Nesting an existing stack
Use the resource import feature to nest an existing stack within another
existing stack. Nested stacks are common components that you declare and reference from within
other templates. That way, you can avoid copying and pasting the same configurations into your
templates and simplify stack updates. If you have a template for a common component, you can
use the AWS::CloudFormation::Stack resource to reference this template from
within another template. For more information on nested stacks, see Split a template into reusable pieces using nested
stacks.
Amazon CloudFormation only supports one level of nesting using resource import. This means
that you can't import a stack into a child stack or import a stack that has children.
If you're new to importing, we recommend that you first review the introductory information in the Import Amazon resources into a CloudFormation stack manually topic.
Nested stack import validation
During a nested stack import operation, Amazon CloudFormation performs the following validations.
-
The nested
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackdefinition in the parent stack template matches the actual nested stack's template. -
The tags for the nested
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackdefinition in the parent stack template match the tags for the actual nested stack resource.
Nest an existing stack using the Amazon Web Services Management Console
-
Add the
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource to the parent stack template with aRetainDeletionPolicy. In the following example parent stack template,MyNestedStackis the target of the import.JSON
{ "AWSTemplateFormatVersion" : "2010-09-09", "Resources" : { "ServiceTable":{ "Type":"AWS::DynamoDB::Table", "Properties":{ "TableName":"Service", "AttributeDefinitions":[ { "AttributeName":"key", "AttributeType":"S" } ], "KeySchema":[ { "AttributeName":"key", "KeyType":"HASH" } ], "ProvisionedThroughput":{ "ReadCapacityUnits":5, "WriteCapacityUnits":1 } } }, "MyNestedStack" : { "Type" : "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack", "DeletionPolicy": "Retain", "Properties" : { "TemplateURL" : "https://s3.amazonaws.com/cloudformation-templates-us-east-2/EC2ChooseAMI.template","Parameters" : { "InstanceType" : "t1.micro", "KeyName" : "mykey"} } } } }YAML
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09 Resources: ServiceTable: Type: 'AWS::DynamoDB::Table' Properties: TableName: Service AttributeDefinitions: - AttributeName: key AttributeType: S KeySchema: - AttributeName: key KeyType: HASH ProvisionedThroughput: ReadCapacityUnits: 5 WriteCapacityUnits: 1 MyNestedStack: Type: 'AWS::CloudFormation::Stack' DeletionPolicy: Retain Properties: TemplateURL: >-https://s3.amazonaws.com/cloudformation-templates-us-east-2/EC2ChooseAMI.templateParameters: InstanceType: t1.micro KeyName: mykey -
Open the Amazon CloudFormation console.
-
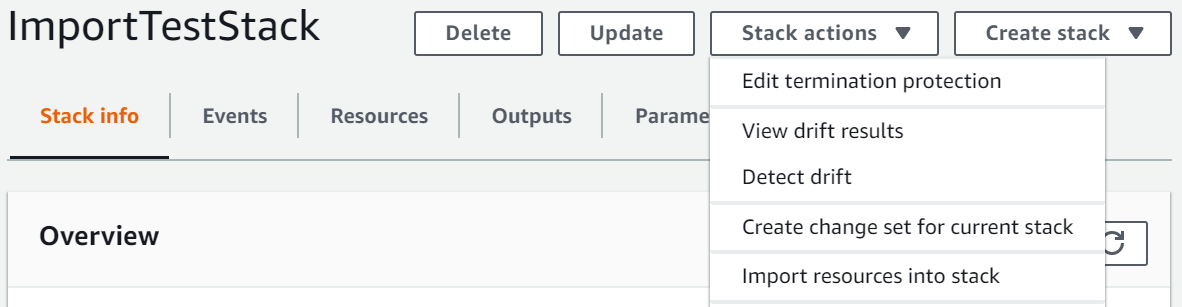
On the Stacks page, with the parent stack selected, choose Stack actions, and then choose Import resources into stack.
-
Read the Import overview page for a list of things you're required to provide during this operation. Then, choose Next.
-
On the Specify template page, provide the updated parent template using one of the following methods, and then choose Next.
-
Choose Amazon S3 URL, and then specify the URL for your template in the text box.
-
Choose Upload a template file, and then browse for your template.
