Help improve this page
To contribute to this user guide, choose the Edit this page on GitHub link that is located in the right pane of every page.
Restrict Pod network traffic with Kubernetes network policies
You can use a Kubernetes network policy to restrict network traffic to and from your Pods. For more information, see Network Policies
You must configure the following in order to use this feature:
-
Set up policy enforcement at Pod startup. You do this in the
aws-nodecontainer of the VPC CNIDaemonSet. -
Enable the network policy parameter for the add-on.
-
Configure your cluster to use the Kubernetes network policy
Before you begin, review the considerations. For more information, see Considerations.
Prerequisites
The following are prerequisites for the feature:
Minimum cluster version
An existing Amazon EKS cluster. To deploy one, see Get started with Amazon EKS. The cluster must be running one of the Kubernetes versions and platform versions listed in the following table. Note that any Kubernetes and platform versions later than those listed are also supported. You can check your current Kubernetes version by replacing my-cluster in the following command with the name of your cluster and then running the modified command:
aws eks describe-cluster --name my-cluster --query cluster.version --output text
| Kubernetes version | Platform version |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minimum VPC CNI version
To create both standard Kubernetes network policies and admin network policies, you need to run version 1.21 of the VPC CNI plugin. You can see which version that you currently have with the following command.
kubectl describe daemonset aws-node --namespace kube-system | grep amazon-k8s-cni: | cut -d : -f 3
If your version is earlier than 1.21, see Update the Amazon VPC CNI (Amazon EKS add-on) to upgrade to version 1.21 or later.
Minimum Linux kernel version
Your nodes must have Linux kernel version 5.10 or later. You can check your kernel version with uname -r. If you’re using the latest versions of the Amazon EKS optimized Amazon Linux, Amazon EKS optimized accelerated Amazon Linux AMIs, and Bottlerocket AMIs, they already have the required kernel version.
The Amazon EKS optimized accelerated Amazon Linux AMI version v20231116 or later have kernel version 5.10.
Step 1: Set up policy enforcement at Pod startup
The Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes configures network policies for pods in parallel with the pod provisioning. Until all of the policies are configured for the new pod, containers in the new pod will start with a default allow policy. This is called standard mode. A default allow policy means that all ingress and egress traffic is allowed to and from the new pods. For example, the pods will not have any firewall rules enforced (all traffic is allowed) until the new pod is updated with the active policies.
With the NETWORK_POLICY_ENFORCING_MODE variable set to strict, pods that use the VPC CNI start with a default deny policy, then policies are configured. This is called strict mode. In strict mode, you must have a network policy for every endpoint that your pods need to access in your cluster. Note that this requirement applies to the CoreDNS pods. The default deny policy isn’t configured for pods with Host networking.
You can change the default network policy by setting the environment variable NETWORK_POLICY_ENFORCING_MODE to strict in the aws-node container of the VPC CNI DaemonSet.
env: - name: NETWORK_POLICY_ENFORCING_MODE value: "strict"
Step 2: Enable the network policy parameter for the add-on
The network policy feature uses port 8162 on the node for metrics by default. Also, the feature uses port 8163 for health probes. If you run another application on the nodes or inside pods that needs to use these ports, the app fails to run. From VPC CNI version v1.14.1 or later, you can change these ports.
Use the following procedure to enable the network policy parameter for the add-on.
Amazon Web Services Management Console
-
Open the Amazon EKS console
. -
In the left navigation pane, select Clusters, and then select the name of the cluster that you want to configure the Amazon VPC CNI add-on for.
-
Choose the Add-ons tab.
-
Select the box in the top right of the add-on box and then choose Edit.
-
On the Configure
Amazon VPC CNIpage:-
Select a
v1.14.0-eksbuild.3or later version in the Version list. -
Expand the Optional configuration settings.
