• Amazon Systems Manager Change Manager is no longer open to new customers. Existing customers can continue to use the service as normal. For more information, see Amazon Systems Manager Change Manager availability change.
• The Amazon Systems Manager CloudWatch Dashboard will no longer be available after April 30, 2026. Customers can continue to use Amazon CloudWatch console to view, create, and manage their Amazon CloudWatch dashboards, just as they do today. For more information, see Amazon CloudWatch Dashboard documentation.
Patch groups
Note
Patch groups are not used in patching operations that are based on patch policies. For information about working with patch policies, see Patch policy configurations in Quick Setup.
Patch group functionality is not supported in the console for account-Region pairs that did not already use patch groups before patch policy support was released on December 22, 2022. Patch group functionality is still available in account-Region pairs that began using patch groups before this date.
You can use a patch group to associate managed nodes with a specific patch baseline in Patch Manager, a tool in Amazon Systems Manager. Patch groups help ensure that you're deploying the appropriate patches, based on the associated patch baseline rules, to the correct set of nodes. Patch groups can also help you avoid deploying patches before they have been adequately tested. For example, you can create patch groups for different environments (such as Development, Test, and Production) and register each patch group to an appropriate patch baseline.
When you run AWS-RunPatchBaseline or other SSM Command documents for
patching, you can target managed nodes using their ID or tags. SSM Agent and Patch Manager
then evaluate which patch baseline to use based on the patch group value that you
added to the managed node.
Using tags to define patch groups
You create a patch group by using tags applied to your Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances and non-EC2 nodes in a hybrid and multicloud environment. Note the following details about using tags for patch groups:
-
A patch group must be defined using either the tag key
Patch GrouporPatchGroupapplied to your managed nodes. When registering a patch group for a patch baseline, any identical values specified for these two keys are interpreted to be part of the same group. For instance, say that you have tagged five nodes with the first of the following key-value pairs, and five with the second:-
key=PatchGroup,value=DEV -
key=Patch Group,value=DEV
The Patch Manager command to create a baseline combines these 10 managed nodes into a single group based on the value
DEV. The Amazon CLI equivalent for the command to create a patch baseline for patch groups is as follows:aws ssm register-patch-baseline-for-patch-group \ --baseline-id pb-0c10e65780EXAMPLE \ --patch-group DEVCombining values from different keys into a single target is unique to this Patch Manager command for creating a new patch group and not supported by other API actions. For example, if you run send-command actions using
PatchGroupandPatch Groupkeys with the same values, you are targeting two completely different sets of nodes:aws ssm send-command \ --document-name AWS-RunPatchBaseline \ --targets "Key=tag:PatchGroup,Values=DEV"aws ssm send-command \ --document-name AWS-RunPatchBaseline \ --targets "Key=tag:Patch Group,Values=DEV" -
-
There are limits on tag-based targeting. Each array of targets for
SendCommandcan contain a maximum of five key-value pairs. -
We recommend that you choose only one of these tag key conventions, either
PatchGroup(without a space) orPatch Group(with a space). However, if you have allowed tags in EC2 instance metadata on an instance, you must usePatchGroup. -
The key is case-sensitive. You can specify any value to help you identify and target the resources in that group, for example "web servers" or "US-EAST-PROD", but the key must be
Patch GrouporPatchGroup.
After you create a patch group and tag managed nodes, you can register the patch group with a patch baseline. Registering the patch group with a patch baseline ensures that the nodes within the patch group use the rules defined in the associated patch baseline.
For more information about how to create a patch group and associate the patch group to a patch baseline, see Creating and managing patch groups and Add a patch group to a patch baseline.
To view an example of creating a patch baseline and patch groups by using the Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI), see Tutorial: Patch a server environment using the Amazon CLI. For more information about Amazon EC2 tags, see Tag your Amazon EC2 resources in the Amazon EC2 User Guide.
