Use capacity reservations with instance fleets in Amazon EMR
To launch On-Demand Instance fleets with capacity reservations options, attach additional service role permissions which are required to use capacity reservation options. Since capacity reservation options must be used together with On-Demand allocation strategy, you also have to include the permissions required for allocation strategy in your service role and managed policy. For more information, see Allocation strategy permissions.
Amazon EMR supports both open and targeted capacity reservations. The following
topics show instance fleets configurations that you can use with the
RunJobFlow action or create-cluster command to
launch instance fleets using On-Demand Capacity Reservations.
Use open capacity reservations on a best-effort basis
If the cluster's On-Demand Instances match the attributes of open capacity reservations (instance type, platform, tenancy and Availability Zone) available in your account, the capacity reservations are applied automatically. However, it is not guaranteed that your capacity reservations will be used. For provisioning the cluster, Amazon EMR evaluates all the instance pools specified in the launch request and uses the one with the lowest price that has sufficient capacity to launch all the requested core nodes. Available open capacity reservations that match the instance pool are applied automatically. If available open capacity reservations do not match the instance pool, they remain unused.
Once the core nodes are provisioned, the Availability Zone is selected and fixed. Amazon EMR provisions task nodes into instance pools, starting with the lowest-priced ones first, in the selected Availability Zone until all the task nodes are provisioned. Available open capacity reservations that match the instance pools are applied automatically.
The following are use cases of Amazon EMR capacity allocation logic for using open capacity reservations on a best-effort basis.
Example 1: Lowest-price instance pool in launch request has available open capacity reservations
In this case, Amazon EMR launches capacity in the lowest-price instance pool with On-Demand Instances. Your available open capacity reservations in that instance pool are used automatically.
| On-Demand Strategy | lowest-price | ||
| Requested Capacity | 100 | ||
| Instance Type | c5.xlarge | m5.xlarge | r5.xlarge |
| Available Open capacity reservations | 150 | 100 | 100 |
| On-Demand Price | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Instances Provisioned | 100 | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open capacity reservation used | 100 | - | - |
| Available Open capacity reservations | 50 | 100 | 100 |
After the instance fleet is launched, you can run describe-capacity-reservations to see how many
unused capacity reservations remain.
Example 2: Lowest-price instance pool in launch request does not have available open capacity reservations
In this case, Amazon EMR launches capacity in the lowest-price instance pool with On-Demand Instances. However, your open capacity reservations remain unused.
| On-Demand Strategy | lowest-price | ||
| Requested Capacity | 100 | ||
| Instance Type | c5.xlarge | m5.xlarge | r5.xlarge |
|
Available Open capacity reservations |
- | - | 100 |
| On-Demand Price | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Instances Provisioned | 100 | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open capacity reservation used | - | - | - |
| Available Open capacity reservations | - | - | 100 |
Configure Instance Fleets to use open capacity reservations on best-effort basis
When you use the RunJobFlow action to create an instance
fleet-based cluster, set the On-Demand allocation strategy to
lowest-price and CapacityReservationPreference
for capacity reservations options to open. Alternatively, if
you leave this field blank, Amazon EMR defaults the On-Demand Instance's capacity
reservation preference to open.
"LaunchSpecifications": {"OnDemandSpecification": { "AllocationStrategy": "lowest-price", "CapacityReservationOptions": { "CapacityReservationPreference": "open" } } }
You can also use the Amazon EMR CLI to create an instance fleet-based cluster using open capacity reservations.
aws emr create-cluster \ --name 'open-ODCR-cluster' \ --release-label emr-5.30.0 \ --service-role EMR_DefaultRole \ --ec2-attributes SubnetId=subnet-22XXXX01,InstanceProfile=EMR_EC2_DefaultRole \ --instance-fleets InstanceFleetType=MASTER,TargetOnDemandCapacity=1,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c4.xlarge}'] \ InstanceFleetType=CORE,TargetOnDemandCapacity=100,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c5.xlarge},{InstanceType=m5.xlarge},{InstanceType=r5.xlarge}'],\ LaunchSpecifications={OnDemandSpecification='{AllocationStrategy=lowest-price,CapacityReservationOptions={CapacityReservationPreference=open}}'}
Where,
-
open-ODCR-clusteris replaced with the name of the cluster using open capacity reservations. -
subnet-22XXXX01is replaced with the subnet ID.
