Help improve this page
To contribute to this user guide, choose the Edit this page on GitHub link that is located in the right pane of every page.
Troubleshooting Kubernetes network policies For Amazon EKS
This is the troubleshooting guide for network policy feature of the Amazon VPC CNI.
This guide covers:
-
Install information, CRD and RBAC permissions New policyendpoints CRD and permissions
-
Logs to examine when diagnosing network policy problems Network policy logs
-
Running the eBPF SDK collection of tools to troubleshoot
-
Known issues and solutions Known issues and solutions
Note
Note that network policies are only applied to pods that are made by Kubernetes Deployments. For more limitations of the network policies in the VPC CNI, see Considerations.
You can troubleshoot and investigate network connections that use network policies by reading the Network policy logs and by running tools from the eBPF SDK.
New policyendpoints CRD and permissions
-
CRD:
policyendpoints.networking.k8s.aws -
Kubernetes API:
apiservicecalledv1.networking.k8s.io -
Kubernetes resource:
Kind: NetworkPolicy -
RBAC:
ClusterRolecalledaws-node(VPC CNI),ClusterRolecalledeks:network-policy-controller(network policy controller in EKS cluster control plane)
For network policy, the VPC CNI creates a new CustomResourceDefinition (CRD) called policyendpoints.networking.k8s.aws. The VPC CNI must have permissions to create the CRD and create CustomResources (CR) of this and the other CRD installed by the VPC CNI (eniconfigs.crd.k8s.amazonaws.com). Both of the CRDs are available in the crds.yaml filepolicyendpoints.
The Kubernetes Network Policy is part of the apiservice called v1.networking.k8s.io, and this is apiversion: networking.k8s.io/v1 in your policy YAML files. The VPC CNI DaemonSet must have permissions to use this part of the Kubernetes API.
The VPC CNI permissions are in a ClusterRole called aws-node. Note that ClusterRole objects aren’t grouped in namespaces. The following shows the aws-node of a cluster:
kubectl get clusterrole aws-node -o yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance: aws-vpc-cni app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm app.kubernetes.io/name: aws-node app.kubernetes.io/version: v1.19.4 helm.sh/chart: aws-vpc-cni-1.19.4 k8s-app: aws-node name: aws-node rules: - apiGroups: - crd.k8s.amazonaws.com resources: - eniconfigs verbs: - list - watch - get - apiGroups: - "" resources: - namespaces verbs: - list - watch - get - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods verbs: - list - watch - get - apiGroups: - "" resources: - nodes verbs: - list - watch - get - apiGroups: - "" - events.k8s.io resources: - events verbs: - create - patch - list - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.aws resources: - policyendpoints verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.aws resources: - policyendpoints/status verbs: - get - apiGroups: - vpcresources.k8s.aws resources: - cninodes verbs: - get - list - watch - patch
Also, a new controller runs in the control plane of each EKS cluster. The controller uses the permissions of the ClusterRole called eks:network-policy-controller. The following shows the eks:network-policy-controller of a cluster:
kubectl get clusterrole eks:network-policy-controller -o yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: amazon-network-policy-controller-k8s name: eks:network-policy-controller rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - namespaces verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - "" resources: - services verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.aws resources: - policyendpoints verbs: - create - delete - get - list - patch - update - watch - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.aws resources: - policyendpoints/finalizers verbs: - update - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.aws resources: - policyendpoints/status verbs: - get - patch - update - apiGroups: - networking.k8s.io resources: - networkpolicies verbs: - get - list - patch - update - watch
Network policy logs
Each decision by the VPC CNI whether connections are allowed or denied by a network policies is logged in flow logs. The network policy logs on each node include the flow logs for every pod that has a network policy. Network policy logs are stored at /var/log/aws-routed-eni/network-policy-agent.log. The following example is from a network-policy-agent.log file:
{"level":"info","timestamp":"2023-05-30T16:05:32.573Z","logger":"ebpf-client","msg":"Flow Info: ","Src IP":"192.168.87.155","Src Port":38971,"Dest IP":"64.6.160","Dest Port":53,"Proto":"UDP","Verdict":"ACCEPT"}
Network policy logs are disabled by default. To enable the network policy logs, follow these steps:
Note
Network policy logs require an additional 1 vCPU for the aws-network-policy-agent container in the VPC CNI aws-node
DaemonSet manifest.
Amazon EKS add-on
- Amazon Web Services Management Console
-
-
Open the Amazon EKS console
. -
In the left navigation pane, select Clusters, and then select the name of the cluster that you want to configure the Amazon VPC CNI add-on for.
-
Choose the Add-ons tab.
