Elastic Fabric Adapter for AI/ML and HPC workloads on Amazon EC2
An Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) is a network device that you can attach to your Amazon EC2 instance to accelerate Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and High Performance Computing (HPC) applications. EFA enables you to achieve the application performance of an on-premises AI/ML or HPC cluster, with the scalability, flexibility, and elasticity provided by the Amazon Cloud.
EFA provides lower and more consistent latency and higher throughput than the TCP transport traditionally used in cloud-based HPC systems. It enhances the performance of inter-instance communication that is critical for scaling AI/ML and HPC applications. It is optimized to work on the existing Amazon network infrastructure and it can scale depending on application requirements.
EFA integrates with Libfabric 1.7.0 and later, and it supports Nvidia Collective Communications Library (NCCL) for AI and ML applications, and Open MPI 4.1 and later and Intel MPI 2019 Update 5 and later for HPC applications.
EFA supports RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) write on most supported instance types that have Nitro version 4 and later. RDMA read is supported on all instances with Nitro version 4 and later. For more information, see Supported instance types.
Contents
EFA basics
An EFA device can be attached to an EC2 instance in two ways:
-
Using a traditional EFA interface, also called EFA with ENA, which creates both an EFA device and an ENA device.
-
Using an EFA-only interface, which creates just the EFA device.
The EFA device provides capabilities like built-in OS-bypass and congestion control through the Scalable Reliable Datagram (SRD) protocol. The EFA device features enable low-latency, reliable transport functionality that allows EFA interface to provide better application performance for HPC and ML applications on Amazon EC2. While the ENA device offers traditional IP networking.
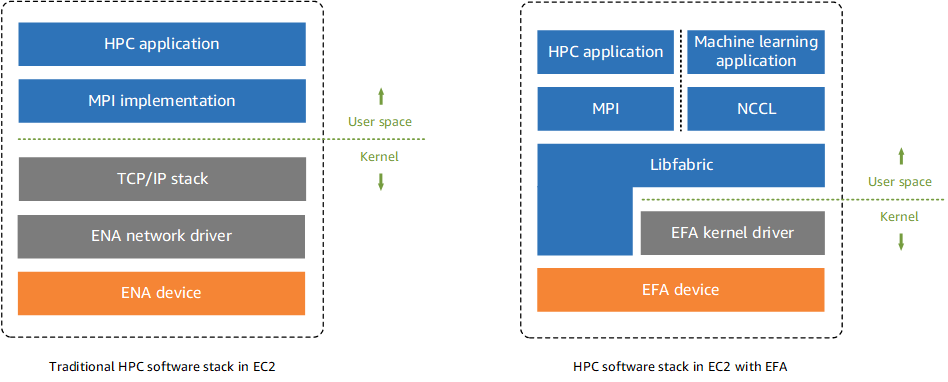
Traditionally, AI/ML applications use NCCL and HPC applications use the Message Passing Interface (MPI) to interface with the system's network transport. In the Amazon cloud, this has meant that applications interface with NCCL or MPI, which then uses the operating system's TCP/IP stack and the ENA device driver to enable network communication between instances.
With a traditional EFA (EFA with ENA) or EFA-only interface, AI/ML applications use NCCL and HPC applications use MPI, to interface directly with the Libfabric API. The Libfabric API bypasses the operating system kernel and communicates directly with the EFA device to put packets on the network. This reduces overhead and enables AI/ML and HPC applications to run more efficiently.
Note
Libfabric is a core component of the OpenFabrics Interfaces (OFI) framework,
which defines and exports the user-space API of OFI. For more information, see
the Libfabric OpenFabrics
Differences between ENA, EFA, and EFA-only network interfaces
Amazon EC2 provides two types of network interfaces:
-
ENA interfaces provide all of the traditional IP networking and routing features that are required to support IP networking for a VPC. For more information, see Enable enhanced networking with ENA on your EC2 instances.
