Help improve this page
To contribute to this user guide, choose the Edit this page on GitHub link that is located in the right pane of every page.
Route internet traffic with Amazon Load Balancer Controller
Tip
Register
The Amazon Load Balancer Controller manages Amazon Elastic Load Balancers for a Kubernetes cluster. You can use the controller to expose your cluster apps to the internet. The controller provisions Amazon load balancers that point to cluster Service or Ingress resources. In other words, the controller creates a single IP address or DNS name that points to multiple pods in your cluster.
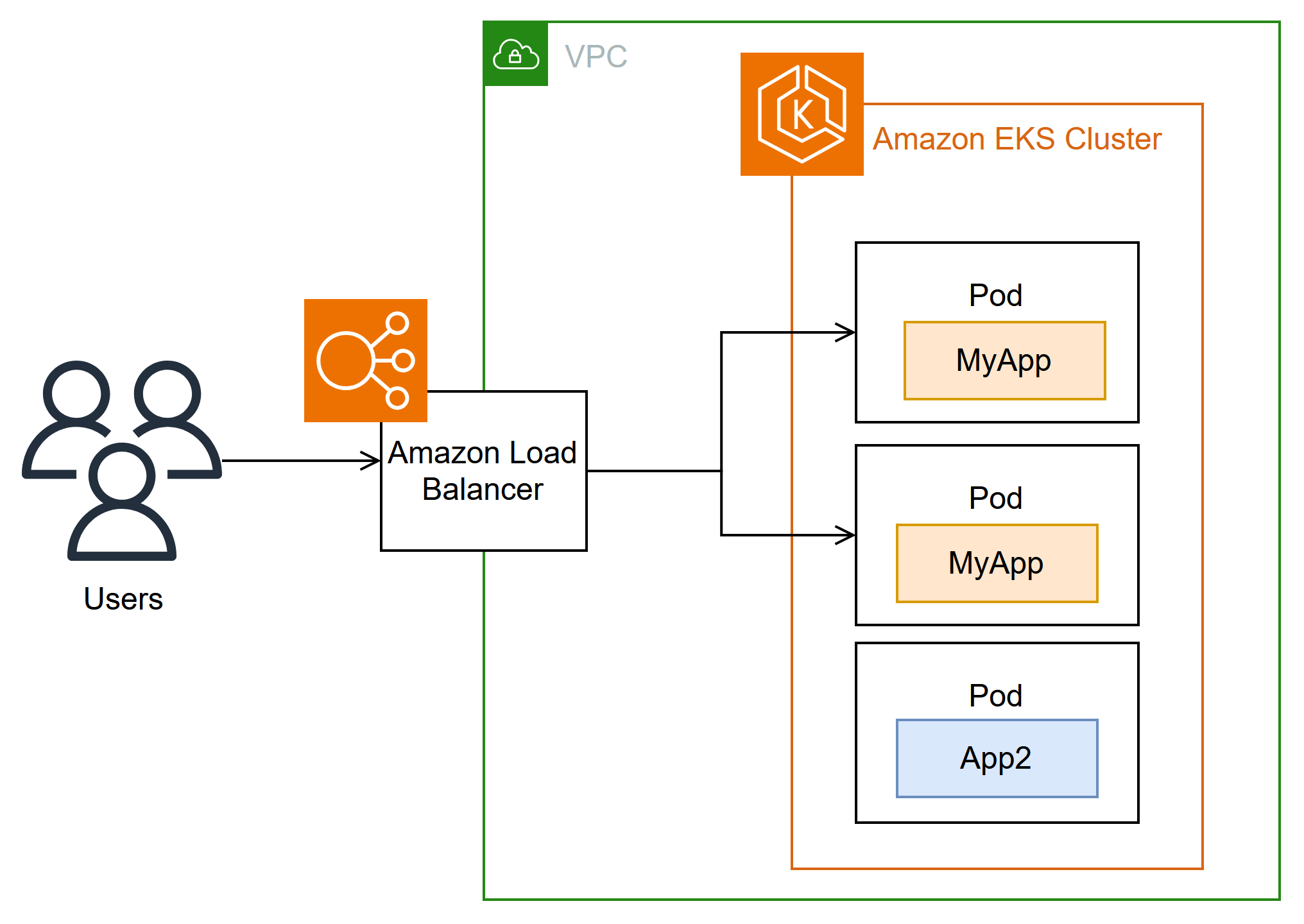
The controller watches for Kubernetes Ingress or Service resources. In response, it creates the appropriate Amazon Elastic Load Balancing resources. You can configure the specific behavior of the load balancers by applying annotations to the Kubernetes resources. For example, you can attach Amazon security groups to load balancers using annotations.