-
Select the box in the top right of the add-on box and then choose Edit.
-
On the Configure
Amazon VPC CNIpage:-
Select a
v1.14.0-eksbuild.3or later version in the Version dropdown list. -
Expand the Optional configuration settings.
-
Enter the top-level JSON key
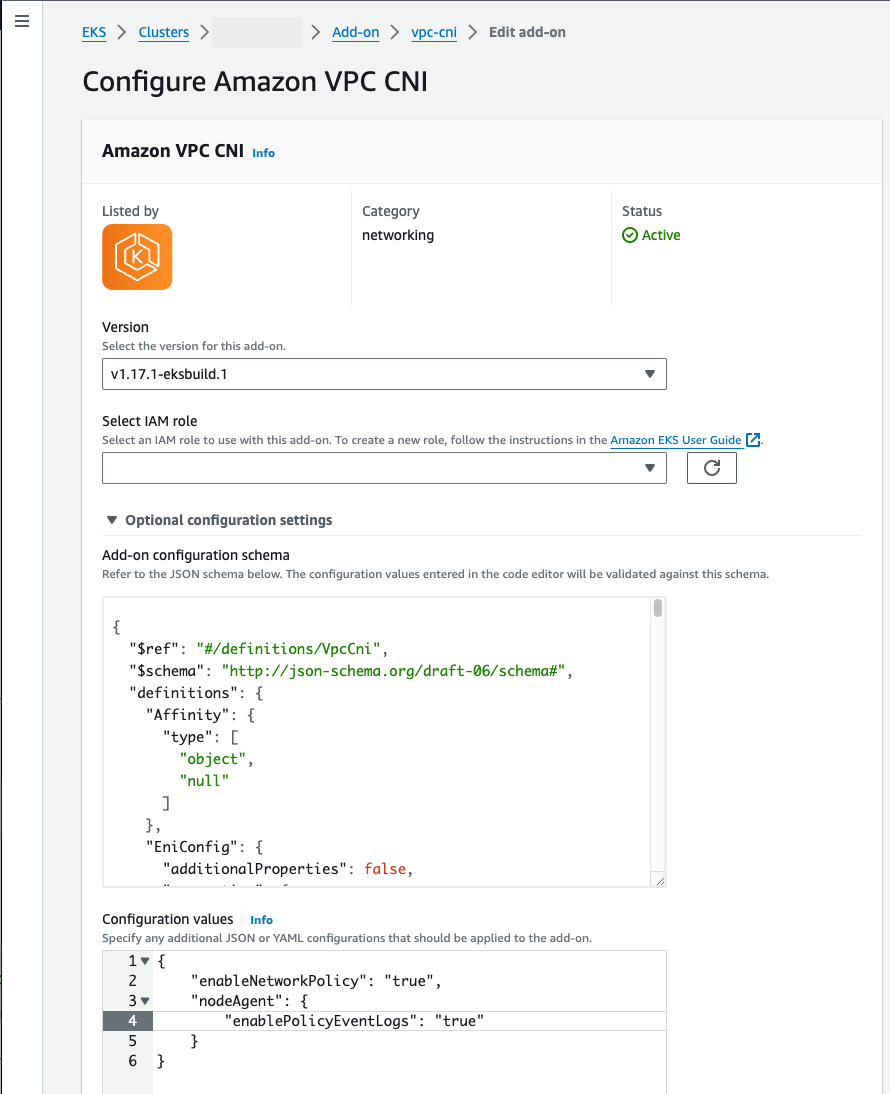
"nodeAgent":and value is an object with a key"enablePolicyEventLogs":and value of"true"in Configuration values. The resulting text must be a valid JSON object. The following example shows network policy and the network policy logs are enabled, and the network policy logs are sent to CloudWatch Logs:{ "enableNetworkPolicy": "true", "nodeAgent": { "enablePolicyEventLogs": "true" } }
-
-
The following screenshot shows an example of this scenario.
- Amazon CLI
-
-
Run the following Amazon CLI command. Replace
my-clusterwith the name of your cluster and replace the IAM role ARN with the role that you are using.aws eks update-addon --cluster-name my-cluster --addon-name vpc-cni --addon-version v1.14.0-eksbuild.3 \ --service-account-role-arn arn:aws-cn:iam::123456789012:role/AmazonEKSVPCCNIRole \ --resolve-conflicts PRESERVE --configuration-values '{"nodeAgent": {"enablePolicyEventLogs": "true"}}'
-
Self-managed add-on
- Helm
-
If you have installed the Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes through
helm, you can update the configuration to write the network policy logs.-
Run the following command to enable network policy.
