Tutorial: Migrating to Amazon OpenSearch Service
Index snapshots are a popular way to migrate from a self-managed OpenSearch or legacy Elasticsearch cluster to Amazon OpenSearch Service. Broadly, the process consists of the following steps:
-
Take a snapshot of the existing cluster, and upload the snapshot to an Amazon S3 bucket.
-
Create an OpenSearch Service domain.
-
Give OpenSearch Service permissions to access the bucket, and ensure you have permissions to work with snapshots.
-
Restore the snapshot on the OpenSearch Service domain.
This walk through provides more detailed steps and alternate options, where applicable.
Take and upload the snapshot
Although you can use the repository-s3opensearch.yml (or
elasticsearch.yml if using an Elasticsearch cluster), restart each
node, add your Amazon credentials, and finally take the snapshot. The plugin is a great
option for ongoing use or for migrating larger clusters.
For smaller clusters, a one-time approach is to take a shared file system snapshot
To take a snapshot and upload it to Amazon S3
-
Add the
path.reposetting toopensearch.yml(orElasticsearch.yml) on all nodes, and then restart each node.path.repo: ["/my/shared/directory/snapshots"] -
Register a snapshot repository
, which is required before you take a snapshot. A repository is just a storage location: a shared file system, Amazon S3, Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), etc. In this case, we'll use a shared file system ("fs"): PUT _snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name{ "type": "fs", "settings": { "location": "/my/shared/directory/snapshots" } } -
Take the snapshot:
PUT _snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name/my-snapshot-name{ "indices": "migration-index1,migration-index2,other-indices-*", "include_global_state": false } -
Install the Amazon CLI
, and run aws configureto add your credentials. -
Navigate to the snapshot directory. Then run the following commands to create a new S3 bucket and upload the contents of the snapshot directory to that bucket:
aws s3 mb s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket--regionus-west-2aws s3 sync . s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket--sse AES256Depending on the size of the snapshot and the speed of your internet connection, this operation can take a while.
Create a domain
Although the console is the easiest way to create a domain, in this case, you already have the terminal open and the Amazon CLI installed. Modify the following command to create a domain that fits your needs:
aws opensearch create-domain \ --domain-namemigration-domain\ --engine-versionOpenSearch_1.0\ --cluster-config InstanceType=c5.large.search,InstanceCount=2 \ --ebs-options EBSEnabled=true,VolumeType=gp2,VolumeSize=100 \ --node-to-node-encryption-options Enabled=true \ --encryption-at-rest-options Enabled=true \ --domain-endpoint-options EnforceHTTPS=true,TLSSecurityPolicy=Policy-Min-TLS-1-2-2019-07 \ --advanced-security-options Enabled=true,InternalUserDatabaseEnabled=true,MasterUserOptions='{MasterUserName=master-user,MasterUserPassword=master-user-password}' \ --access-policies '{"Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement":[{"Effect":"Allow","Principal": {"Amazon": "arn:aws:iam::aws-region:user/UserName"},"Action":["es:ESHttp*"],"Resource":"arn:aws:es:aws-region:111122223333:domain/migration-domain/*"}]}' \ --regionaws-region
As is, the command creates an internet-accessible domain with two data nodes, each with 100 GiB of storage. It also enables fine-grained access control with HTTP basic authentication and all encryption settings. Use the OpenSearch Service console if you need a more advanced security configuration, such as a VPC.
Before issuing the command, change the domain name, master user credentials, and account number. Specify the same Amazon Web Services Region that you used for the S3 bucket and an OpenSearch/Elasticsearch version that is compatible with your snapshot.
Important
Snapshots are only forward-compatible, and only by one major version. For example, you can't restore a snapshot from an OpenSearch 1.x cluster on an Elasticsearch 7.x cluster, only an OpenSearch 1.x or 2.x cluster. Minor version matters, too. You can't restore a snapshot from a self-managed 5.3.3 cluster on a 5.3.2 OpenSearch Service domain. We recommend choosing the most recent version of OpenSearch or Elasticsearch that your snapshot supports. For a table of compatible versions, see Using a snapshot to migrate data.
Provide permissions to the S3 bucket
In the Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) console, create a role with the following permissions and trust relationship. When creating the role, choose S3
as the Amazon Service. Name the role
OpenSearchSnapshotRole so it's easy to find.
Permissions
Trust relationship
Then give your personal IAM role permissions to assume
OpenSearchSnapshotRole. Create the following policy and attach it to
your identity:
Permissions
Map the snapshot role in OpenSearch Dashboards (if using fine-grained access control)
If you enabled fine-grained access control,
even if you use HTTP basic authentication for all other purposes, you need to map
the manage_snapshots role to your IAM role so you can work with
snapshots.
To give your identity permissions to work with snapshots
-
Log in to Dashboards using the master user credentials you specified when you created the OpenSearch Service domain. You can find the Dashboards URL in the OpenSearch Service console. It takes the form of
https://.domain-endpoint/_dashboards/ -
From the main menu choose Security, Roles, and select the manage_snapshots role.
-
Choose Mapped users, Manage mapping.
-
Add the domain ARN of your personal IAM role in the appropriate field. The ARN takes one of the following formats:
arn:aws:iam::123456789123:user/user-namearn:aws:iam::123456789123:role/role-name -
Select Map and confirm role shows up under Mapped users.