Use open capacity reservations first
You can choose to override the lowest-price allocation strategy and prioritize using available open capacity reservations first while provisioning an Amazon EMR cluster. In this case, Amazon EMR evaluates all the instance pools with capacity reservations specified in the launch request and uses the one with the lowest price that has sufficient capacity to launch all the requested core nodes. If none of the instance pools with capacity reservations have sufficient capacity for the requested core nodes, Amazon EMR falls back to the best-effort case described in the previous topic. That is, Amazon EMR re-evaluates all the instance pools specified in the launch request and uses the one with the lowest price that has sufficient capacity to launch all the requested core nodes. Available open capacity reservations that match the instance pool are applied automatically. If available open capacity reservations do not match the instance pool, they remain unused.
Once the core nodes are provisioned, the Availability Zone is selected and fixed. Amazon EMR provisions task nodes into instance pools with capacity reservations, starting with the lowest-priced ones first, in the selected Availability Zone until all the task nodes are provisioned. Amazon EMR uses the available open capacity reservations available across each instance pool in the selected Availability Zone first, and only if required, uses the lowest-price strategy to provision any remaining task nodes.
The following are use cases of Amazon EMR capacity allocation logic for using open capacity reservations first.
Example 1: Instance pool with available open capacity reservations in launch request has sufficient capacity for core nodes
In this case, Amazon EMR launches capacity in the instance pool with available open capacity reservations regardless of instance pool price. As a result, your open capacity reservations are used whenever possible, until all core nodes are provisioned.
| On-Demand Strategy | lowest-price | ||
| Requested Capacity | 100 | ||
| Usage Strategy | use-capacity-reservations-first | ||
| Instance Type | c5.xlarge | m5.xlarge | r5.xlarge |
| Available Open capacity reservations | - | - | 150 |
| On-Demand Price | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Instances Provisioned | - | - | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open capacity reservation used | - | - | 100 |
| Available Open capacity reservations | - | - | 50 |
Example 2: Instance pool with available open capacity reservations in launch request does not have sufficient capacity for core nodes
In this case, Amazon EMR falls back to launching core nodes using lowest-price strategy with a best-effort to use capacity reservations.
| On-Demand Strategy | lowest-price | ||
| Requested Capacity | 100 | ||
| Usage Strategy | use-capacity-reservations-first | ||
| Instance Type | c5.xlarge | m5.xlarge | r5.xlarge |
| Available Open capacity reservations | 10 | 50 | 50 |
| On-Demand Price | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Instances Provisioned | 100 | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open capacity reservation used | 10 | - | - |
| Available open capacity reservations | - | 50 | 50 |
After the instance fleet is launched, you can run describe-capacity-reservations to see how many
unused capacity reservations remain.
Configure Instance Fleets to use open capacity reservations first
When you use the RunJobFlow action to create an instance
fleet-based cluster, set the On-Demand allocation strategy to
lowest-price and UsageStrategy for
CapacityReservationOptions to
use-capacity-reservations-first.
