Valkey or Redis OSS nodes and shards
A shard (in the API and CLI, a node group) is a hierarchical arrangement of nodes, each wrapped in a cluster. Shards support replication. Within a shard, one node functions as the read/write primary node. All the other nodes in a shard function as read-only replicas of the primary node. Valkey, or Redis OSS version 3.2 and later, support multiple shards within a cluster (in the API and CLI, a replication group). This support enables partitioning your data in a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster.
The following diagram illustrates the differences between a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster and a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster.
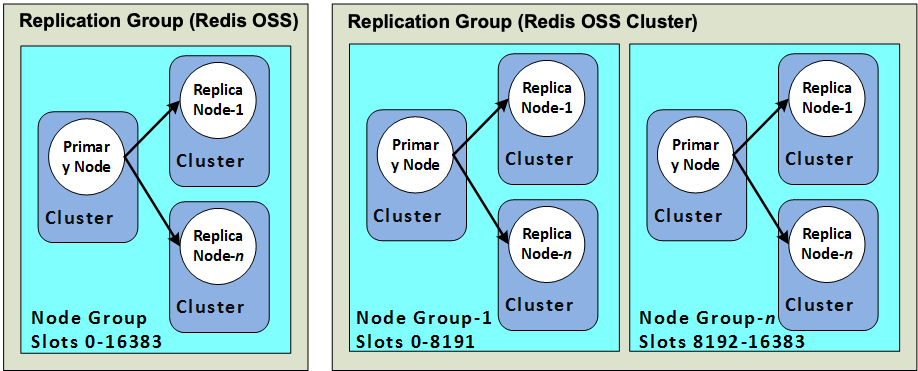
Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) clusters support replication via shards. The API operation DescribeReplicationGroups (CLI: describe-replication-groups) lists the node groups with the member nodes, the node's role within the node group, and also other information.
When you create a Valkey or Redis OSS cluster, you specify whether you want to create a cluster with clustering enabled. Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) clusters never have more than one shard, which can be scaled horizontally by adding (up to a total of five) or deleting read replica nodes. For more information, see High availability using replication groups, Adding a read replica for Valkey or Redis OSS (Cluster Mode Disabled) or Deleting a read replica for Valkey or Redis OSS (Cluster Mode Disabled). Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) clusters can also scale vertically by changing node types. For more information, see Scaling replica nodes for Valkey or Redis OSS (Cluster Mode Disabled).
The node or shard limit can be increased to a maximum of 500 per cluster if the engine is Valkey or Redis OSS version 5.0.6 or higher. For example, you can choose to configure a 500 node cluster that ranges between 83 shards (one primary and 5 replicas per shard) and 500 shards (single primary and no replicas). Make sure there are enough available IP addresses to accommodate the increase. Common pitfalls include the subnets in the subnet group have too small a CIDR range or the subnets are shared and heavily used by other clusters. For more information, see Creating a subnet group.
For versions below 5.0.6, the limit is 250 per cluster.
To request a limit increase, see Amazon
Service Limits
After a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster is created, it can be altered (scaled in or out). For more information, see Scaling ElastiCache and Replacing nodes (Valkey and Redis OSS).
When you create a new cluster, you can seed it with data from the old cluster so it doesn't start out empty. This approach works only if the cluster group has the same number of shards as the old cluster. Doing this can be helpful if you need change your node type or engine version. For more information, see Taking manual backups and Restoring from a backup into a new cache.