Restore the snapshot
At this point, you have two ways to access your OpenSearch Service domain: HTTP basic authentication with your master user credentials or Amazon authentication using your IAM credentials. Because snapshots use Amazon S3, which has no concept of the master user, you must use your IAM credentials to register the snapshot repository with your OpenSearch Service domain.
Most programming languages have libraries to assist with signing requests, but the
simpler approach is to use a tool like Postman
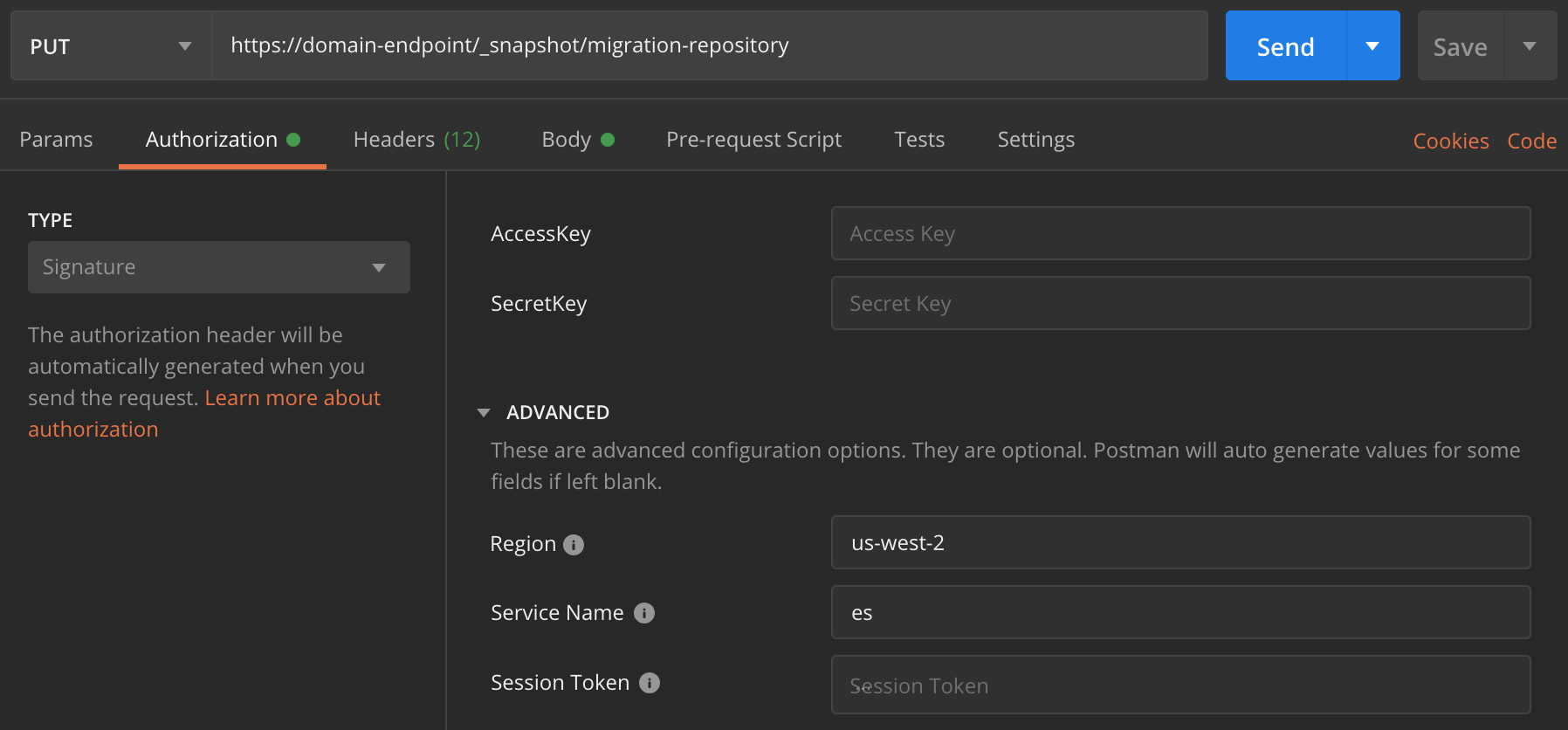
To restore the snapshot
-
Regardless of how you choose to sign your requests, the first step is to register the repository:
PUT _snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name{ "type": "s3", "settings": { "bucket": "amzn-s3-demo-bucket", "region": "us-west-2", "role_arn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/OpenSearchSnapshotRole" } } -
Then list the snapshots in the repository, and find the one you want to restore. At this point, you can continue using Postman or switch to a tool like curl
. Shorthand
GET _snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name/_allcurl
curl -XGET -u 'master-user:master-user-password' https://domain-endpoint/_snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name/_all -
Restore the snapshot.
Shorthand
POST _snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name/my-snapshot-name/_restore { "indices": "migration-index1,migration-index2,other-indices-*", "include_global_state": false }curl
curl -XPOST -u 'master-user:master-user-password' https://domain-endpoint/_snapshot/my-snapshot-repo-name/my-snapshot-name/_restore \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{"indices":"migration-index1,migration-index2,other-indices-*","include_global_state":false}' -
Finally, verify that your indexes restored as expected.
Shorthand
GET _cat/indices?vcurl
curl -XGET -u 'master-user:master-user-password' https://domain-endpoint/_cat/indices?v
At this point, the migration is complete. You might configure your clients to use the new OpenSearch Service endpoint, resize the domain to suit your workload, check the shard count for your indexes, switch to an IAM master user, or start building visualizations in OpenSearch Dashboards.