Amazon RDS Proxy for Aurora
By using Amazon RDS Proxy, you can allow your applications to pool and share database connections to improve their ability to scale. RDS Proxy makes applications more resilient to database failures by automatically connecting to a standby DB instance while preserving application connections. By using RDS Proxy, you can enforce Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) authentication for clients connecting to the proxy, and the proxy can connect to databases using either IAM database authentication or credentials stored in Amazon Secrets Manager.
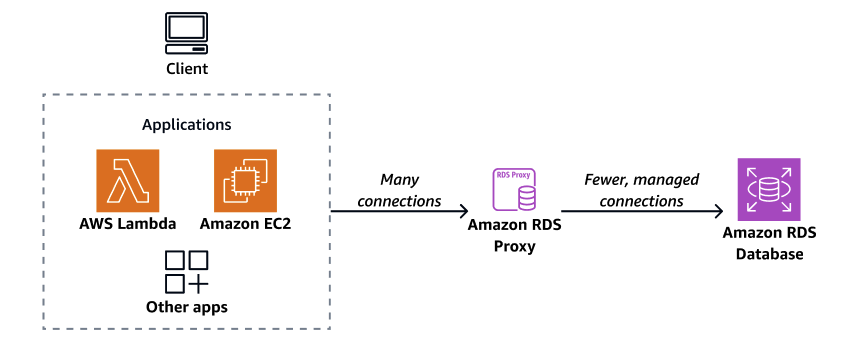
Using RDS Proxy, you can handle unpredictable surges in database traffic. Otherwise, these surges might cause issues due to oversubscribing connections or new connections being created at a fast rate. RDS Proxy establishes a database connection pool and reuses connections in this pool. This approach avoids the memory and CPU overhead of opening a new database connection each time. To protect a database against oversubscription, you can control the number of database connections that are created.
RDS Proxy queues or throttles application connections that can't be served immediately from the connection pool. Although latencies might increase, your application can continue to scale without abruptly failing or overwhelming the database. If connection requests exceed the limits you specify, RDS Proxy rejects application connections (that is, it sheds load). At the same time, it maintains predictable performance for the load that RDS can serve with the available capacity.
You can reduce the overhead to process credentials and establish a secure connection for each new connection. RDS Proxy can handle some of that work on behalf of the database.
RDS Proxy is fully compatible with the engine versions that it supports. You can enable RDS Proxy for most applications with no code changes. For a list of supported engine versions, see Supported Regions and Aurora DB engines for Amazon RDS Proxy.
Topics
Region and version availability
For information about database engine version support and availability of RDS Proxy in a given Amazon Web Services Region, see Supported Regions and Aurora DB engines for Amazon RDS Proxy.
Quotas and limitations for RDS Proxy
The following quotas and limitations apply to RDS Proxy:
-
Each Amazon Web Services account ID is limited to 20 proxies. If your application requires more proxies, request an increase via the Service Quotas page within the Amazon Web Services Management Console. In the Service Quotas page, select Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) and locate Proxies to request a quota increase. Amazon can automatically increase your quota or pending review of your request by Amazon Web Services Support.
-
Each proxy can have up to 200 associated Secrets Manager secrets, thus limiting connections to up to 200 different user accounts when using secrets.
