What is Amazon EC2?
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) provides on-demand, scalable computing capacity in the Amazon Web Services (Amazon) Cloud. Using Amazon EC2 reduces hardware costs so you can develop and deploy applications faster. You can use Amazon EC2 to launch as many or as few virtual servers as you need, configure security and networking, and manage storage. You can add capacity (scale up) to handle compute-heavy tasks, such as monthly or yearly processes, or spikes in website traffic. When usage decreases, you can reduce capacity (scale down) again.
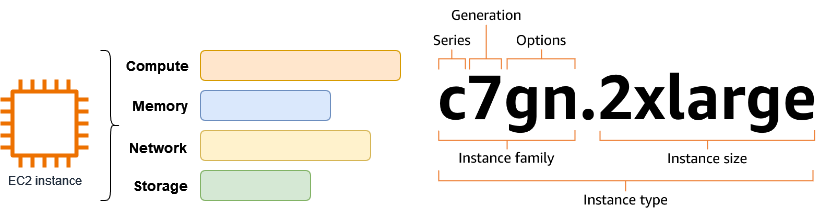
An EC2 instance is a virtual server in the Amazon Cloud. When you launch an EC2 instance, the instance type that you specify determines the hardware available to your instance. Each instance type offers a different balance of compute, memory, network, and storage resources. For more information, see the Amazon EC2 Instance Types Guide.
Features of Amazon EC2
Amazon EC2 provides the following high-level features:
- Instances
-
Virtual servers.
- Amazon Machine Images (AMIs)
-
Preconfigured templates for your instances that package the components you need for your server (including the operating system and additional software).
- Instance types
-
Various configurations of CPU, memory, storage, networking capacity, and graphics hardware for your instances.
- Amazon EBS volumes
-
Persistent storage volumes for your data using Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS).
- Instance store volumes
-
Storage volumes for temporary data that is deleted when you stop, hibernate, or terminate your instance.
- Key pairs
-
Secure login information for your instances. Amazon stores the public key and you store the private key in a secure place.
- Security groups
-
A virtual firewall that allows you to specify the protocols, ports, and source IP ranges that can reach your instances, and the destination IP ranges to which your instances can connect.
Amazon EC2 supports the processing, storage, and transmission
of credit card data by a merchant or service provider, and has been
validated as being compliant with Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard (DSS).
For more information about PCI DSS, including how to request a copy of the Amazon Web Services PCI Compliance Package,
see PCI DSS Level 1
Related services
Services to use with Amazon EC2
You can use other Amazon Web Services services with the instances that you deploy using Amazon EC2.
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling
-
Helps ensure you have the correct number of Amazon EC2 instances available to handle the load for your application.
- Amazon Backup
-
Automate backing up your Amazon EC2 instances and the Amazon EBS volumes attached to them.
- Amazon CloudWatch
-
Monitor your instances and Amazon EBS volumes.
- Elastic Load Balancing
-
Automatically distribute incoming application traffic across multiple instances.
- Amazon GuardDuty
-
Detect potentially unauthorized or malicious use of your EC2 instances.
- EC2 Image Builder
-
Automate the creation, management, and deployment of customized, secure, and up-to-date server images.
- Amazon Launch Wizard
-
Size, configure, and deploy Amazon resources for third-party applications without having to manually identify and provision individual Amazon resources.
- Amazon Systems Manager
-
Perform operations at scale on EC2 instances with this secure end-to-end management solution.
Additional compute services
You can launch instances using another Amazon compute service instead of using Amazon EC2.
- Amazon Lightsail
-
Build websites or web applications using Amazon Lightsail, a cloud platform that provides the resources that you need to deploy your project quickly, for a low, predictable monthly price. To compare Amazon EC2 and Lightsail, see Amazon Lightsail or Amazon EC2.
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS)
-
Deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications on a cluster of EC2 instances. For more information, see Choosing an Amazon container service.
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS)
-
Run your Kubernetes applications on Amazon. For more information, see Choosing an Amazon container service.