helm upgrade --set nodeAgent.enablePolicyEventLogs=true aws-vpc-cni --namespace kube-system eks/aws-vpc-cni
-
- kubectl
-
If you have installed the Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes through
kubectl, you can update the configuration to write the network policy logs.-
Open the
aws-nodeDaemonSetin your editor.kubectl edit daemonset -n kube-system aws-node -
Replace the
falsewithtruein the command argument--enable-policy-event-logs=falsein theargs:in theaws-network-policy-agentcontainer in the VPC CNIaws-nodeDaemonSetmanifest.- args: - --enable-policy-event-logs=true
-
Send network policy logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs
You can monitor the network policy logs using services such as Amazon CloudWatch Logs. You can use the following methods to send the network policy logs to CloudWatch Logs.
For EKS clusters, the policy logs will be located under /aws/eks/ and for self-managed K8S clusters, the logs will be placed under cluster-name/cluster//aws/k8s-cluster/cluster/.
Send network policy logs with Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes
If you enable network policy, a second container is add to the aws-node pods for a node agent. This node agent can send the network policy logs to CloudWatch Logs.
Note
Only the network policy logs are sent by the node agent. Other logs made by the VPC CNI aren’t included.
Prerequisites
-
Add the following permissions as a stanza or separate policy to the IAM role that you are using for the VPC CNI.
{ "Version":"2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "VisualEditor0", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "logs:DescribeLogGroups", "logs:CreateLogGroup", "logs:CreateLogStream", "logs:PutLogEvents" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }
Amazon EKS add-on
- Amazon Web Services Management Console
-
-
Open the Amazon EKS console
. -
In the left navigation pane, select Clusters, and then select the name of the cluster that you want to configure the Amazon VPC CNI add-on for.
-
Choose the Add-ons tab.
-
Select the box in the top right of the add-on box and then choose Edit.
-
On the Configure
Amazon VPC CNIpage:-
Select a
v1.14.0-eksbuild.3or later version in the Version dropdown list. -
Expand the Optional configuration settings.
-
Enter the top-level JSON key
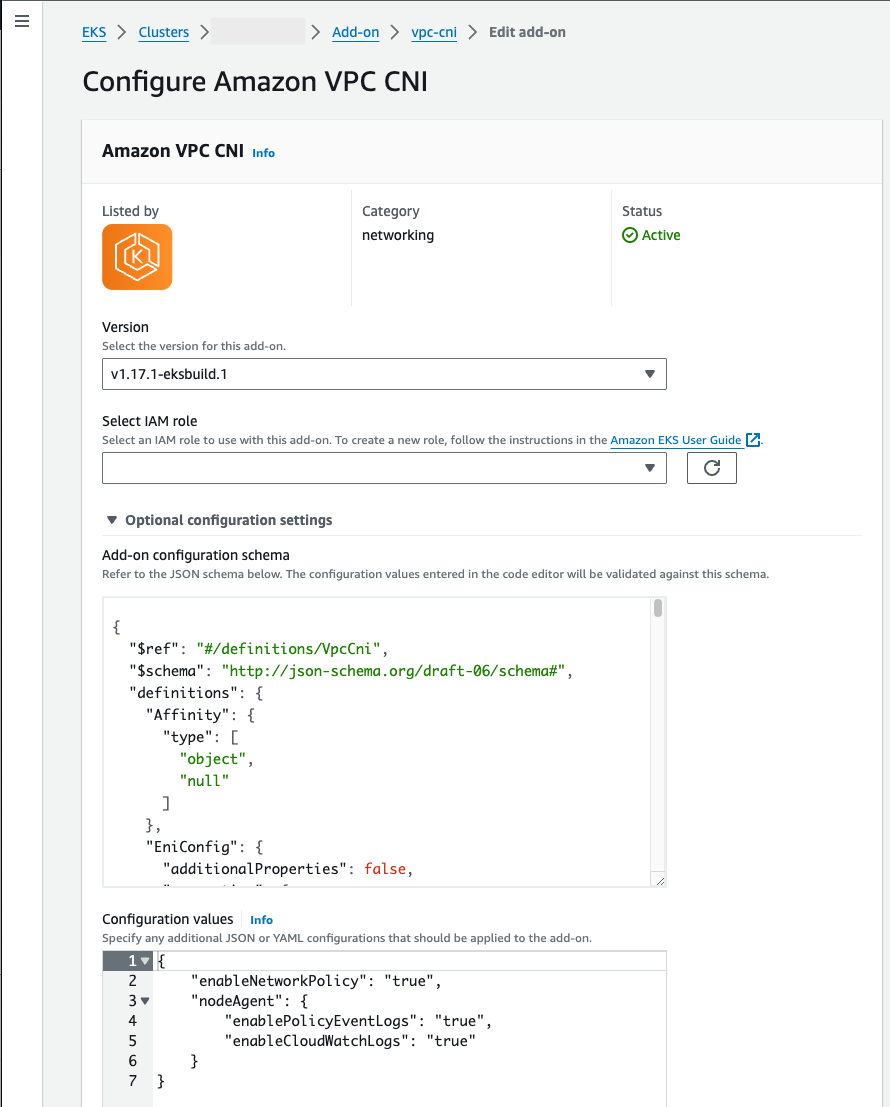
"nodeAgent":and value is an object with a key"enableCloudWatchLogs":and value of"true"in Configuration values. The resulting text must be a valid JSON object. The following example shows network policy and the network policy logs are enabled, and the logs are sent to CloudWatch Logs:{ "enableNetworkPolicy": "true", "nodeAgent": { "enablePolicyEventLogs": "true", "enableCloudWatchLogs": "true", } }
-
The following screenshot shows an example of this scenario.
