switch
switch compares a condition-expression with the
literal labels, within a set of literal label and
return-expression pairings. It then returns the
return-expression corresponding to the first literal label
that's equal to the condition-expression. If no label equals to
the condition-expression, switch returns the
default-expression. Every
return-expression and
default-expression must have the same datatype.
Syntax
switch(condition-expression,label-1,return-expression-1[,label-n,return-expression-n...],default-expression)
Arguments
switch requires one or more
if,then expression pairings, and
requires exactly one expression for the else argument.
- condition-expression
-
The expression to be compared with the label-literals. It can be a field name like
address, a literal value like 'Unknown', or another scalar function liketoString(salesAmount). - label
-
The literal to be compared with the condition-expression argument, all of the literals must have the same data type as condition-expression argument.
switchaccepts up to 5000 labels. - return-expression
-
The expression to return if the value of its label equals to the value of the condition-expression. It can be a field name like
address, a literal value like 'Unknown', or another scalar function liketoString(salesAmount). All of the return-expression arguments must have the same data type as the default-expression. - default-expression
-
The expression to return if no value of any label arguments equals to the value of condition-expression. It can be a field name like
address, a literal value like 'Unknown', or another scalar function liketoString(salesAmount). The default-expression must have the same data type as all of the return-expression arguments.
Return type
switch returns a value of the same data type as the values in
return-expression. All data returned
return-expression and
default-expression must be of the same data type or be
converted to the same data type.
General Examples
The following example returns the Amazon Web Services Region code of input region name.
switch(region_name, "US East (N. Virginia)", "us-east-1", "Europe (Ireland)", "eu-west-1", "US West (N. California)", "us-west-1", "other regions")
The following are the given field values.
"US East (N. Virginia)" "US West (N. California)" "Asia Pacific (Tokyo)"
For these field values the following values are returned.
"us-east-1" "us-west-1" "other regions"
Use switch to replace
ifelse
The following ifelse use case is an equivalent of the previous
example, for ifelse evaluating whether values of one field equals
to different literal values, using switch instead is a better
choice.
ifelse(region_name = "US East (N. Virginia)", "us-east-1", region_name = "Europe (Ireland)", "eu-west-1", region_name = "US West (N. California)", "us-west-1", "other regions")
Expression as return value
The following example uses expressions in return-expressions:
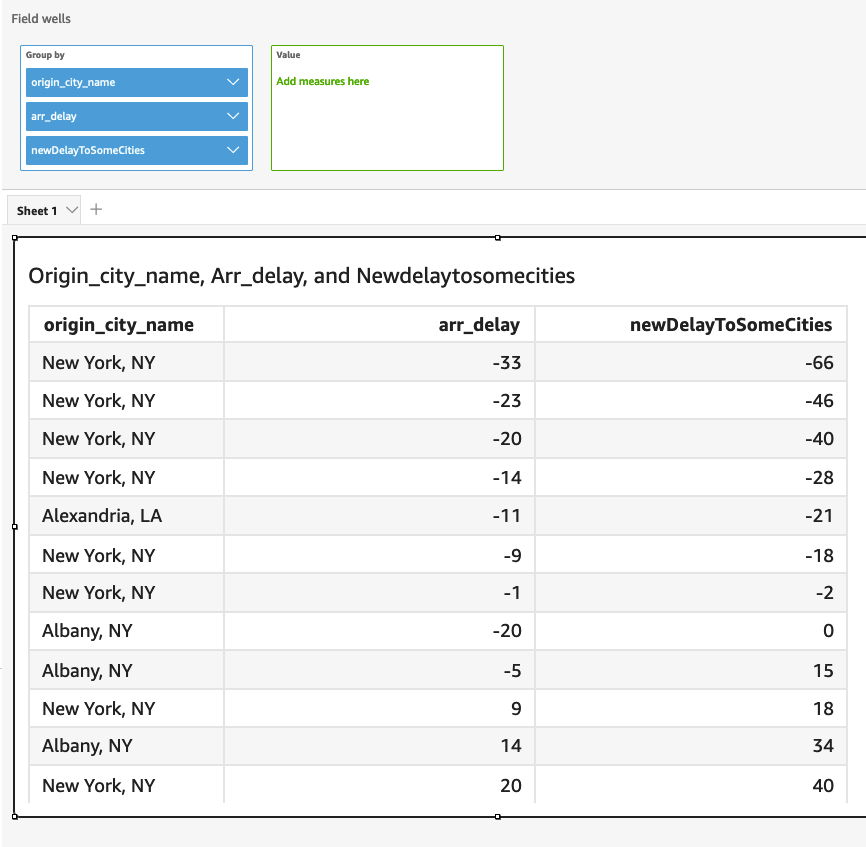
switch({origin_city_name}, "Albany, NY", {arr_delay} + 20, "Alexandria, LA", {arr_delay} - 10, "New York, NY", {arr_delay} * 2, {arr_delay})
The preceding example changes the expected delay time for each flight from a particular city.