How it works
When the system runs the task to apply a patch baseline to a managed node, SSM Agent verifies that a patch group value is defined for the node. If the node is assigned to a patch group, Patch Manager then verifies which patch baseline is registered to that group. If a patch baseline is found for that group, Patch Manager notifies SSM Agent to use the associated patch baseline. If a node isn't configured for a patch group, Patch Manager automatically notifies SSM Agent to use the currently configured default patch baseline.
Important
A managed node can only be in one patch group.
A patch group can be registered with only one patch baseline for each operating system type.
You can't apply the Patch Group tag (with a space) to an
Amazon EC2 instance if the Allow tags in instance metadata
option is enabled on the instance. Allowing tags in instance metadata
prevents tag key names from containing spaces. If you have allowed tags in EC2 instance metadata, you must use the tag key
PatchGroup (without a space).
Diagram 1: General example of patching operations process flow
The following illustration shows a general example of the processes that Systems Manager performs when sending a Run Command task to your fleet of servers to patch using Patch Manager. These processes determine which patch baselines to use in patching operations. (A similar process is used when a maintenance window is configured to send a command to patch using Patch Manager.)
The full process is explained below the illustration.
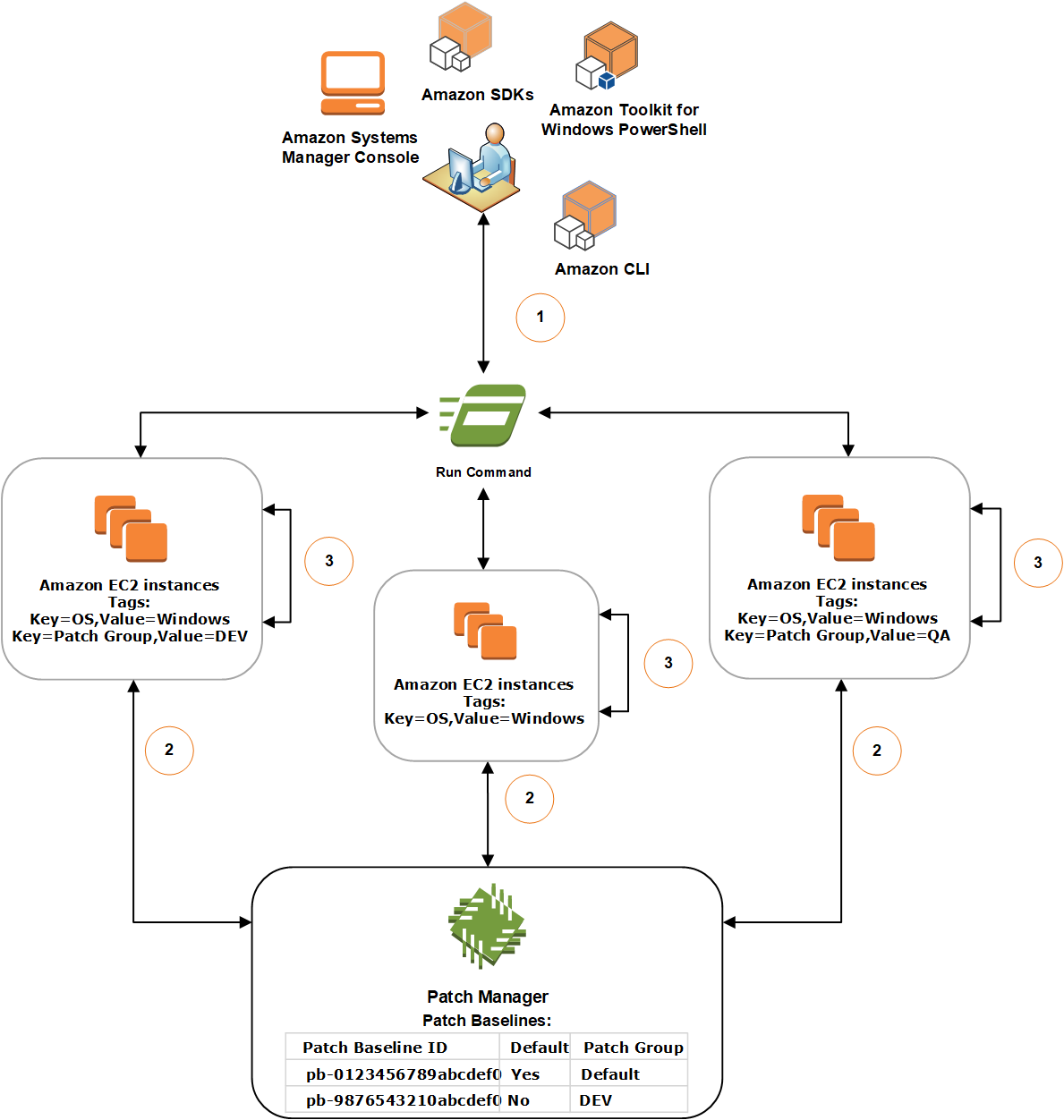
In this example, we have three groups of EC2 instances for Windows Server with the following tags applied:
| EC2 instances group | Tags |
|---|---|
|
Group 1 |
|
|
Group 2 |
|
|
Group 3 |
|
For this example, we also have these two Windows Server patch baselines:
| Patch baseline ID | Default | Associated patch group |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Yes |
|
|
|
No |
|
The general process to scan or install patches using Run Command, a tool in Amazon Systems Manager, and Patch Manager is as follows:
-
Send a command to patch: Use the Systems Manager console, SDK, Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI), or Amazon Tools for Windows PowerShell to send a Run Command task using the document
AWS-RunPatchBaseline. The diagram shows a Run Command task to patch managed instances by targeting the tagkey=OS,value=Windows. -
