Repairing and resuming a workflow run
If one or more nodes (jobs or crawlers) in a workflow do not successfully complete, this means that the workflow only partially ran. After you find the root causes and make corrections, you can select one or more nodes to resume the workflow run from, and then resume the workflow run. The selected nodes and all nodes that are downstream from those nodes are then run.
Topics
Resuming a workflow run: How it works
Consider the workflow W1 in the following diagram.
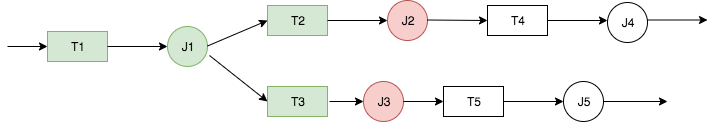
The workflow run proceeds as follows:
-
Trigger T1 starts job J1.
-
Successful completion of J1 fires triggers T2 and T3, which run jobs J2 and J3, respectively.
-
Jobs J2 and J3 fail.
-
Triggers T4 and T5 depend on the successful completion of J2 and J3, so they don't fire, and jobs J4 and J5 don't run. Workflow W1 is only partially run.
Now assume that the issues that caused J2 and J3 to fail are corrected. J2 and J3 are selected as the starting points to resume the workflow run from.
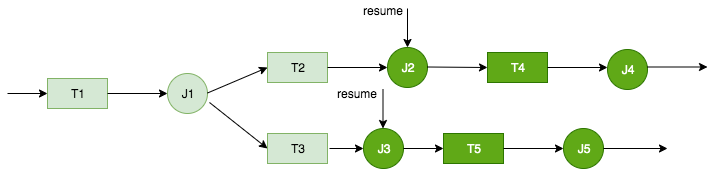
The workflow run resumes as follows:
-
Jobs J2 and J3 run successfully.
-
Triggers T4 and T5 fire.
-
Jobs J4 and J5 run successfully.
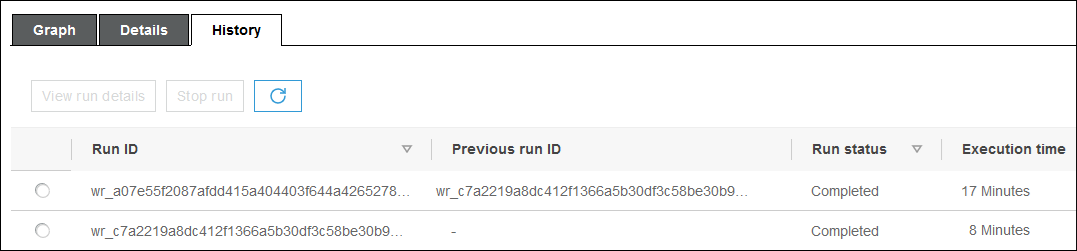
The resumed workflow run is tracked as a separate workflow run with a new run ID. When
you view the workflow history, you can view the previous run ID for any workflow run. In
the example in the following screenshot, the workflow run with run ID
wr_c7a22... (the second row) had a node that did not complete. The user
fixed the problem and resumed the workflow run, which resulted in run ID
wr_a07e55... (the first row).
Note
For the rest of this discussion, the term "resumed workflow run" refers to the workflow run that was created when the previous workflow run was resumed. The "original workflow run" refers to the workflow run that only partially ran and that needed to be resumed.
Resumed workflow run graph
In a resumed workflow run, although only a subset of nodes are run, the run graph is a complete graph. That is, the nodes that didn't run in the resumed workflow are copied from the run graph of the original workflow run. Copied job and crawler nodes that ran in the original workflow run include run details.
Consider again the workflow W1 in the previous diagram. When the workflow run is resumed starting with J2 and J3, the run graph for the resumed workflow run shows all jobs, J1 though J5, and all triggers, T1 through T5. The run details for J1 are copied from the original workflow run.
Workflow run snapshots
When a workflow run is started, Amazon Glue takes a snapshot of the workflow design graph at that point in time. That snapshot is used for the duration of the workflow run. If you make changes to any triggers after the run starts, those changes don't affect the current workflow run. Snapshots ensure that workflow runs proceed in a consistent manner.