-
Enter the JSON key
"enableNetworkPolicy":and value"true"in Configuration values. The resulting text must be a valid JSON object. If this key and value are the only data in the text box, surround the key and value with curly braces{ }.The following example has network policy feature enabled and metrics and health probes are set to the default port numbers:
{ "enableNetworkPolicy": "true", "nodeAgent": { "healthProbeBindAddr": "8163", "metricsBindAddr": "8162" } }
-
Helm
If you have installed the Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes through helm, you can update the configuration to change the ports.
-
Run the following command to change the ports. Set the port number in the value for either key
nodeAgent.metricsBindAddror keynodeAgent.healthProbeBindAddr, respectively.helm upgrade --set nodeAgent.metricsBindAddr=8162 --set nodeAgent.healthProbeBindAddr=8163 aws-vpc-cni --namespace kube-system eks/aws-vpc-cni
kubectl
-
Open the
aws-nodeDaemonSetin your editor.kubectl edit daemonset -n kube-system aws-node -
Replace the port numbers in the following command arguments in the
args:in theaws-network-policy-agentcontainer in the VPC CNIaws-nodedaemonset manifest.- args: - --metrics-bind-addr=:8162 - --health-probe-bind-addr=:8163
Step 3: Configure your cluster to use Kubernetes network policies
You can set this for an Amazon EKS add-on or self-managed add-on.
Using the Amazon CLI, you can configure the cluster to use Kubernetes network policies by running the following command. Replace my-cluster with the name of your cluster and the IAM role ARN with the role that you are using.
aws eks update-addon --cluster-name my-cluster --addon-name vpc-cni --addon-version v1.14.0-eksbuild.3 \ --service-account-role-arn arn:aws-cn:iam::123456789012:role/AmazonEKSVPCCNIRole \ --resolve-conflicts PRESERVE --configuration-values '{"enableNetworkPolicy": "true"}'
To configure this using the Amazon Management Console, follow the below steps:
-
Open the Amazon EKS console
. -
In the left navigation pane, select Clusters, and then select the name of the cluster that you want to configure the Amazon VPC CNI add-on for.
-
Choose the Add-ons tab.
-
Select the box in the top right of the add-on box and then choose Edit.
-
On the Configure
Amazon VPC CNIpage:-
Select a
v1.14.0-eksbuild.3or later version in the Version list. -
Expand the Optional configuration settings.
-
Enter the JSON key
"enableNetworkPolicy":and value"true"in Configuration values. The resulting text must be a valid JSON object. If this key and value are the only data in the text box, surround the key and value with curly braces{ }. The following example shows network policy is enabled:{ "enableNetworkPolicy": "true" }The following screenshot shows an example of this scenario.
