Standalone game session servers with a WebSocket-based backend
Using an Amazon API Gateway WebSocket-based architecture, you can make matchmaking requests with WebSockets and send push notifications for matchmaking completion using server-initiated messages. This architecture improves performance by having two-way communication between the client and the server.
For more information about using API Gateway WebSock APIs, see Working with WebSocket APIs.
The following diagram shows a WebSocket-based backend architecture that uses API Gateway and other Amazon Web Services services to match players into games running on Amazon GameLift Servers fleets. The following list provides a description for each numbered callout in the diagram.
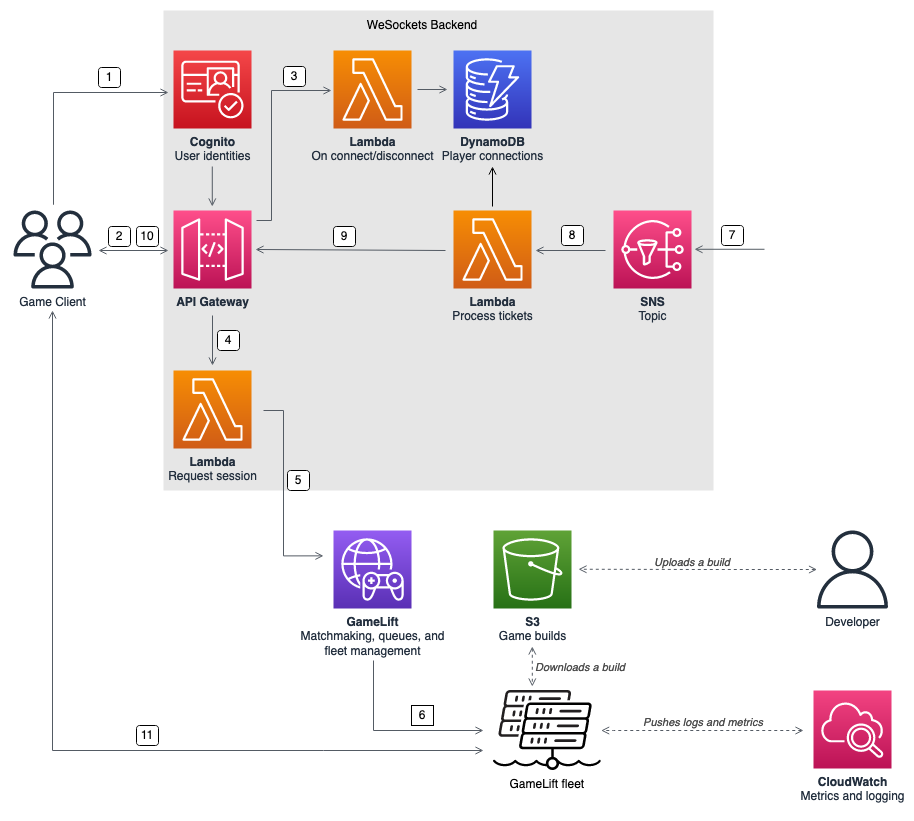
-
The game client requests an Amazon Cognito user identity from an Amazon Cognito identity pool.
-
The game client signs a WebSocket connection to an API Gateway API with the Amazon Cognito credentials.
-
API Gateway calls an Amazon Lambda function on the connection. The function stores the connection information in an Amazon DynamoDB table.
-
The game client sends a message to a Lambda function, through the API Gateway API over the WebSocket connection, to request a session.
-
A Lambda function receives the message and then requests a match through Amazon GameLift Servers FlexMatch matchmaking.
-
After FlexMatch matches a group of players, FlexMatch requests a game session placement through a Amazon GameLift Servers queue.
-
After Amazon GameLift Servers places the session on one of the fleet's locations, Amazon GameLift Servers sends an event notification to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic.
-
A Lambda function receives the Amazon SNS event and processes it.
-
If the matchmaking ticket is a
MatchmakingSucceededevent, then the Lambda function requests the correct player connection from DynamoDB. The function then sends a message to the game client through the API Gateway API over the WebSocket connection. In this architecture, the game client doesn't actively poll the status of matchmaking. -
The game client receives the port and IP address of the game server, along with the player session ID, through the WebSocket connection.
-
The game client connects to the game server using TCP or UDP using the port and IP address that the backend service provides. The game client also sends the player session ID to the game server, which then validates the ID using the server SDK for Amazon GameLift Servers.