Patch baseline determination: SSM Agent verifies the patch group tags applied to the EC2 instance and queries Patch Manager for the corresponding patch baseline.
-
Matching patch group value associated with patch baseline:
-
SSM Agent, which is installed on EC2 instances in group one, receives the command issued in Step 1 to begin a patching operation. SSM Agent validates that the EC2 instances have the patch group tag-value
DEVapplied and queries Patch Manager for an associated patch baseline. -
Patch Manager verifies that patch baseline
pb-9876543210abcdef0has the patch groupDEVassociated and notifies SSM Agent. -
SSM Agent retrieves a patch baseline snapshot from Patch Manager based on the approval rules and exceptions configured in
pb-9876543210abcdef0and proceeds to the next step.
-
-
No patch group tag added to instance:
-
SSM Agent, which is installed on EC2 instances in group two, receives the command issued in Step 1 to begin a patching operation. SSM Agent validates that the EC2 instances don't have a
Patch GrouporPatchGrouptag applied and as a result, SSM Agent queries Patch Manager for the default Windows patch baseline. -
Patch Manager verifies that the default Windows Server patch baseline is
pb-0123456789abcdef0and notifies SSM Agent. -
SSM Agent retrieves a patch baseline snapshot from Patch Manager based on the approval rules and exceptions configured in the default patch baseline
pb-0123456789abcdef0and proceeds to the next step.
-
-
No matching patch group value associated with a patch baseline:
-
SSM Agent, which is installed on EC2 instances in group three, receives the command issued in Step 1 to begin a patching operation. SSM Agent validates that the EC2 instances have the patch group tag-value
QAapplied and queries Patch Manager for an associated patch baseline. -
Patch Manager doesn't find a patch baseline that has the patch group
QAassociated. -
Patch Manager notifies SSM Agent to use the default Windows patch baseline
pb-0123456789abcdef0. -
SSM Agent retrieves a patch baseline snapshot from Patch Manager based on the approval rules and exceptions configured in the default patch baseline
pb-0123456789abcdef0and proceeds to the next step.
-
-
-
Patch scan or install: After determining the appropriate patch baseline to use, SSM Agent begins either scanning for or installing patches based on the operation value specified in Step 1. The patches that are scanned for or installed are determined by the approval rules and patch exceptions defined in the patch baseline snapshot provided by Patch Manager.
- More info