Creating a blue/green deployment in Amazon RDS
When you create a blue/green deployment, you specify the source DB instance to copy in the deployment. The DB instance you choose is the production DB instance, and it becomes the primary DB instance in the blue environment. This DB instance is copied to the green environment, and RDS configures replication from the DB instance in the blue environment to the DB instance in the green environment.
RDS copies the blue environment's topology and features to a staging area. If the blue DB instance has read replicas, they are copied as replicas of the green instance. The allocated storage of all green replicas matches the green primary instance, while other storage parameters are inherited from the blue replicas.
If the blue DB instance is a Multi-AZ DB instance deployment, then the green DB instance is created as a Multi-AZ DB instance deployment.
Topics
Preparing for a blue/green deployment
There are certain steps you must take before you create a blue/green deployment, depending on the engine that your DB instance is running.
Topics
Preparing an RDS for MySQL or RDS for MariaDB DB instance for a blue/green deployment
Before you create a blue/green deployment for an RDS for MySQL or RDS for MariaDB DB instance, you must enable automated backups. For instructions, see Enabling automated backups.
Preparing an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance for a blue/green deployment with physical replication
Before you create an RDS for PostgreSQL blue/green deployment that uses physical replication, make sure to do the following. For a list of versions that use physical replication versus logical replication, see PostgreSQL replication methods for blue/green deployments.
-
Enable automated backups on the DB instance. For instructions, see Enabling automated backups.
-
Confirm that the DB instance isn't the source or target of external replication. For more information, see General limitations for blue/green deployments.
Preparing an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance for a blue/green deployment with logical replication
Before you create an RDS for PostgreSQL blue/green deployment that uses logical replication, make sure to do the following. For a list of versions that use logical replication versus physical replication, see PostgreSQL replication methods for blue/green deployments.
-
Associate the instance with a custom DB parameter group with logical replication (
rds.logical_replication) turned on. Logical replication is required for replication from the blue environment to the green environment. For instructions, see Modifying parameters in a DB parameter group in Amazon RDS.Because blue/green deployments require at least one background worker per database, make sure to tune the following configuration settings according to your workload. For instructions to tune each setting, see Configuration Settings
in the PostgreSQL documentation. -
max_replication_slots -
max_wal_senders -
max_logical_replication_workers -
max_worker_processes
After you enable logical replication and set all configuration options, make sure to reboot the DB instance so that your changes take effect. Blue/green deployments require that the DB instance be in sync with the DB parameter group, otherwise creation fails. For more information, see Rebooting a DB instance.
-
-
Confirm that the DB instance isn't the source or target of external replication. For more information, see General limitations for blue/green deployments.
-
Make sure that all tables in the DB instance have a primary key. PostgreSQL logical replication doesn't allow
UPDATEorDELETEoperations on tables that don't have a primary key. -
RDS for PostgreSQL uses PostgreSQL's native logical replication, storing write-ahead logs (WAL) segments on the blue instance until they're replayed on the green environment. Before you create a blue/green deployment, verify that the blue instance has adequate capacity by checking the following metrics:
-
FreeStorageSpace -
TransactionLogsGeneration -
TransactionLogsDiskUsage -
OldestReplicationSlotLag
To estimate the additional storage required on the blue instance, monitor the
TransactionLogsGenerationCloudWatch metric during peak workload periods. For example, if your workload generates 100 GB of WAL data over 24 hours, ensure you have at least 100 GB of extra storage to accommodate one day's worth of WAL segments. For more information, see Monitoring metrics in an Amazon RDS instance. -
Specifying changes when creating a blue/green deployment
You can make the following changes to the DB instance in the green environment when you create the blue/green deployment.
You can make other modifications to the DB instance in the green environment after it is deployed. For example, you might specify a higher engine version or a different parameter group.
For information about modifying a DB instance, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance.
Topics
Specify a higher engine version
You can specify a higher engine version if you want to test a DB engine upgrade. Upon switchover, the database is upgraded to the major or minor DB engine version that you specify.
Specify a different DB parameter group
You can test how parameter changes affect the DB instances in the green environment or specify a parameter group for a new major DB engine version in the case of an upgrade.
If you specify a different DB parameter group, the specified DB parameter group is associated with all of the DB instances in the green environment. If you don't specify a different parameter group, each DB instance in the green environment is associated with the parameter group of its corresponding blue DB instance.