"LaunchSpecifications": {"OnDemandSpecification": { "AllocationStrategy": "lowest-price", "CapacityReservationOptions": { "UsageStrategy": "use-capacity-reservations-first" } } }
You can also use the Amazon EMR CLI to create an instance-fleet based cluster using capacity reservations first.
aws emr create-cluster \ --name 'use-CR-first-cluster' \ --release-label emr-5.30.0 \ --service-role EMR_DefaultRole \ --ec2-attributes SubnetId=subnet-22XXXX01,InstanceProfile=EMR_EC2_DefaultRole \ --instance-fleets \ InstanceFleetType=MASTER,TargetOnDemandCapacity=1,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c4.xlarge}'] \ InstanceFleetType=CORE,TargetOnDemandCapacity=100,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c5.xlarge},{InstanceType=m5.xlarge},{InstanceType=r5.xlarge}'],\ LaunchSpecifications={OnDemandSpecification='{AllocationStrategy=lowest-price,CapacityReservationOptions={UsageStrategy=use-capacity-reservations-first}}'}
Where,
-
use-CR-first-clusteris replaced with the name of the cluster using open capacity reservations. -
subnet-22XXXX01is replaced with the subnet ID.
Use targeted capacity reservations first
When you provision an Amazon EMR cluster, you can choose to override the lowest-price allocation strategy and prioritize using available targeted capacity reservations first. In this case, Amazon EMR evaluates all the instance pools with targeted capacity reservations specified in the launch request and picks the one with the lowest price that has sufficient capacity to launch all the requested core nodes. If none of the instance pools with targeted capacity reservations have sufficient capacity for core nodes, Amazon EMR falls back to the best-effort case described earlier. That is, Amazon EMR re-evaluates all the instance pools specified in the launch request and selects the one with the lowest price that has sufficient capacity to launch all the requested core nodes. Available open capacity reservations which match the instance pool get applied automatically. However, targeted capacity reservations remain unused.
Once the core nodes are provisioned, the Availability Zone is selected and fixed. Amazon EMR provisions task nodes into instance pools with targeted capacity reservations, starting with the lowest-priced ones first, in the selected Availability Zone until all the task nodes are provisioned. Amazon EMR tries to use the available targeted capacity reservations available across each instance pool in the selected Availability Zone first. Then, only if required, Amazon EMR uses the lowest-price strategy to provision any remaining task nodes.
The following are use cases of Amazon EMR capacity allocation logic for using targeted capacity reservations first.
Example 1: Instance pool with available targeted capacity reservations in launch request has sufficient capacity for core nodes
In this case, Amazon EMR launches capacity in the instance pool with available targeted capacity reservations regardless of instance pool price. As a result, your targeted capacity reservations are used whenever possible until all core nodes are provisioned.
| On-Demand Strategy | lowest-price | ||
| Usage Strategy | use-capacity-reservations-first | ||
| Requested Capacity | 100 | ||
| Instance Type | c5.xlarge | m5.xlarge | r5.xlarge |
| Available targeted capacity reservations | - | - | 150 |
| On-Demand Price | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Instances Provisioned | - | - | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted capacity reservation used | - | - | 100 |
| Available targeted capacity reservations | - | - | 50 |
Example 2: Instance pool with available targeted capacity reservations in launch request does not have sufficient capacity for core nodes
| On-Demand Strategy | lowest-price | ||
| Requested Capacity | 100 | ||
| Usage Strategy | use-capacity-reservations-first | ||
| Instance Type | c5.xlarge | m5.xlarge | r5.xlarge |
| Available targeted capacity reservations | 10 | 50 | 50 |
| On-Demand Price | $ | $$ | $$$ |
| Instances Provisioned | 100 | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted capacity reservations used | 10 | - | - |
| Available targeted capacity reservations | - | 50 | 50 |
After the instance fleet is launched, you can run describe-capacity-reservations to see how many
unused capacity reservations remain.
Configure Instance Fleets to use targeted capacity reservations first
When you use the RunJobFlow action to create an
instance-fleet based cluster, set the On-Demand allocation strategy to
lowest-price, UsageStrategy for
CapacityReservationOptions to
use-capacity-reservations-first, and
CapacityReservationResourceGroupArn for
CapacityReservationOptions to <your resource group
ARN>. For more information, see Work with
capacity reservations in the
Amazon EC2 User Guide.
