Orchestrate Amazon Lambda functions with Step Functions
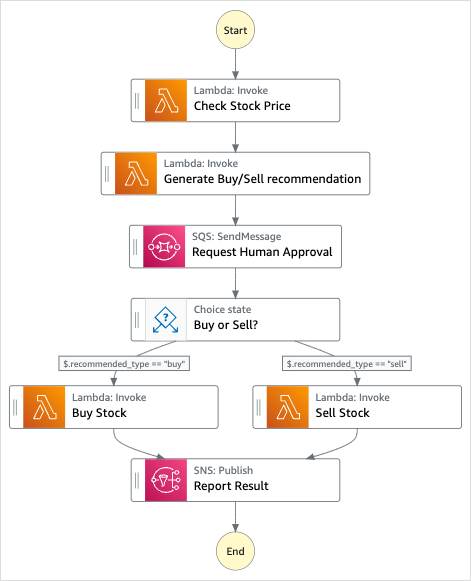
The Orchestrate Lambda functions template uses several Lambda functions in a sample stock trading workflow. One function checks a stock price, then a human is prompted to choose to buy or sell the stock. A choice state selects the next function based on the recommended_type variable to complete the purchase or sale. After either function finishes, the result of the trade is then published before reaching the end of the workflow.
To implement the human approval step, the workflow execution pauses until a unique TaskToken is returned. In this project, the workflow passes a
message with the task token to an Amazon SQS queue. The message triggers another Lambda function that's
configured to handle a callback based on the payload of the message. The workflow pauses until it receives
the task token back from a SendTaskSuccess API call. For more information about task
tokens, see Wait for a Callback with Task Token.
Step 1: Create the state machine
-
Open the Step Functions console
and choose Create state machine. -
Choose Create from template and find the related starter template. Choose Next to continue.
-
Choose how to use the template:
-
Run a demo – creates a read-only state machine. After review, you can create the workflow and all related resources.
-
Build on it – provides an editable workflow definition that you can review, customize, and deploy with your own resources. (Related resources, such as functions or queues, will not be created automatically.)
-
-
Choose Use template to continue with your selection.
Note
Standard charges apply for services deployed to your account.
Step 2: Run the demo state machine
If you chose the Run a demo option, all related resources will be deployed and ready to run. If you chose the Build on it option, you might need to set placeholder values and create additional resources before you can run your custom workflow.
Choose Deploy and run.
Wait for the Amazon CloudFormation stack to deploy. This can take up to 10 minutes.
After the Start execution option appears, review the Input and choose Start execution.
Congratulations!
You should now have a running demo of your state machine. You can choose states in the Graph view to review input, output, variables, definition, and events.
For more information about Step Functions service integrations, see Integrating services with Step Functions.