Modify storage and performance settings
Adjust storage and performance settings in the green environment to optimize resource allocation. These settings include allocated storage, provisioned IOPS, storage type, and storage throughput (for gp3 storage).
You can change the storage type of the green DB instance to gp2, gp3, io1, or io2. For gp3 storage, you can also adjust storage throughput to enhance data transfer performance for high-demand workloads, or to reduce costs for less intensive applications. For more information, see Amazon RDS DB instance storage.
You can also choose to increase or decrease allocated storage in the green environment. However, a storage reduction only occurs if the target allocated storage is at least 20% more than the current storage usage. If you decrease the allocated storage, Amazon RDS initiates a storage configuration upgrade. For more information, see Upgrade the storage configuration.
If the blue DB instance uses magnetic storage, you must change the green DB instance to a General Purpose or Provisioned IOPS storage type in order to increase or decrease the allocated storage.
Enable RDS Optimized Writes
You can use a blue/green deployment to upgrade to a DB instance class that supports RDS Optimized Writes. You can only enable RDS Optimized Writes on a database that was created with a supported DB instance class. Thus, this option creates a green database that uses a supported DB instance class, which enables you to turn on RDS Optimized Writes on the green DB instance.
If you're upgrading from a DB instance class that doesn't support RDS Optimized Writes to one that does, you must also upgrade the storage configuration of the green DB instance. For more information, see Upgrade the storage configuration.
You can only upgrade the DB instance class of the primary green DB instance. By default, read replicas in the green environment inherit the DB instance settings from the blue environment. After the green environment is successfully created, you must manually modify the DB instance class of the read replicas in the green environment.
Some instance class upgrades aren't supported depending on the engine version and instance class of the blue DB instance. For more information about DB instance classes, see DB instance classes.
Upgrade the storage configuration
If your blue database isn't on the latest storage configuration, RDS can migrate the green DB instance from the older storage configuration (32-bit file system) to the preferred configuration. You can use RDS Blue/Green Deployments to overcome the scaling limitations on storage and file size for older 32-bit file systems. In addition, this setting changes the storage configuration to be compatible with RDS Optimized Writes if the specified DB instance class supports Optimized Writes.
Note
Upgrading the storage configuration is an I/O-intensive operation and leads to longer creation times for blue/green deployments. The storage upgrade process is faster if the blue DB instance uses Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 or io2 Block Express) storage, and if you provisoned the green environment with an instance size of 4xlarge or larger. Storage upgrades involving General Purpose SSD (gp2) storage can deplete your I/O credit balance, resulting in longer upgrade times. For more information, see Amazon RDS DB instance storage.
During the storage upgrade, the green DB instance is temporarily unavailable, while the blue DB instance remains available. Replication pauses during this time. Monitor storage on the blue instance, and consider scaling if storage reaches 90%, as the green instance automatically scales by 10% after the upgrade.
This option is only available if your blue database is not on the latest storage configuration, or if you're changing the DB instance class within the same request. You can only upgrade the storage configuration when initially creating a blue/green deployment.
Lazy loading and storage initialization for blue/green deployments
When you create a blue/green deployment, Amazon RDS creates the primary DB instance in the green environment by restoring from a DB snapshot. After it's created, the green DB instance and its read replicas continue to load data in the background through a process known as lazy loading.
Lazy loading only loads data blocks as applications request them. If you attempt to access data that hasn't been loaded yet, Amazon EBS immediately retrieves it from Amazon S3, while remaining data continues to load in the background. For more information, see Amazon EBS snapshots.
To accelerate full volume performance, Amazon RDS provides storage initialization, which reads all blocks in the green environment volume. Amazon EBS proactively downloads blocks from Amazon S3, providing maximum volume performance from the first use. Storage initialization occurs entirely in the background, ensuring no impact on your DB instance availability or ongoing activities, such as patching or upgrades.
Storage initialization is available only for instances in blue/green deployments with
gp2, gp3, io1, and io2 volume types. It
supports all instance classes except the t3 and t4 families. If you modify a green DB instance in a
Single-AZ deployment to a Multi-AZ DB instance deployment, storage initialization includes the
secondary node in the Multi-AZ configuration.