-
- Amazon CLI
-
-
Run the following Amazon CLI command. Replace
my-clusterwith the name of your cluster and replace the IAM role ARN with the role that you are using.aws eks update-addon --cluster-name my-cluster --addon-name vpc-cni --addon-version v1.14.0-eksbuild.3 \ --service-account-role-arn arn:aws-cn:iam::123456789012:role/AmazonEKSVPCCNIRole \ --resolve-conflicts PRESERVE --configuration-values '{"nodeAgent": {"enablePolicyEventLogs": "true", "enableCloudWatchLogs": "true"}}'
-
Self-managed add-on
- Helm
-
If you have installed the Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes through
helm, you can update the configuration to send network policy logs to CloudWatch Logs.-
Run the following command to enable network policy logs and send them to CloudWatch Logs.
helm upgrade --set nodeAgent.enablePolicyEventLogs=true --set nodeAgent.enableCloudWatchLogs=true aws-vpc-cni --namespace kube-system eks/aws-vpc-cni
-
- kubectl
-
-
Open the
aws-nodeDaemonSetin your editor.kubectl edit daemonset -n kube-system aws-node -
Replace the
falsewithtruein two command arguments--enable-policy-event-logs=falseand--enable-cloudwatch-logs=falsein theargs:in theaws-network-policy-agentcontainer in the VPC CNIaws-nodeDaemonSetmanifest.- args: - --enable-policy-event-logs=true - --enable-cloudwatch-logs=true
-
Send network policy logs with a Fluent Bit DaemonSet
If you are using Fluent Bit in a DaemonSet to send logs from your nodes, you can add configuration to include the network policy logs from network policies. You can use the following example configuration:
[INPUT] Name tail Tag eksnp.* Path /var/log/aws-routed-eni/network-policy-agent*.log Parser json DB /var/log/aws-routed-eni/flb_npagent.db Mem_Buf_Limit 5MB Skip_Long_Lines On Refresh_Interval 10
Included eBPF SDK
The Amazon VPC CNI plugin for Kubernetes installs eBPF SDK collection of tools on the nodes. You can use the eBPF SDK tools to identify issues with network policies. For example, the following command lists the programs that are running on the node.
sudo /opt/cni/bin/aws-eks-na-cli ebpf progs
To run this command, you can use any method to connect to the node.
Known issues and solutions
The following sections describe known issues with the Amazon VPC CNI network policy feature and their solutions.
Network policy logs generated despite enable-policy-event-logs set to false
Issue: EKS VPC CNI is generating network policy logs even when the enable-policy-event-logs setting is set to false.
Solution: The enable-policy-event-logs setting only disables the policy "decision" logs, but it won’t disable all Network Policy agent logging. This behavior is documented in the aws-network-policy-agent README
Network policy map cleanup issues
Issue: Problems with network policyendpoint still existing and not being cleaned up after pods are deleted.
Solution: This issue was caused by a problem with the VPC CNI add-on version 1.19.3-eksbuild.1. Update to a newer version of the VPC CNI add-on to resolve this issue.
Network policies aren’t applied
Issue: Network policy feature is enabled in the Amazon VPC CNI plugin, but network policies are not being applied correctly.
If you make a network policy kind: NetworkPolicy and it doesn’t effect the pod, check that the policyendpoint object was created in the same namespace as the pod.
If there aren’t policyendpoint objects in the namespaces, the network policy controller (part of the EKS cluster) was unable to create network policy rules for the network policy agent (part of the VPC CNI) to apply.