Access Amazon EC2
You can create and manage your Amazon EC2 instances using the following interfaces:
- Amazon EC2 console
-
A simple web interface to create and manage Amazon EC2 instances and resources. If you've signed up for an Amazon account, you can access the Amazon EC2 console by signing into the Amazon Web Services Management Console and selecting EC2 from the console home page.
- Amazon Command Line Interface
-
Enables you to interact with Amazon services using commands in your command-line shell. It is supported on Windows, Mac, and Linux. For more information about the Amazon CLI , see Amazon Command Line Interface User Guide. You can find the Amazon EC2 commands in the Amazon CLI Command Reference.
- Amazon CloudFormation
-
Amazon EC2 supports creating resources using Amazon CloudFormation. You create a template, in JSON or YAML format, that describes your Amazon resources, and Amazon CloudFormation provisions and configures those resources for you. You can reuse your CloudFormation templates to provision the same resources multiple times, whether in the same Region and account or in multiple Regions and accounts. For more information about supported resource types and properties for Amazon EC2, see EC2 resource type reference in the Amazon CloudFormation User Guide.
- Amazon SDKs
-
If you prefer to build applications using language-specific APIs instead of submitting a request over HTTP or HTTPS, Amazon provides libraries, sample code, tutorials, and other resources for software developers. These libraries provide basic functions that automate tasks such as cryptographically signing your requests, retrying requests, and handling error responses, making it easier for you to get started. For more information, see Tools to Build on Amazon
. - Amazon Tools for PowerShell
-
A set of PowerShell modules that are built on the functionality exposed by the Amazon SDK for .NET. The Tools for PowerShell enable you to script operations on your Amazon resources from the PowerShell command line. To get started, see the Amazon Tools for PowerShell User Guide. You can find the cmdlets for Amazon EC2, in the Amazon Tools for PowerShell Cmdlet Reference.
- Query API
-
Amazon EC2 provides a Query API. These requests are HTTP or HTTPS requests that use the HTTP verbs GET or POST and a Query parameter named
Action. For more information about the API actions for Amazon EC2, see Actions in the Amazon EC2 API Reference.
Pricing for Amazon EC2
Amazon EC2 provides the following pricing options:
- On-Demand Instances
-
Pay for the instances that you use by the second, with a minimum of 60 seconds, with no long-term commitments or upfront payments.
- Reserved Instances
-
You can reduce your Amazon EC2 costs by making a commitment to a specific instance configuration, including instance type and Region, for a term of 1 or 3 years.
- Spot Instances
-
Request unused EC2 instances, which can reduce your Amazon EC2 costs significantly.
- Dedicated Hosts
-
Reduce costs by using a physical EC2 server that is fully dedicated for your use, either On-Demand or as part of a Savings Plan. You can use your existing server-bound software licenses and get help meeting compliance requirements.
- On-Demand Capacity Reservations
-
Reserve compute capacity for your EC2 instances in a specific Availability Zone for any duration of time.
- Per-second billing
-
Removes the cost of unused minutes and seconds from your bill.
For a complete list of charges and prices for Amazon EC2 and more information about the purchase
models, see Amazon EC2 pricing
Estimates, billing, and cost optimization
To create estimates for your Amazon use cases, use the Amazon Pricing Calculator
To estimate the cost of transforming Microsoft
workloads to a modern architecture that uses open source and
cloud-native services deployed on Amazon, use the Amazon
Modernization Calculator for Microsoft Workloads
To see your bill, go to the Billing and Cost Management
Dashboard in the Amazon Billing and Cost Management
console
If you have questions concerning Amazon billing, accounts, and events, contact Amazon Support
When calculating the cost of a provisioned environment, remember to include incidental costs such as snapshot storage for EBS volumes.
You can optimize the cost, security, and performance of your Amazon environment
using Amazon Trusted Advisor
You can use Amazon Cost Explorer to analyze the cost and usage of your EC2 instances. You can view data up to the last 13 months, and forecast how much you are likely to spend for the next 12 months. For more information, see Analyzing your costs and usage with Amazon Cost Explorer in the Amazon Cost Management User Guide.