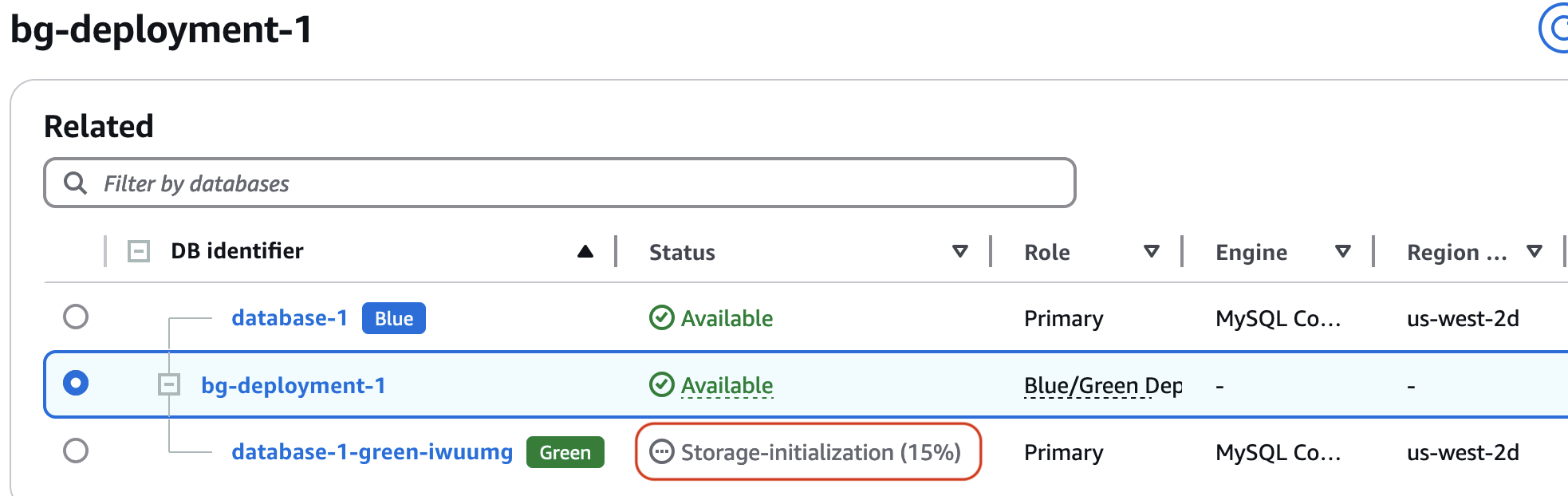
During storage initialization, the instance remains fully available and usable for database operations, though storage might not reach full performance until initialization completes. While the storage initialization is underway, the overall instance status changes to Storage-initialization, and the progress indicator reflects the minimum initialization level across all volumes of the DB instance.
Use the console, Amazon CLI, or Amazon RDS API to monitor storage initialization.
The progress indicator updates as the background initialization job advances, allowing you to track storage readiness before full storage initialization completes. Storage initialization enables optimized performance as your green DB instance becomes fully operational.
Creating a blue/green deployment
You can create a blue/green deployment using the Amazon Web Services Management Console, the Amazon CLI, or the RDS API.
To create a blue/green deployment
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases, and then choose the DB instance that you want to copy to a green environment.
-
Choose Actions, Create blue/green deployment.
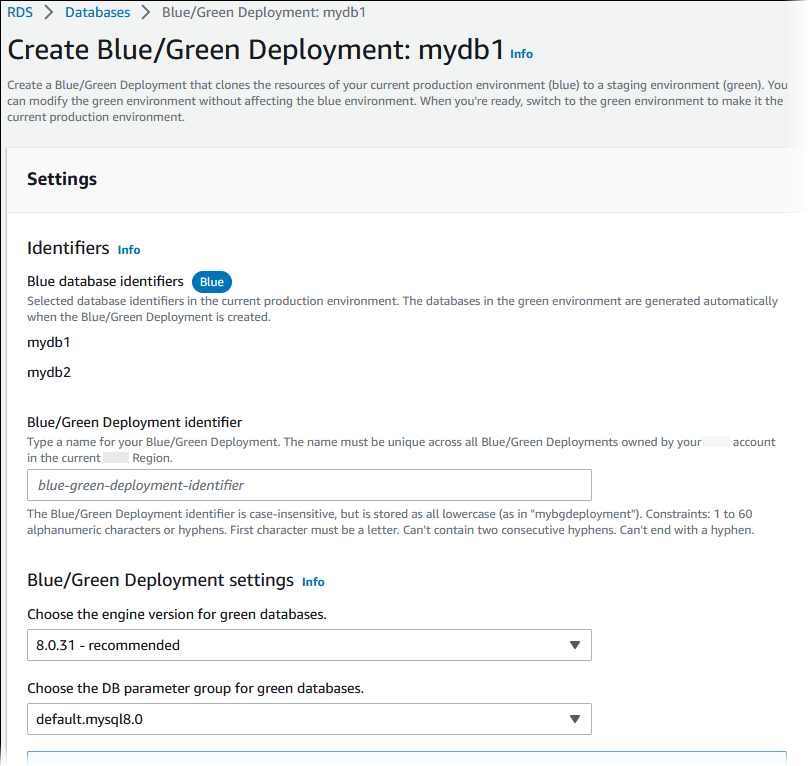
The Create blue/green deployment page appears.