Snapshots make only triggers immutable. Changes that you make to downstream jobs and crawlers during the workflow run take effect for the current run.
Resuming a workflow run
Follow these steps to resume a workflow run. You can resume a workflow run by using the Amazon Glue console, API, or Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI).
To resume a workflow run (console)
-
Open the Amazon Glue console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/glue/
. Sign in as a user who has permissions to view workflows and resume workflow runs.
Note
To resume workflow runs, you need the
glue:ResumeWorkflowRunAmazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) permission. -
In the navigation pane, choose Workflows.
-
Select a workflow, and then choose the History tab.
-
Select the workflow run that only partially ran, and then choose View run details.
-
In the run graph, select the first (or only) node that you want to restart and that you want to resume the workflow run from.
-
In the details pane to the right of the graph, select the Resume check box.
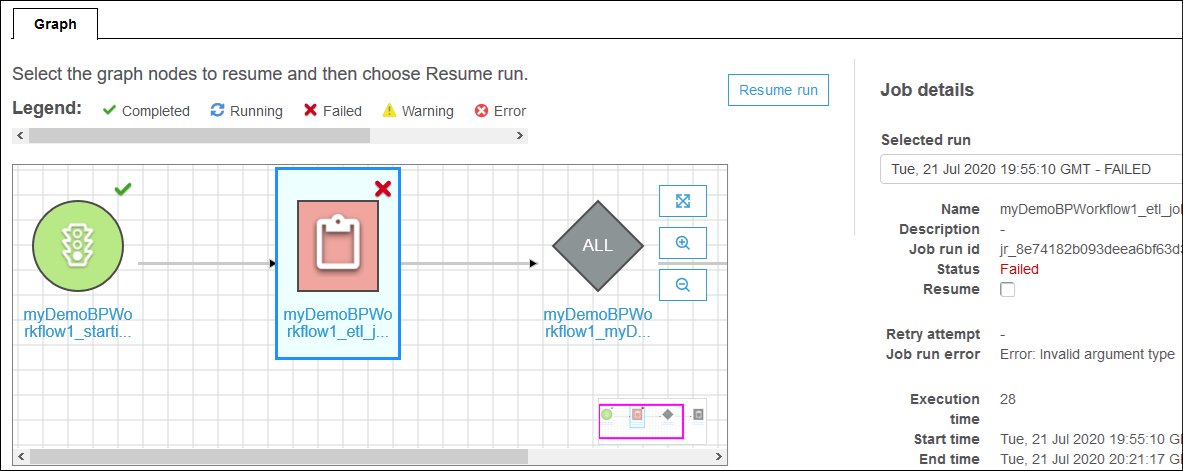
The node changes color and shows a small resume icon at the upper right.
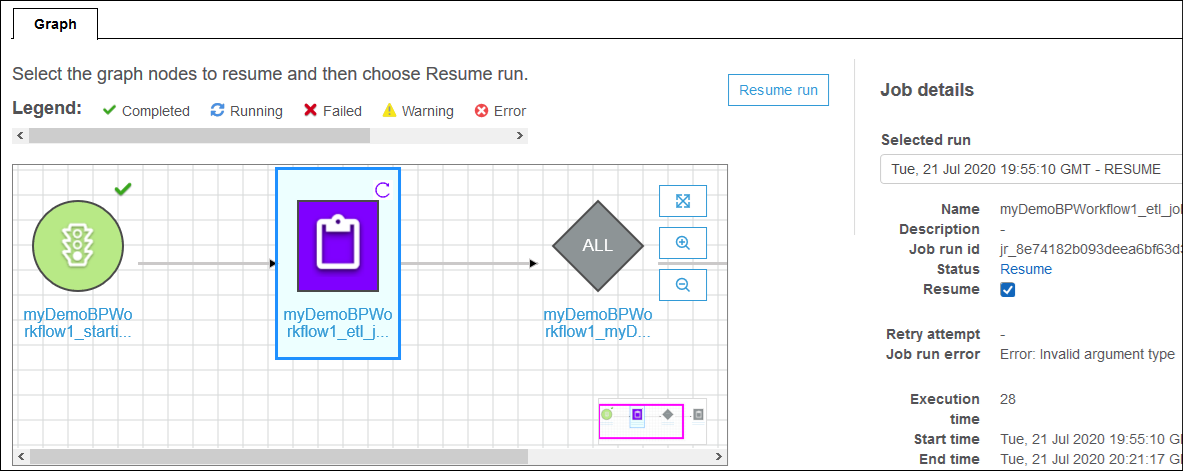
-
Complete the previous two steps for any additional nodes to restart.