-
EFA (EFA with ENA) interfaces provide both the ENA device for IP networking and the EFA device for low-latency, high-throughput communication.
-
EFA-only interfaces support only the EFA device capabilities, without the ENA device for traditional IP networking.
The following table provides a comparison of ENA, EFA, and EFA-only network interfaces.
| ENA | EFA (EFA with ENA) | EFA-only | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supports IP networking functionality | Yes | Yes | No |
| Can be assigned IPv4 or IPv6 addresses | Yes | Yes | No |
| Can be used as primary network interface for instance | Yes | Yes | No |
| Counts towards ENI attachment limit for instance | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Instance type support | Supported on all Nitro-based instances types | Supported instance types | Supported instance types |
| Parameter naming in EC2 APIs | interface |
efa |
efa-only |
| Field naming in EC2 console | No selection | EFA with ENA | EFA-only |
Supported interfaces and libraries
EFAs support the following interfaces and libraries:
-
Open MPI 4.1 and later
-
Intel MPI 2019 Update 5 and later
-
NVIDIA Collective Communications Library (NCCL) 2.4.2 and later
-
Amazon Neuron SDK version 2.3 and later
Supported instance types
All of the following instance types support EFA. Additionally, the tables indicate RDMA read and RDMA write support for the instance types.
To see the available instance types that support EFAs in a specific Region
The available instance types vary by Region. To see the available instance types that
support EFAs in a Region, use the describe-instance-types
command with the --region parameter. Include the --filters
parameter to scope the results to the instance types that support EFA and the
--query parameter to scope the output to the value of
InstanceType.
aws ec2 describe-instance-types \ --regionus-east-1\ --filters Name=network-info.efa-supported,Values=true \ --query "InstanceTypes[*].[InstanceType]" \ --output text | sort
Supported operating systems
Operating system support differs depending on the processor type. The following table shows the supported operating systems.
| Operating system | Intel/AMD (x86_64) instance types |
Amazon Graviton (arm64) instance types |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Linux 2023 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Amazon Linux 2 | ✓ | ✓ |
| RHEL 8 and 9 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Debian 11, 12, and 13 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Rocky Linux 8 and 9 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ubuntu 22.04 and 24.04 | ✓ | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP2 and later | ✓ | ✓ |
| OpenSUSE Leap 15.5 and later | ✓ |
Note
Some of the listed operating systems might not be supported with Intel MPI. If you are using
Intel MPI, refer to the
Intel MPI documentation
EFA limitations
EFAs have the following limitations:
-
RDMA write is not supported with all instance types. For more information, see Supported instance types.
-
EFA traffic1 between P4d/P4de/DL1 instances and other instance types is currently not supported.
-
Instance types that support multiple network cards can be configured with one EFA per network card. All other supported instance types support only one EFA per instance.
-
c7g.16xlarge,m7g.16xlarge, andr7g.16xlargeDedicated Instances and Dedicated Hosts are not supported when an EFA is attached. -
EFA traffic1 can't cross Availability Zones or VPCs. This does not apply to normal IP traffic from the ENA device of an EFA interface.
-
EFA traffic1 is not routable. Normal IP traffic from the ENA device of an EFA interface remains routable.
-
EFA is not supported on Amazon Outposts.
-
The EFA device of an EFA (EFA with ENA) interface is supported on Windows instances only for Amazon Cloud Digital Interface Software Development Kit (Amazon CDI SDK) based applications. If you attach an EFA (EFA with ENA) interface to a Windows instance for non-CDI SDK based applications, it functions as an ENA interface, without the added EFA device capabilities. The EFA-only interface is not supported by Amazon CDI based applications on Windows or Linux. For more information, see the Amazon Cloud Digital Interface Software Development Kit (Amazon CDI SDK) User Guide.
1EFA traffic refers to the traffic transmitted through the EFA device of either an EFA (EFA with ENA) or EFA-only interface.
EFA pricing
EFA is available as an optional Amazon EC2 networking feature that you can enable on any supported instance at no additional cost.