Understanding Valkey and Redis OSS replication
Redis OSS implements replication in two ways:
-
With a single shard that contains all of the cluster's data in each node—Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled)
-
With data partitioned across up to 500 shards—Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled)
Each shard in a replication group has a single read/write primary node and up to 5 read-only replica nodes. You can create a cluster with higher number of shards and lower number of replicas totaling up to 90 nodes per cluster. This cluster configuration can range from 90 shards and 0 replicas to 15 shards and 5 replicas, which is the maximum number of replicas allowed.
The node or shard limit can be increased to a maximum of 500 per cluster if the Redis OSS engine version is 5.0.6 or higher. For example, you can choose to configure a 500 node cluster that ranges between 83 shards (one primary and 5 replicas per shard) and 500 shards (single primary and no replicas). Make sure there are enough available IP addresses to accommodate the increase. Common pitfalls include the subnets in the subnet group have too small a CIDR range or the subnets are shared and heavily used by other clusters. For more information, see Creating a subnet group.
For versions below 5.0.6, the limit is 250 per cluster.
To request a limit increase, see
Amazon Service Limits
Valkey or Redis OSS (Cluster Mode Disabled)
A Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster has a single shard, inside of which is a collection of nodes; one primary read/write node and up to five secondary, read-only replica nodes. Each read replica maintains a copy of the data from the cluster's primary node. Asynchronous replication mechanisms are used to keep the read replicas synchronized with the primary. Applications can read from any node in the cluster. Applications can write only to the primary node. Read replicas improve read throughput and guard against data loss in cases of a node failure.
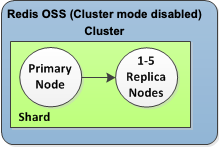
Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster with a single shard and replica nodes
You can use Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) clusters with replica nodes to scale your solution for ElastiCache to handle applications that are read-intensive or to support large numbers of clients that simultaneously read from the same cluster.
All of the nodes in a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster must reside in the same region.
When you add a read replica to a cluster, all of the data from the primary is copied to the new node. From that point on, whenever data is written to the primary, the changes are asynchronously propagated to all the read replicas.
To improve fault tolerance and reduce write downtime, enable Multi-AZ with Automatic Failover for your Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster with replicas. For more information, see Minimizing downtime in ElastiCache by using Multi-AZ with Valkey and Redis OSS.
You can change the roles of the nodes within the Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) cluster, with the primary and one of the replicas exchanging roles. You might decide to do this for performance tuning reasons. For example, with a web application that has heavy write activity, you can choose the node that has the lowest network latency. For more information, see Promoting a read replica to primary, for Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode disabled) replication groups.
Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled)
A Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster is comprised of from 1 to 500 shards (API/CLI: node groups). Each shard has a primary node and up to five read-only replica nodes. The configuration can range from 90 shards and 0 replicas to 15 shards and 5 replicas, which is the maximum number of replicas allowed.
The node or shard limit can be increased to a maximum of 500 per cluster if the engine version is Valkey 7.2 and higher, or Redis OSS 5.0.6 and higher. For example, you can choose to configure a 500 node cluster that ranges between 83 shards (one primary and 5 replicas per shard) and 500 shards (single primary and no replicas). Make sure there are enough available IP addresses to accommodate the increase. Common pitfalls include the subnets in the subnet group have too small a CIDR range or the subnets are shared and heavily used by other clusters. For more information, see Creating a subnet group.
For versions below 5.0.6, the limit is 250 per cluster.
To request a limit increase, see
Amazon Service Limits
Each read replica in a shard maintains a copy of the data from the shard's primary. Asynchronous replication mechanisms are used to keep the read replicas synchronized with the primary. Applications can read from any node in the cluster. Applications can write only to the primary nodes. Read replicas enhance read scalability and guard against data loss. Data is partitioned across the shards in a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster.
Applications use the Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster's configuration endpoint to connect with the nodes in the cluster. For more information, see Finding connection endpoints in ElastiCache.

Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster with multiple shards and replica nodes
All of the nodes in a Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) cluster must reside in the same region. To improve fault tolerance, you can provision both primaries and read replicas in multiple Availability Zones within that region.
Currently, Valkey or Redis OSS (cluster mode enabled) features have some limitations.
-
You cannot manually promote any of the replica nodes to primary.