Using SCRAM for PostgreSQL password encryption
The Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism
(SCRAM) is an alternative to PostgreSQL's default message digest (MD5)
algorithm for encrypting passwords. The SCRAM authentication mechanism is considered more secure
than MD5. To learn more about these two different approaches to securing passwords, see Password Authentication
We recommend that you use SCRAM rather than MD5 as the password encryption scheme for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster. SCRAM is supported in Aurora PostgreSQL version 10 and all higher major and minor versions. It's a cryptographic challenge-response mechanism that uses the scram-sha-256 algorithm for password authentication and encryption.
You might need to update libraries for your client applications to support SCRAM. For
example, JDBC versions before 42.2.0 don't support SCRAM. For more information, see PostgreSQL JDBC
Driver
Aurora PostgreSQL version 14 and higher support scram-sha-256 for password
encryption by default for new DB clusters. For these versions, the default DB cluster parameter group
(default.aurora-postgresql14) has its password_encryption value set
to scram-sha-256. SCRAM isn't supported for Aurora Serverless v1.
Setting up Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster to require SCRAM
For Aurora PostgreSQL 14.3 and higher versions, you can require the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster to accept only passwords that use the scram-sha-256 algorithm.
Important
For existing RDS Proxies with PostgreSQL databases, if you modify the database
authentication to use SCRAM only, the proxy becomes unavailable for up to 60
seconds. To avoid the issue, do one of the following:
-
Ensure that the database allows both
SCRAMandMD5authentication. -
To use only
SCRAMauthentication, create a new proxy, migrate your application traffic to the new proxy, then delete the proxy previously associated with the database.
Before making changes to your system, be sure you understand the complete process, as follows:
-
Get information about all roles and password encryption for all database users.
-
Double-check the parameter settings for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster for the parameters that control password encryption.
-
If your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster uses a default parameter group, you need to create a custom DB cluster parameter group and apply it to your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster so that you can modify parameters when needed. If your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster uses a custom parameter group, you can modify the necessary parameters later in the process, as needed.
-
Change the
password_encryptionparameter toscram-sha-256. -
Notify all database users that they need to update their passwords. Do the same for your
postgresaccount. The new passwords are encrypted and stored using the scram-sha-256 algorithm. -
Verify that all passwords are encrypted using as the type of encryption.
-
If all passwords use scram-sha-256, you can change the
rds.accepted_password_auth_methodparameter frommd5+scramtoscram-sha-256.
Warning
After you change rds.accepted_password_auth_method to scram-sha-256 alone,
any users (roles) with md5–encrypted passwords can't connect.
Getting ready to require SCRAM for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster
Before making any changes to your Aurora PostgreSQL DB
cluster,
check all existing
database user accounts. Also, check the type of encryption used for passwords. You can do
these tasks by using the rds_tools extension. To see which PostgreSQL versions
support rds_tools, see Extension
versions for Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL.
To get a list of database users (roles) and password encryption methods
-
Use
psqlto connect to the primary instance of your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster , as shown in the following.psql --host=cluster-name-instance-1.111122223333.aws-region.rds.amazonaws.com --port=5432 --username=postgres --password -
Install the
rds_toolsextension.postgres=>CREATE EXTENSION rds_tools;CREATE EXTENSION -
Get a listing of roles and encryption.
postgres=>SELECT * FROM rds_tools.role_password_encryption_type();You see output similar to the following.
rolname | encryption_type ----------------------+----------------- pg_monitor | pg_read_all_settings | pg_read_all_stats | pg_stat_scan_tables | pg_signal_backend | lab_tester | md5 user_465 | md5 postgres | md5 (8 rows)
Creating a custom DB cluster parameter group
Note
If your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster already uses a custom parameter group, you don't need to create a new one.
For an overview of parameter groups for Aurora, see Creating a DB cluster parameter group in Amazon Aurora.
The password encryption type used for passwords is set in one parameter,
password_encryption. The encryption that the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster
allows is set in another
parameter, rds.accepted_password_auth_method. Changing either of these from the
default values requires that you create a custom DB cluster parameter
group
and apply it to your cluster.
You can also use the Amazon Web Services Management Console or the RDS API to create a custom DB cluster parameter group . For more information, see Creating a DB cluster parameter group in Amazon Aurora.
You can now associate the custom parameter group with your DB instance.
To create a custom DB cluster parameter group
-
Use the
create-db-cluster-parameter-groupCLI command to create the custom parameter group for the cluster. The following example usesaurora-postgresql13as the source for this custom parameter group.For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-cluster-parameter-group --db-cluster-parameter-group-name 'docs-lab-scram-passwords' \ --db-parameter-group-family aurora-postgresql13 --description 'Custom DB cluster parameter group for SCRAM'For Windows:
aws rds create-db-cluster-parameter-group --db-cluster-parameter-group-name "docs-lab-scram-passwords" ^ --db-parameter-group-family aurora-postgresql13 --description "Custom DB cluster parameter group for SCRAM"You can now associate the custom parameter group with your cluster.