-
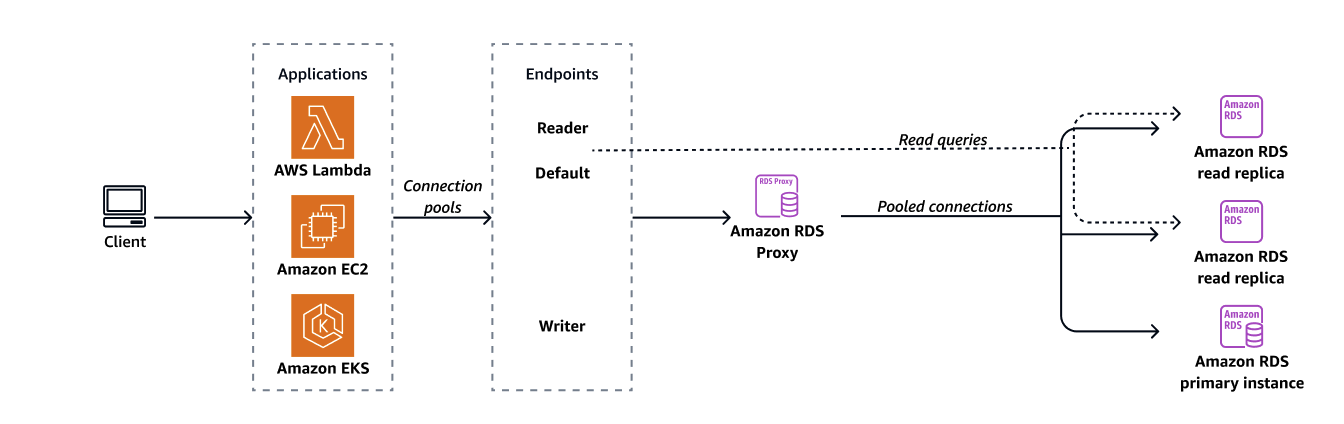
Each proxy has a default endpoint. You can also add up to 20 proxy endpoints for each proxy. You can create, view, modify, and delete these endpoints.
-
In an Aurora cluster, all of the connections using the default proxy endpoint are handled by the Aurora writer instance. To perform load balancing for read-intensive workloads, you can create a read-only endpoint for a proxy. That endpoint passes connections to the reader endpoint of the cluster. That way, your proxy connections can take advantage of Aurora read scalability. For more information, see Overview of proxy endpoints.
-
You can use RDS Proxy with Aurora Serverless v2 clusters, but not with Aurora Serverless v1 clusters.
-
Your RDS Proxy must be in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as the database. The proxy can't be publicly accessible, although the database can be. For example, if you're prototyping your database on a local host, you can't connect to your proxy unless you set up the necessary network requirements to allow connection to the proxy. This is because your local host is outside of the proxy’s VPC.
Note
For Aurora DB clusters, you can turn on cross-VPC access. To do this, create an additional endpoint for a proxy and specify a different VPC, subnets, and security groups with that endpoint. For more information, see Accessing Aurora databases across VPCs.
-
You can't use RDS Proxy with a VPC that has its tenancy set to
dedicated. -
You can't use RDS Proxy in a VPC that has encryption controls with
Enforce Modeenabled. -
For IPv6 endpoint network types, configure your VPC and subnets to support only IPv6. For both IPv4 and IPv6 target connection network types, configure your VPC and subnets to support dual-stack mode.
-
If you use RDS Proxy with an Aurora DB cluster that has IAM authentication enabled, the proxy can connect to the database using either IAM authentication or credentials stored in Secrets Manager. Clients connecting to the proxy must authenticate using IAM credentials. For detailed configuration instructions, see Setting up database credentials for RDS Proxy and Configuring IAM authentication for RDS Proxy
-
You can't use RDS Proxy with custom DNS when using SSL hostname validation.
-
Each proxy can be associated with a single target DB cluster. However, you can associate multiple proxies with the same DB cluster.
Any statement with a text size greater than 16 KB causes the proxy to pin the session to the current connection.
-
Certain Regions have Availability-Zone (AZ) restrictions to consider while creating your proxy. US East (N. Virginia) Region does not support RDS Proxy in the
use1-az3Availability Zone. US West (N. California) Region does not support RDS Proxy in theusw1-az2Availability Zone. When selecting subnets while creating your proxy, make sure that you don't select subnets in the Availability Zones mentioned above. -
Currently, RDS Proxy doesn't support any global condition context keys.
For more information about global condition context keys, see Amazon global condition context keys in the IAM User Guide.
-
You can't use RDS Proxy with RDS Custom for SQL Server.
