are named based on their instance family
and instance size. The first position of the instance family indicates
the series, for example c. The second position indicates
the generation, for example 7. The third position indicates
the options, for example gn. After the period (.)
is the instance size, such as small or 4xlarge, or metal
for bare metal instances.
| Series |
Options |
-
C – Compute optimized
-
D – Dense storage
-
F – FPGA
-
G – Graphics intensive
-
Hpc – High performance computing
-
I – Storage optimized
-
Im – Storage optimized (1 to 4 ratio of vCPU to memory)
-
Is – Storage optimized (1 to 6 ratio of vCPU to memory)
-
Inf – Amazon Inferentia
-
M – General purpose
-
Mac – macOS
-
P – GPU accelerated
-
R – Memory optimized
-
T – Burstable performance
-
Trn – Amazon Trainium
-
U – High memory
-
VT – Video transcoding
-
X – Memory intensive
-
Z – High memory
|
-
a – AMD processors
-
b*00 | gb*00 – Accelerated by NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs
-
g – Amazon Graviton processors
-
i – Intel processors
-
m* | m*pro– Apple chip
-
b – Block storage optimization
-
d – Instance store volumes
-
e – Extra instance storage (for
storage optimized instance types), extra memory (for memory optimized instance
types), or extra GPU memory (for accelerated computing instance types).
-
flex – Flex instance
-
n – Network and EBS optimized
-
q – Qualcomm inference accelerators
-
*tb – Amount of memory for
high-memory instances (3 TiB to 32 TiB)
-
z – High CPU frequency
|