"LaunchSpecifications": {"OnDemandSpecification": { "AllocationStrategy": "lowest-price", "CapacityReservationOptions": { "UsageStrategy": "use-capacity-reservations-first", "CapacityReservationResourceGroupArn": "arn:aws:resource-groups:sa-east-1:123456789012:group/MyCRGroup" } } }
Where
arn:aws:resource-groups:sa-east-1:123456789012:group/MyCRGroup
is replaced with your resource group ARN.
You can also use the Amazon EMR CLI to create an instance fleet-based cluster using targeted capacity reservations.
aws emr create-cluster \ --name 'targeted-CR-cluster' \ --release-label emr-5.30.0 \ --service-role EMR_DefaultRole \ --ec2-attributes SubnetId=subnet-22XXXX01,InstanceProfile=EMR_EC2_DefaultRole \ --instance-fleets InstanceFleetType=MASTER,TargetOnDemandCapacity=1,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c4.xlarge}'] \ InstanceFleetType=CORE,TargetOnDemandCapacity=100,\ InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c5.xlarge},{InstanceType=m5.xlarge},{InstanceType=r5.xlarge}'],\ LaunchSpecifications={OnDemandSpecification='{AllocationStrategy=lowest-price,CapacityReservationOptions={UsageStrategy=use-capacity-reservations-first,CapacityReservationResourceGroupArn=arn:aws:resource-groups:sa-east-1:123456789012:group/MyCRGroup}}'}
Where,
-
targeted-CR-clusteris replaced with the name of your cluster using targeted capacity reservations. -
subnet-22XXXX01is replaced with the subnet ID. -
arn:aws:resource-groups:sa-east-1:123456789012:group/MyCRGroupis replaced with your resource group ARN.
Avoid using available open capacity reservations
Example
If you want to avoid unexpectedly using any of your open capacity
reservations when launching an Amazon EMR cluster, set the On-Demand
allocation strategy to lowest-price and
CapacityReservationPreference for
CapacityReservationOptions to none.
Otherwise, Amazon EMR defaults the On-Demand Instance's capacity reservation
preference to open and tries using available open capacity
reservations on a best-effort basis.
"LaunchSpecifications": {"OnDemandSpecification": { "AllocationStrategy": "lowest-price", "CapacityReservationOptions": { "CapacityReservationPreference": "none" } } }
You can also use the Amazon EMR CLI to create an instance fleet-based cluster without using any open capacity reservations.
aws emr create-cluster \ --name 'none-CR-cluster' \ --release-label emr-5.30.0 \ --service-role EMR_DefaultRole \ --ec2-attributes SubnetId=subnet-22XXXX01,InstanceProfile=EMR_EC2_DefaultRole \ --instance-fleets \ InstanceFleetType=MASTER,TargetOnDemandCapacity=1,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c4.xlarge}'] \ InstanceFleetType=CORE,TargetOnDemandCapacity=100,InstanceTypeConfigs=['{InstanceType=c5.xlarge},{InstanceType=m5.xlarge},{InstanceType=r5.xlarge}'],\ LaunchSpecifications={OnDemandSpecification='{AllocationStrategy=lowest-price,CapacityReservationOptions={CapacityReservationPreference=none}}'}
Where,
-
none-CR-clusteris replaced with the name of your cluster that is not using any open capacity reservations. -
subnet-22XXXX01is replaced with the subnet ID.
Scenarios for using capacity reservations
You can benefit from using capacity reservations in the following scenarios.