-
To reflect any database parameter group modification to your proxy, an instance reboot is required even if your chose to apply your changes immediately. For cluster-level parameters, a cluster-wide reboot is required.
-
Your proxy automatically creates the
rdsproxyadminDB user when you register a proxy target. This is a protected user that is essential for proxy functionality. You should avoid tampering with therdsproxyadminuser in any capacity. Deleting or modifying therdsproxyadminuser or its permissions can result in complete unavailability of the proxy to your application.
For additional limitations for each DB engine, see the following sections:
Additional limitations for Aurora MySQL
The following additional limitations apply to RDS Proxy with Aurora MySQL databases:
-
RDS Proxy support for
caching_sha2_passwordauthentication requires a secure (TLS) connection. -
RDS Proxy support for
caching_sha2_passwordis known to have compatibility issues with certain go-sql driver versions. -
When using the MySQL 8.4 C driver, the
mysql_stmt_bind_named_paramAPI might form malformed packets if parameter count exceeds placeholder count in a prepared statements. This results in incorrect responses. For more information, see MySQL bug report. -
Currently, all proxies listen on port 3306 for MySQL. The proxies still connect to your database using the port that you specified in the database settings.
-
You can't use RDS Proxy with self-managed MySQL databases in EC2 instances.
-
You can't use RDS Proxy with an RDS for MySQL DB instance that has the
read_onlyparameter in its DB parameter group set to1. -
RDS Proxy doesn't support MySQL compressed mode. For example, it doesn't support the compression used by the
--compressor-Coptions of themysqlcommand. -
Database connections processing a
GET DIAGNOSTICcommand might return inaccurate information when RDS Proxy reuses the same database connection to run another query. This can happen when RDS Proxy multiplexes database connections. -
Some SQL statements and functions such as
SET LOCALcan change the connection state without causing pinning. For the most current pinning behavior, see Avoiding pinning an RDS Proxy. -
Using the
ROW_COUNT()function in a multi-statement query is not supported. -
RDS Proxy does not support client applications that can't handle multiple response messages in one TLS record.
-
RDS Proxy does not support the MySQL dual passwords.
-
RDS Proxy might not work as expected when you configure the
init_connectparameter in your RDS DB parameter group to set session state variables. Instead, set the initialization query for your proxy to run session initialization statements when using proxy to connect to your database.
Important
For proxies associated with MySQL databases, don't set the configuration parameter
sql_auto_is_null to true or a nonzero value in the initialization
query. Doing so might cause incorrect application behavior.
Additional limitations for Aurora PostgreSQL
The following additional limitations apply to RDS Proxy with Aurora PostgreSQL databases:
RDS Proxy doesn't support session pinning filters for PostgreSQL.
-
Currently, all proxies listen on port 5432 for PostgreSQL.
-
For PostgreSQL, RDS Proxy doesn't currently support canceling a query from a client by issuing a
CancelRequest. This is the case, for example, when you cancel a long-running query in an interactive psql session by using Ctrl+C. -
The results of the PostgreSQL function lastval
aren't always accurate. As a work-around, use the INSERT statement with the RETURNINGclause. RDS Proxy currently doesn't support streaming replication mode.
-
The default
postgresdatabase must exist on the RDS for PostgreSQL instance for RDS Proxy to function. Don't delete this database even if your application uses different databases. -
If you use
ALTER ROLEto change the user role withSET ROLE, subsequent connections as that user to the proxy might not use this role setting, if those connections encounter pinning. To prevent this, when using proxy, useSET ROLEin the initialization query of the proxy. For more information, see Initialization query in Creating a proxy for Amazon Aurora.
Important
For existing proxies with PostgreSQL databases, if you modify the database authentication to use SCRAM only,
the proxy becomes unavailable for up to 60 seconds. To avoid the issue, do one of the following:
Ensure that the database allows both
SCRAMandMD5authentication.To use only
SCRAMauthentication, create a new proxy, migrate your application traffic to the new proxy, then delete the proxy previously associated with the database.