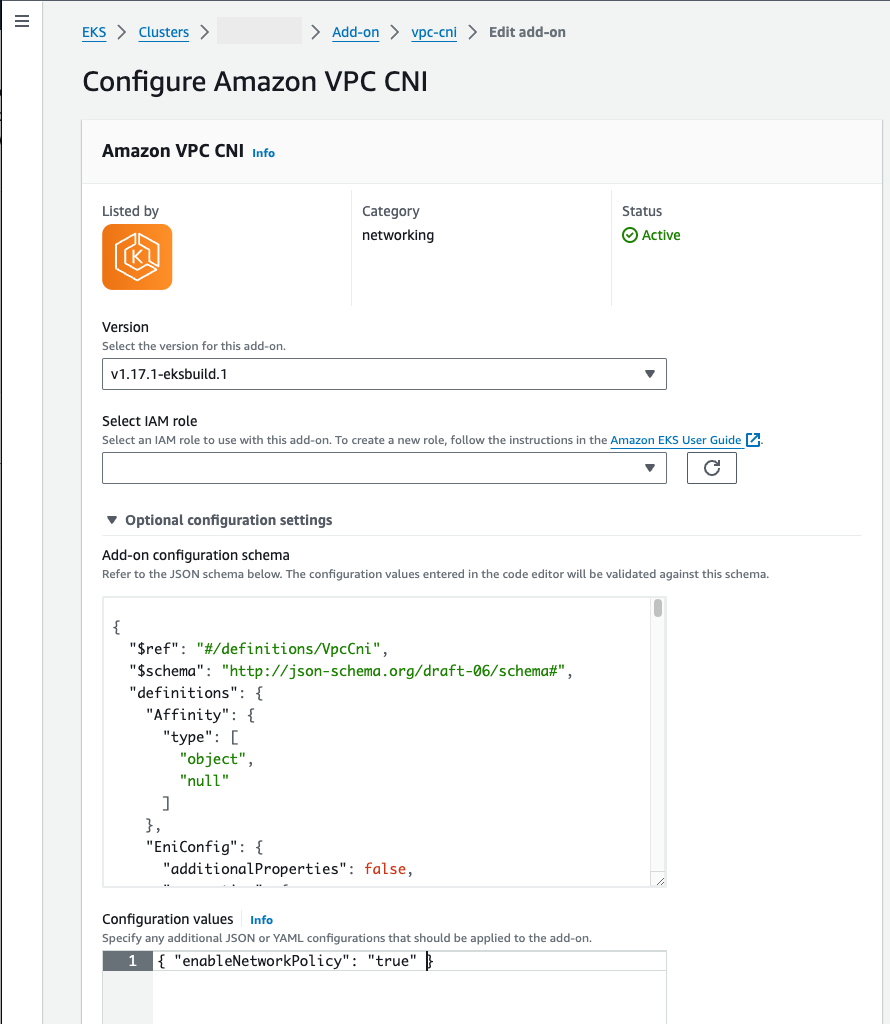
-
Helm
If you have installed the Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes through helm, you can update the configuration to enable network policy.
-
Run the following command to enable network policy.
helm upgrade --set enableNetworkPolicy=true aws-vpc-cni --namespace kube-system eks/aws-vpc-cni
kubectl
-
Open the
amazon-vpc-cniConfigMapin your editor.kubectl edit configmap -n kube-system amazon-vpc-cni -o yaml -
Add the following line to the
datain theConfigMap.enable-network-policy-controller: "true"Once you’ve added the line, your
ConfigMapshould look like the following example.apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: amazon-vpc-cni namespace: kube-system data: enable-network-policy-controller: "true" -
Open the
aws-nodeDaemonSetin your editor.kubectl edit daemonset -n kube-system aws-node-
Replace the
falsewithtruein the command argument--enable-network-policy=falsein theargs:in theaws-network-policy-agentcontainer in the VPC CNIaws-nodedaemonset manifest.- args: - --enable-network-policy=true
-
Step 4. Next steps
After you complete the configuration, confirm that the aws-node pods are running on your cluster.
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep 'aws-node\|amazon'
An example output is as follows.
aws-node-gmqp7 2/2 Running 1 (24h ago) 24h aws-node-prnsh 2/2 Running 1 (24h ago) 24h
There are 2 containers in the aws-node pods in versions 1.14 and later. In previous versions and if network policy is disabled, there is only a single container in the aws-node pods.
You can now deploy Kubernetes network policies to your cluster.
To implement Kubernetes network policies, you can create Kubernetes NetworkPolicy or ClusterNetworkPolicy objects and deploy them to your cluster. NetworkPolicy objects are scoped to a namespace, while ClusterNetworkPolicy objects can be scoped to the whole cluster or multiple namespaces. You implement policies to allow or deny traffic between Pods based on label selectors, namespaces, and IP address ranges. For more information about creating NetworkPolicy objects, see Network Policies
Enforcement of Kubernetes NetworkPolicy objects is implemented using the Extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF). Relative to iptables based implementations, it offers lower latency and performance characteristics, including reduced CPU utilization and avoiding sequential lookups. Additionally, eBPF probes provide access to context rich data that helps debug complex kernel level issues and improve observability. Amazon EKS supports an eBPF-based exporter that leverages the probes to log policy results on each node and export the data to external log collectors to aid in debugging. For more information, see the eBPF documentation