Amazon Aurora DB clusters
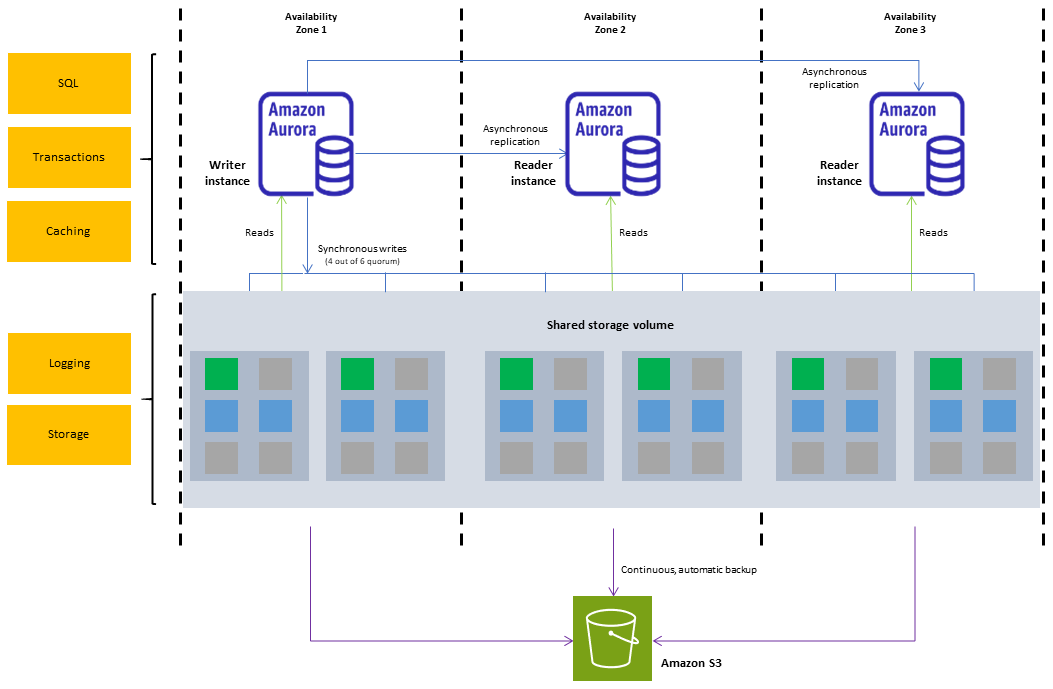
An Amazon Aurora DB cluster consists of one or more DB instances and a cluster volume that manages the data for those DB instances. An Aurora cluster volume is a virtual database storage volume that spans multiple Availability Zones, with each Availability Zone having a copy of the DB cluster data. Two types of DB instances make up an Aurora DB cluster:
-
Primary (writer) DB instance – Supports read and write operations, and performs all of the data modifications to the cluster volume. Each Aurora DB cluster has one primary DB instance.
-
Aurora Replica (reader DB instance) – Connects to the same storage volume as the primary DB instance but supports only read operations. Each Aurora DB cluster can have up to 15 Aurora Replicas in addition to the primary DB instance. Maintain high availability by locating Aurora Replicas in separate Availability Zones. Aurora automatically fails over to an Aurora Replica in case the primary DB instance becomes unavailable. You can specify the failover priority for Aurora Replicas. Aurora Replicas can also offload read workloads from the primary DB instance.
The following diagram illustrates the relationship between the cluster volume, the writer DB instance, and reader DB instances in an Aurora DB cluster.
Note
The preceding information applies to all Aurora DB clusters—provisioned, parallel query, Aurora Global Database, Aurora Serverless, Aurora MySQL-Compatible, and Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible.
The Aurora DB cluster illustrates the separation of compute capacity and storage. For example, an Aurora configuration with only a single DB instance is still a cluster, because the underlying storage volume involves multiple storage nodes distributed across multiple Availability Zones (AZs).
Input/output (I/O) operations in Aurora DB clusters are counted the same way, regardless of whether they're on a writer or reader DB instance. For more information, see Storage configurations for Amazon Aurora DB clusters.