-
Choose Resume run.
To resume a workflow run (Amazon CLI)
-
Ensure that you have the
glue:ResumeWorkflowRunIAM permission. -
Retrieve the node IDs for the nodes that you want to restart.
-
Run the
get-workflow-runcommand for the original workflow run. Supply the workflow name and run ID, and add the--include-graphoption, as shown in the following example. Get the run ID from the History tab on the console, or by running theget-workflowcommand.aws glue get-workflow-run --name cloudtrailtest1 --run-id wr_a07e55f2087afdd415a404403f644a4265278f68b13ba3da08c71924ebe3c3a8 --include-graphThe command returns the nodes and edges of the graph as a large JSON object.
-
Locate the nodes of interest by the
TypeandNameproperties of the node objects.The following is an example node object from the output.
{ "Type": "JOB", "Name": "test1_post_failure_4592978", "UniqueId": "wnode_d1b2563c503078b153142ee76ce545fe5ceef66e053628a786ddd74a05da86fd", "JobDetails": { "JobRuns": [ { "Id": "jr_690b9f7fc5cb399204bc542c6c956f39934496a5d665a42de891e5b01f59e613", "Attempt": 0, "TriggerName": "test1_aggregate_failure_649b2432", "JobName": "test1_post_failure_4592978", "StartedOn": 1595358275.375, "LastModifiedOn": 1595358298.785, "CompletedOn": 1595358298.785, "JobRunState": "FAILED", "PredecessorRuns": [], "AllocatedCapacity": 0, "ExecutionTime": 16, "Timeout": 2880, "MaxCapacity": 0.0625, "LogGroupName": "/aws-glue/python-jobs" } ] } }
-
Get the node ID from the
UniqueIdproperty of the node object.
-
-
Run the
resume-workflow-runcommand. Provide the workflow name, run ID, and list of node IDs separated by spaces, as shown in the following example.aws glue resume-workflow-run --name cloudtrailtest1 --run-id wr_a07e55f2087afdd415a404403f644a4265278f68b13ba3da08c71924ebe3c3a8 --node-ids wnode_ca1f63e918fb855e063aed2f42ec5762ccf71b80082ae2eb5daeb8052442f2f3 wnode_d1b2563c503078b153142ee76ce545fe5ceef66e053628a786ddd74a05da86fdThe command outputs the run ID of the resumed (new) workflow run and a list of nodes that will be started.
{ "RunId": "wr_2ada0d3209a262fc1156e4291134b3bd643491bcfb0ceead30bd3e4efac24de9", "NodeIds": [ "wnode_ca1f63e918fb855e063aed2f42ec5762ccf71b80082ae2eb5daeb8052442f2f3" ] }Note that although the example
resume-workflow-runcommand listed two nodes to restart, the example output indicated that only one node would be restarted. This is because one node was downstream of the other node, and the downstream node would be restarted anyway by the normal flow of the workflow.
Notes and limitations for resuming workflow runs
Keep the following notes and limitations in mind when resuming workflow runs.
-
You can resume a workflow run only if it's in the
COMPLETEDstate.Note
Even if one ore more nodes in a workflow run don't complete, the workflow run state is shown as
COMPLETED. Be sure to check the run graph to discover any nodes that didn't successfully complete. -
You can resume a workflow run from any job or crawler node that the original workflow run attempted to run. You can't resume a workflow run from a trigger node.
-
Restarting a node does not reset its state. Any data that was partially processed is not rolled back.
-
You can resume a failed workflow run multiple times. However, a resumed run can only be resumed once more. For additional retries, resume the original failed run instead
-
If you select two nodes to restart and they're dependent upon each other, the upstream node is run before the downstream node. In fact, selecting the downstream node is redundant, because it will be run according to the normal flow of the workflow.