-
-
On the Identify resources page, identify the
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource.-
Under Identifier property, choose the type of resource identifier. For example, an
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource can be identified using theStackIdproperty. -
Under Identifier value, type the ARN of the stack you're importing. For example,
arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:stack/mystack/5b918d10-cd98-11ea-90d5-0a9cd3354c10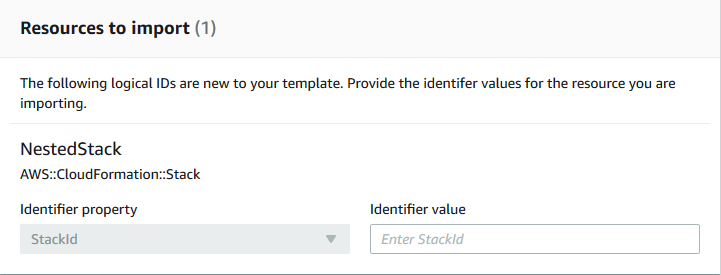
-
Choose Next.
-
-
On the Specify stack details page, modify any parameters, and then choose Next. This automatically creates a change set.
Important
The import operation fails if you modify existing parameters that initiate a create, update, or delete operation.
-
On the Review
MyParentStackpage, confirm that the correct resource is being imported, and then choose Import resources. This automatically executes the change set created in the last step. Any stack-level tags are applied to imported resources at this time. -
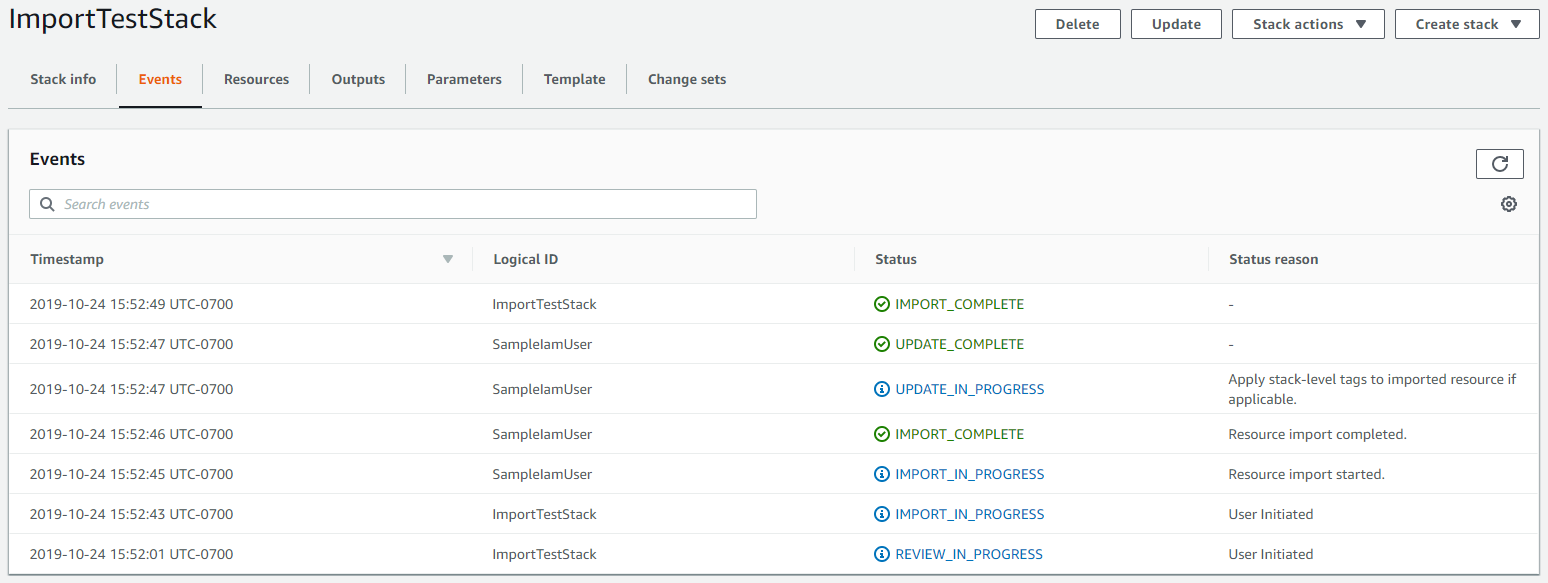
The Events pane of the Stack details page for your parent stack displays.
Note
It's not necessary to run drift detection on the parent stack after this import operation because the
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource was already managed by Amazon CloudFormation.
