Sharing a data lake using Lake Formation fine-grained access control
This tutorial provides step-by-step instructions on how you can quickly and easily share datasets using Lake Formation when managing multiple Amazon Web Services accounts with Amazon Organizations. You define granular permissions to control access to sensitive data.
The following procedures also show how a data lake administrator of Account A can provide fine-grained access for Account B, and how a user in Account B, acting as a data steward, can grant fine-grained access to the shared table for other users in their account. Data stewards within each account can independently delegate access to their own users, giving each team or lines of business (LOB) autonomy.
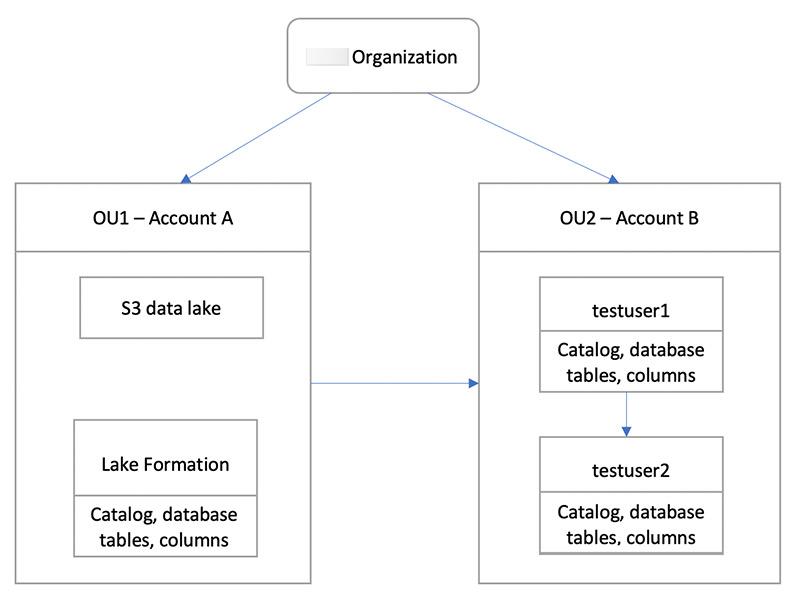
The use case assumes you are using Amazon Organizations to manage your Amazon Web Services accounts. The user of Account A in one organizational unit (OU1) grants access to users of Account B in OU2. You can use the same approach when not using Organizations, such as when you only have a few accounts. The following diagram illustrates the fine-grained access control of datasets in a data lake. The data lake is available in the Account A. The data lake administrator of Account A provides fine-grained access for Account B. The diagram also shows that a user of Account B provides column-level access of the Account A data lake table to another user in Account B.
Topics
Intended audience
This tutorial is intended for data stewards, data engineers, and data analysts. The following table lists the roles that are used in this tutorial:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| IAM administrator | User who has the Amazon managed policy: AdministratorAccess. |
| Data lake administrator |
User who has the Amazon managed policy: |
| Data analyst | User who has the Amazon managed policy: AmazonAthenaFullAccess
attached. |
Prerequisites
Before you start this tutorial, you must have an Amazon Web Services account that you can use to sign in as an administrative user with correct permissions. For more information, see Complete initial Amazon configuration tasks.
The tutorial assumes that you are familiar with IAM. For information about IAM, see the IAM User Guide
You need the following resources for this tutorial:
-
Two organizational units:
OU1 – Contains Account A
OU2 – Contains Account B
An Amazon S3 data lake location (bucket) in Account A.
A data lake administrator user in Account A. You can create a data lake administrator using the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
) or the PutDataLakeSettingsoperation of the Lake Formation API.Lake Formation configured in Account A, and the Amazon S3 data lake location registered with Lake Formation in Account A.
Two users in Account B with the following IAM managed policies:
testuser1 – has the Amazon managed policies
AWSLakeFormationDataAdminattached.testuser2 – Has the Amazon managed policy
AmazonAthenaFullAccessattached.
A database testdb in the Lake Formation database for Account B.
Step 1: Provide fine-grained access to another account
Learn how a data lake administrator of Account A provides fine-grained access for Account B.
Grant fine-grained access to another account
Sign into Amazon Web Services Management Console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/connect/
in Account A as a data lake administrator. Open the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
), and choose Get started. in the navigation pane, choose Databases.
Choose Create database.
In the Database details section, select Database.
For Name, enter a name (for this tutorial, we use
sampledb01).Make sure that Use only IAM access control for new tables in this database is not selected. Leaving this unselected allows us to control access from Lake Formation.
Choose Create database.
On the Databases page, choose your database
sampledb01.On the Actions menu, choose Grant.
In the Grant permissions section, select External account.
For Amazon Web Services account ID or Amazon organization ID, enter the account ID for Account B in OU2.
For Table, choose the table you want Account B to have access to (for this post, we use table
acc_a_area). Optionally, you can grant access to columns within the table, which we do in this post.For Include columns¸ choose the columns you want Account B to have access to (for this post, we grant permissions to type, name, and identifiers).
For Columns, choose Include columns.
For Table permissions, select Select.
For Grantable permissions, select Select. Grantable permissions are required so admin users in Account B can grant permissions to other users in Account B.
Choose Grant.
In the navigation pane, choose Tables.
You could see one active connection in the Amazon Web Services accounts and Amazon organizations with access section.
Create a resource link
Integrated services like Amazon Athena can not directly access databases or tables across accounts.
Hence, you need to create a resource link so that Athena can access resource links in your account to databases and tables in other accounts.
Create a resource link to the table (acc_a_area) so Account B users can query its data with Athena.
Sign into the Amazon console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/connect/
in Account B as testuser1.On the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
), in the navigation pane, choose Tables. You should see the tables that Account A has provided access. Choose the table
acc_a_area.On the Actions menu, choose Create resource link.
For Resource link name, enter a name (for this tutorial,
acc_a_area_rl).For Database, choose your database (
testdb).Choose Create.
In the navigation pane, choose Tables.
Choose the table
acc_b_area_rl.On the Actions menu, choose View data.
You are redirected to the Athena console, where you should see the database and table.
You can now run a query on the table to see the column value for which access was provided to testuser1 from Account B.
Step 2: Provide fine-grained access to a user in the same account
This section shows how a user in Account B (testuser1), acting as a data steward, provides fine-grained access to another user in the same account (testuser2) to the column name in the shared table aac_b_area_rl.
Grant fine-grained access to a user in the same account
Sign into the Amazon console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/connect/
in Account B as testuser1.On the Lake Formation console, in the navigation pane, choose Tables.
You can grant permissions on a table through its resource link. To do so, on the Tables page, select the resource link
acc_b_area_rl, and on the Actions menu, choose Grant on target.In the Grant permissions section, select My account.
For IAM users and roles¸ choose the user
testuser2.For Column, choose the column name.
For Table permissions, select Select.
Choose Grant.
When you create a resource link, only you can view and access it. To permit other users in your account to access the resource link, you need to grant permissions on the resource link itself. You need to grant DESCRIBE or DROP permissions. On the Tables page, select your table again and on the Actions menu, choose Grant.
In the Grant permissions section, select My account.
For IAM users and roles, select the user
testuser2.For Resource link permissions¸ select Describe.
Choose Grant.
Sign into the Amazon console in Account B as
testuser2.On the Athena console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/athena/
), you should see the database and table acc_b_area_rl. You can now run a query on the table to see the column value thattestuser2has access to.