-
Use the
modify-db-clusterCLI command to apply this custom parameter group to your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds modify-db-cluster --db-cluster-identifier 'your-instance-name' \ --db-cluster-parameter-group-name "docs-lab-scram-passwordsFor Windows:
aws rds modify-db-cluster --db-cluster-identifier "your-instance-name" ^ --db-cluster-parameter-group-name "docs-lab-scram-passwordsTo resynchronize your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster with your custom DB cluster parameter group, reboot the primary and all other instances of the cluster.
Configuring password encryption to use SCRAM
The password encryption mechanism used by an Aurora PostgreSQL DB
cluster
is set in the DB cluster parameter group
in the
password_encryption parameter. Allowed values are unset, md5, or
scram-sha-256. The default value depends on the Aurora PostgreSQL
version, as follows:
-
Aurora PostgreSQL 14 – Default is
scram-sha-256 -
Aurora PostgreSQL 13 – Default is
md5
With a custom DB cluster parameter group attached to your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, you can modify values for the password encryption parameter.
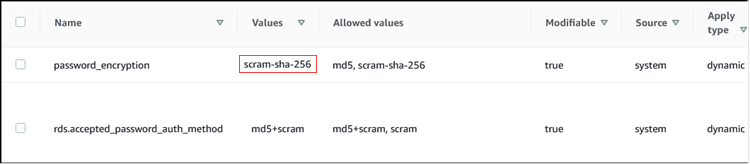
To change password encryption setting to scram-sha-256
-
Change the value of the password encryption to scram-sha-256, as shown following. The change can be applied immediately because the parameter is dynamic, so a restart isn't required for the change to take effect.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds modify-db-cluster-parameter-group --db-cluster-parameter-group-name \ 'docs-lab-scram-passwords' --parameters 'ParameterName=password_encryption,ParameterValue=scram-sha-256,ApplyMethod=immediate'For Windows:
aws rds modify-db-parameter-group --db-parameter-group-name ^ "docs-lab-scram-passwords" --parameters "ParameterName=password_encryption,ParameterValue=scram-sha-256,ApplyMethod=immediate"
Migrating passwords for user roles to SCRAM
You can migrate passwords for user roles to SCRAM as described following.
To migrate database user (role) passwords from MD5 to SCRAM
-
Log in as the administrator user (default user name,
postgres) as shown following.psql --host=cluster-name-instance-1.111122223333.aws-region.rds.amazonaws.com --port=5432 --username=postgres --password -
Check the setting of the
password_encryptionparameter on your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance by using the following command.postgres=>SHOW password_encryption;password_encryption --------------------- md5 (1 row) -
Change the value of this parameter to scram-sha-256. For more information, see Configuring password encryption to use SCRAM.
-
Check the value again to make sure that it's now set to
scram-sha-256, as follows.postgres=>SHOW password_encryption;password_encryption --------------------- scram-sha-256 (1 row) -
Notify all database users to change their passwords. Be sure to also change your own password for account
postgres(the database user withrds_superuserprivileges).labdb=>ALTER ROLE postgres WITH LOGIN PASSWORD 'change_me';ALTER ROLE -
Repeat the process for all databases on your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.
Changing parameter to require SCRAM
This is the final step in the process. After you make the change in the following
procedure, any user accounts (roles) that still use md5 encryption for
passwords can't log in to the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.
The rds.accepted_password_auth_method specifies the encryption method that
the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster accepts for a user password during the login process.
The default value is md5+scram, meaning that either method is accepted. In the
following image, you can find the default setting for this parameter.
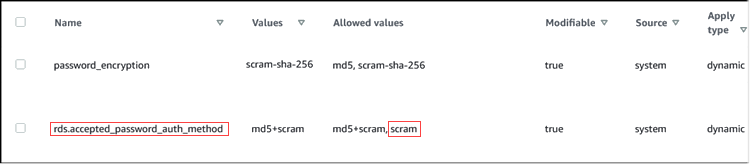
The allowed values for this parameter are md5+scram or scram
alone. Changing this parameter value to scram makes this a requirement.
To change the parameter value to require SCRAM authentication for passwords
-
Verify that all database user passwords for all databases on your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster use
scram-sha-256for password encryption. To do so, queryrds_toolsfor the role (user) and encryption type, as follows.postgres=>SELECT * FROM rds_tools.role_password_encryption_type();rolname | encryption_type ----------------------+----------------- pg_monitor | pg_read_all_settings | pg_read_all_stats | pg_stat_scan_tables | pg_signal_backend | lab_tester | scram-sha-256 user_465 | scram-sha-256 postgres | scram-sha-256 ( rows) -
Repeat the query across all DB instances in your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.
If all passwords use scram-sha-256, you can proceed.
-
Change the value of the accepted password authentication to scram-sha-256, as follows.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds modify-db-cluster-parameter-group --db-cluster-parameter-group-name 'docs-lab-scram-passwords' \ --parameters 'ParameterName=rds.accepted_password_auth_method,ParameterValue=scram,ApplyMethod=immediate'For Windows:
aws rds modify-db-cluster-parameter-group --db-cluster-parameter-group-name "docs-lab-scram-passwords" ^ --parameters "ParameterName=rds.accepted_password_auth_method,ParameterValue=scram,ApplyMethod=immediate"