Solution: The solution is to fix the permissions of the VPC CNI (ClusterRole : aws-node) and the network policy controller (ClusterRole : eks:network-policy-controller) and to allow these actions in any policy enforcement tool such as Kyverno. Ensure that Kyverno policies are not blocking the creation of policyendpoint objects. See previous section for the permissions necessary permissions in New policyendpoints CRD and permissions.
Pods don’t return to default deny state after policy deletion in strict mode
Issue: When network policies are enabled in strict mode, pods start with a default deny policy. After policies are applied, traffic is allowed to the specified endpoints. However, when policies are deleted, the pod doesn’t return to the default deny state and instead goes to a default allow state.
Solution: This issue was fixed in the VPC CNI release 1.19.3, which included the network policy agent 1.2.0 release. After the fix, with strict mode enabled, once policies are removed, the pod will fall back to the default deny state as expected.
Security Groups for Pods startup latency
Issue: When using the Security Groups for Pods feature in EKS, there is increased pod startup latency.
Solution: The latency is due to rate limiting in the resource controller from API throttling on the CreateNetworkInterface API, which the VPC resource controller uses to create branch ENIs for the pods. Check your account’s API limits for this operation and consider requesting a limit increase if needed.
FailedScheduling due to insufficient vpc.amazonaws.com/pod-eni
Issue: Pods fail to schedule with the error: FailedScheduling 2m53s (x28 over 137m) default-scheduler 0/5 nodes are available: 5 Insufficient vpc.amazonaws.com/pod-eni. preemption: 0/5 nodes are available: 5 No preemption victims found for incoming pod.
Solution: As with the previous issue, assigning Security Groups to pods increases pod scheduling latency and it can increase beyond the CNI threshold for time to add each ENI, causing failures to start pods. This is expected behavior when using Security Groups for Pods. Consider the scheduling implications when designing your workload architecture.
IPAM connectivity issues and segmentation faults
Issue: Multiple errors occur including IPAM connectivity issues, throttling requests, and segmentation faults:
-
Checking for IPAM connectivity … -
Throttling request took 1.047064274s -
Retrying waiting for IPAM-D -
panic: runtime error: invalid memory address or nil pointer dereference
Solution: This issue occurs if you install systemd-udev on AL2023, as the file is re-written with a breaking policy. This can happen when updating to a different releasever that has an updated package or manually updating the package itself. Avoid installing or updating systemd-udev on AL2023 nodes.
Failed to find device by name error
Issue: Error message: {"level":"error","ts":"2025-02-05T20:27:18.669Z","caller":"ebpf/bpf_client.go:578","msg":"failed to find device by name eni9ea69618bf0: %!w(netlink.LinkNotFoundError={0xc000115310})"}
Solution: This issue has been identified and fixed in the latest versions of the Amazon VPC CNI network policy agent (v1.2.0). Update to the latest version of the VPC CNI to resolve this issue.
CVE vulnerabilities in Multus CNI image
Issue: Enhanced EKS ImageScan CVE Report identifies vulnerabilities in the Multus CNI image version v4.1.4-eksbuild.2_thick.
Solution: Update to the new version of the Multus CNI image and the new Network Policy Controller image, which have no vulnerabilities. The scanner can be updated to address the vulnerabilities found in the previous version.
Flow Info DENY verdicts in logs
Issue: Network policy logs show DENY verdicts: {"level":"info","ts":"2024-11-25T13:34:24.808Z","logger":"ebpf-client","caller":"events/events.go:193","msg":"Flow Info: ","Src IP":"","Src Port":9096,"Dest IP":"","Dest Port":56830,"Proto":"TCP","Verdict":"DENY"}
Solution: This issue has been resolved in the new version of the Network Policy Controller. Update to the latest EKS platform version to resolve logging issues.
Pod-to-pod communication issues after migrating from Calico
Issue: After upgrading an EKS cluster to version 1.30 and switching from Calico to Amazon VPC CNI for network policy, pod-to-pod communication fails when network policies are applied. Communication is restored when network policies are deleted.
Solution: The network policy agent in the VPC CNI can’t have as many ports specified as Calico does. Instead, use port ranges in the network policies. The maximum number of unique combinations of ports for each protocol in each ingress: or egress: selector in a network policy is 24. Use port ranges to reduce the number of unique ports and avoid this limitation.
Network policy agent doesn’t support standalone pods
Issue: Network policies applied to standalone pods may have inconsistent behavior.
Solution: The Network Policy agent currently only supports pods that are deployed as part of a deployment/replicaset. If network policies are applied to standalone pods, there might be some inconsistencies in the behavior. This is documented at the top of this page, in the Considerations, and in the aws-network-policy-agent GitHub issue #327