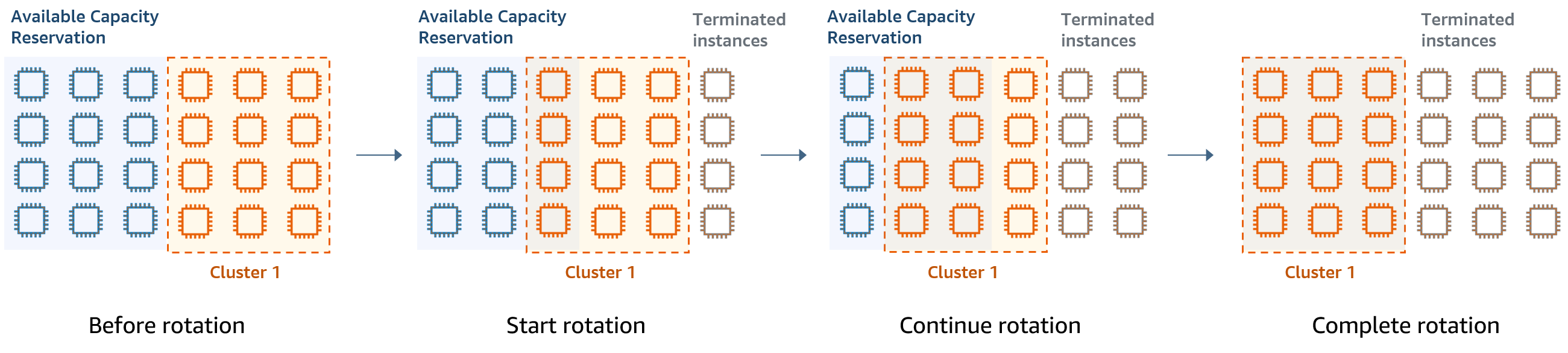
Scenario 1: Rotate a long-running cluster using capacity reservations
When rotating a long running cluster, you might have strict requirements on the instance types and Availability Zones for the new instances you provision. With capacity reservations, you can use capacity assurance to complete the cluster rotation without interruptions.
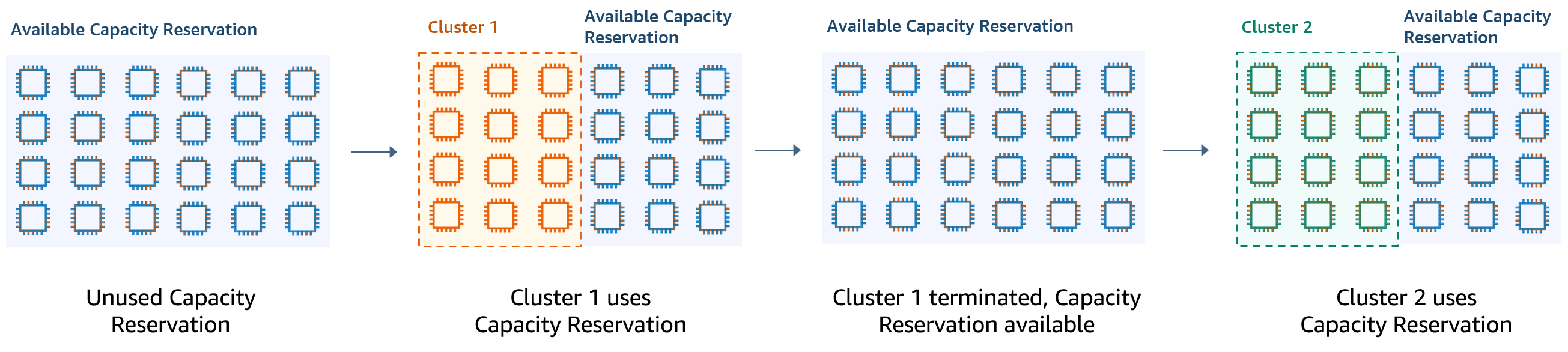
Scenario 2: Provision successive short-lived clusters using capacity reservations
You can also use capacity reservations to provision a group of successive, short-lived clusters for individual workloads so that when you terminate a cluster, the next cluster can use the capacity reservations. You can use targeted capacity reservations to ensure that only the intended clusters use the capacity reservations.