Nest an existing stack using the Amazon CLI
-
Add the
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource to the parent stack template with aRetainDeletionPolicy. In the following example parent template,MyNestedStackis the target of the import.JSON
{ "AWSTemplateFormatVersion" : "2010-09-09", "Resources" : { "ServiceTable":{ "Type":"AWS::DynamoDB::Table", "Properties":{ "TableName":"Service", "AttributeDefinitions":[ { "AttributeName":"key", "AttributeType":"S" } ], "KeySchema":[ { "AttributeName":"key", "KeyType":"HASH" } ], "ProvisionedThroughput":{ "ReadCapacityUnits":5, "WriteCapacityUnits":1 } } }, "MyNestedStack" : { "Type" : "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack", "DeletionPolicy": "Retain", "Properties" : { "TemplateURL" : "https://s3.amazonaws.com/cloudformation-templates-us-east-2/EC2ChooseAMI.template","Parameters" : { "InstanceType" : "t1.micro", "KeyName" : "mykey"} } } } }YAML
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09 Resources: ServiceTable: Type: 'AWS::DynamoDB::Table' Properties: TableName: Service AttributeDefinitions: - AttributeName: key AttributeType: S KeySchema: - AttributeName: key KeyType: HASH ProvisionedThroughput: ReadCapacityUnits: 5 WriteCapacityUnits: 1MyNestedStack: Type: 'AWS::CloudFormation::Stack' DeletionPolicy: Retain Properties: TemplateURL: >-https://s3.amazonaws.com/cloudformation-templates-us-east-2/EC2ChooseAMI.templateParameters: InstanceType: t1.micro KeyName: mykey -
Compose a JSON string as shown in the following example, with these modifications:
-
Replace
MyNestedStackwith the logical ID of the target resource as specified in the template. -
Replace
arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:stack/mystack/5b918d10-cd98-11ea-90d5-0a9cd3354c10with the ARN of the stack you want to import.
[{"ResourceType":"AWS::CloudFormation::Stack","LogicalResourceId":"MyNestedStack","ResourceIdentifier":{"StackId":"arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/mystack/5b918d10-cd98-11ea-90d5-0a9cd3354c10"}}]Alternatively, you can specify the parameters in a configuration file.
For example, to import
MyNestedStack, you might create aResourcesToImport.txtfile that contains the following configuration.JSON
[ { "ResourceType":"AWS::CloudFormation::Stack", "LogicalResourceId":"MyNestedStack", "ResourceIdentifier": { "StackId":"arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:stack/mystack/5b918d10-cd98-11ea-90d5-0a9cd3354c10" } } ]YAML
ResourceType: 'AWS::CloudFormation::Stack' LogicalResourceId:MyNestedStackResourceIdentifier: StackId: >-arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:stack/mystack/5b918d10-cd98-11ea-90d5-0a9cd3354c10 -
-
To create a change set, use the following create-change-set command and replace the placeholder text. For the
--change-set-typeoption, specify a value ofIMPORT. For the--resources-to-importoption, replace the sample JSON string with the actual JSON string you just created.aws cloudformation create-change-set \ --stack-nameMyParentStack--change-set-nameImportChangeSet\ --change-set-typeIMPORT\ --template-bodyfile://TemplateToImport.json\ --resources-to-import'[{"ResourceType":"AWS::CloudFormation::Stack","LogicalResourceId":"MyNestedStack","ResourceIdentifier":{"StackId":"arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:stack/mystack/5b918d10-cd98-11ea-90d5-0a9cd3354c10"}}]'Note
--resources-to-importdoesn't support inline YAML. The requirements for escaping quotes in the JSON string vary depending on your terminal. For more information, see Using quotation marks inside strings in the Amazon Command Line Interface User Guide.Alternatively, you can use a file URL as input for the
--resources-to-importoption, as shown in the following example.--resources-to-importfile://ResourcesToImport.txtIf successful, this command returns the following sample output.
{ "Id": "arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:changeSet/ImportChangeSet/8ad75b3f-665f-46f6-a200-0b4727a9442e", "StackId": "arn:aws-cn:cloudformation:us-west-2:12345678910:stack/MyParentStack/4e345b70-1281-11ef-b027-027366d8e82b" } -
Review the change set to make sure the correct stack is being imported.
aws cloudformation describe-change-set --change-set-nameImportChangeSet -
To initiate the change set and import the stack into the source parent stack, use the following execute-change-set command and replace the placeholder text. Any stack-level tags are applied to imported resources at this time. On successful completion of the import operation
(IMPORT_COMPLETE), the stack is successfully nested.aws cloudformation execute-change-set --change-set-nameImportChangeSetNote
It's not necessary to run drift detection on the parent stack after this import operation because the
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource is already managed by Amazon CloudFormation.