The controller provisions the following resources:
-
Kubernetes
Ingress -
The LBC creates an Amazon Application Load Balancer (ALB) when you create a Kubernetes
Ingress. Review the annotations you can apply to an Ingress resource. -
Kubernetes service of the
LoadBalancertype -
The LBC creates an Amazon Network Load Balancer (NLB)when you create a Kubernetes service of type
LoadBalancer. Review the annotations you can apply to a Service resource.In the past, the Kubernetes network load balancer was used for instance targets, but the LBC was used for IP targets. With the Amazon Load Balancer Controller version
2.3.0or later, you can create NLBs using either target type. For more information about NLB target types, see Target type in the User Guide for Network Load Balancers.
The controller is an open-source project
Before deploying the controller, we recommend that you review the prerequisites and considerations in Route application and HTTP traffic with Application Load Balancers and Route TCP and UDP traffic with Network Load Balancers. In those topics, you will deploy a sample app that includes an Amazon load balancer.
-
Kubernetes
GatewayAPI -
With the Amazon Load Balancer Controller version
2.14.0or later, the LBC creates an Amazon Application Load Balancer (ALB) when you create a KubernetesGateway. Kubernetes Gateway standardizes more configuration than Ingress, which needed custom annotations for many common options. Review the configuration that you can apply to an Gateway resource.For more information about the GatewayAPI, see Gateway APIin the Kubernetes documentation.
Install the controller
You can use one of the following procedures to install the Amazon Load Balancer Controller:
-
If you are new to Amazon EKS, we recommend that you use Helm for the installation because it simplifies the Amazon Load Balancer Controller installation. For more information, see Install Amazon Load Balancer Controller with Helm.
-
For advanced configurations, such as clusters with restricted network access to public container registries, use Kubernetes Manifests. For more information, see Install Amazon Load Balancer Controller with manifests.
Migrate from deprecated controller versions
-
If you have deprecated versions of the Amazon Load Balancer Controller installed, see Migrate apps from deprecated ALB Ingress Controller.
-
Deprecated versions cannot be upgraded. They must be removed and a current version of the Amazon Load Balancer Controller installed.
-
Deprecated versions include:
-
Amazon ALB Ingress Controller for Kubernetes ("Ingress Controller"), a predecessor to the Amazon Load Balancer Controller.
-
Any
0.1.version of the Amazon Load Balancer Controllerx
-
Legacy cloud provider
Kubernetes includes a legacy cloud provider for Amazon. The legacy cloud provider is capable of provisioning Amazon load balancers, similar to the Amazon Load Balancer Controller. The legacy cloud provider creates Classic Load Balancers. If you do not install the Amazon Load Balancer Controller, Kubernetes will default to using the legacy cloud provider. You should install the Amazon Load Balancer Controller and avoid using the legacy cloud provider.
Important
In versions 2.5 and newer, the Amazon Load Balancer Controller becomes the default controller for Kubernetes service resources with the type: LoadBalancer and makes an Amazon Network Load Balancer (NLB) for each service. It does this by making a mutating webhook for services, which sets the spec.loadBalancerClass field to service.k8s.aws/nlb for new services of type: LoadBalancer. You can turn off this feature and revert to using the legacy Cloud ProviderenableServiceMutatorWebhook to false. The cluster won’t provision new Classic Load Balancers for your services unless you turn off this feature. Existing Classic Load Balancers will continue to work.