-
Review the blue database identifiers. Make sure that they match the DB instances that you expect in the blue environment. If they don't, choose Cancel.
-
For Blue/green deployment name, enter a name for your blue/green deployment.
-
In the remaining sections, specify the settings for the green environment. For information about each setting, see Settings for creating blue/green deployments.
You can make other modifications to the databases in the green environment after it is deployed.
-
Choose Create.
To create a blue/green deployment using the Amazon CLI, use the create-blue-green-deployment command. For information about all available options, see Settings for creating blue/green deployments.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-blue-green-deployment \ --blue-green-deployment-namemy-blue-green-deployment\ --source arn:aws:rds:us-east-2:123456789012:db:mydb1\ --target-engine-version8.0.31\ --target-db-parameter-group-namemydbparametergroup
For Windows:
aws rds create-blue-green-deployment ^ --blue-green-deployment-namemy-blue-green-deployment^ --source arn:aws:rds:us-east-2:123456789012:db:mydb1^ --target-engine-version8.0.31^ --target-db-parameter-group-namemydbparametergroup
To create a blue/green deployment by using the Amazon RDS API, use the CreateBlueGreenDeployment operation. For information about each
option, see Settings for creating blue/green
deployments.
Settings for creating blue/green deployments
The following table explains the settings that you can choose when you create a blue/green deployment. For more information about the Amazon CLI options, see create-blue-green-deployment. For more information about the RDS API parameters, see CreateBlueGreenDeployment.
| Console setting | Setting description | CLI option and RDS API parameter |
|---|---|---|
|
Allocated storage |
The amount of storage to allocate for your green DB instance (in gibibytes). You can choose to increase or decrease the allocated storage. If your blue DB instance uses magnetic ( For more information, see Amazon RDS DB instance storage. |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
|
Blue/Green Deployment identifier |
A name for the blue/green deployment. |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
| Blue database identifier |
The identifier of the instance that you want to copy to the green environment. When using the CLI or API, specify the instance Amazon Resource Name (ARN). |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
| DB parameter group for green databases | A parameter group to associate with the databases in the green environment. |
CLI option:
API parameter:
|
| Enable Optimized Writes for green database |
Enable RDS Optimized Writes on the green primary DB instance. For more information, see Enable RDS Optimized Writes. If you're changing from a DB instance class that doesn't support Optimized Writes to one that does, you also need to perform a storage configuration upgrade. For more information, see Upgrade the storage configuration. |
For the CLI and API, specifying a target DB instance class that supports RDS Optimized Writes automatically enables it on the green primary DB instance. |
|
Engine version for green databases |
Upgrade the databases in the green environment to the specified DB engine version. If not specified, each database in the green environment is created with the same engine version as the corresponding DB instance in the blue environment. If you choose an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance that uses logical replication, review and acknowledge the logical replication limitations. For more information, see Logical replication-specific limitations for blue/green deployments. |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|
| Green DB instance class |
The compute and memory capacity of each DB instance in the green environment, for
example This option is only visible when you enable RDS Optimized Writes for the green database. |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|
| Provisioned IOPS |
The amount of provisioned input/output operations per second (IOPS) to be initially allocated for the green database. This value applies only to the green primary DB instance, not green replicas. |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|
| Storage configuration upgrade |
Choose whether to upgrade your storage file system configuration. If you enable this setting, RDS migrates the green database from the old storage file system to the preferred configuration. This option is only available if your blue database is not on the latest storage configuration, or if you're enabling RDS Optimized Writes within the same request. You can only upgrade the storage configuration when initially creating a blue/green deployment. For more information, see Upgrading the storage file system for a DB instance. |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|
| Storage throughput |
The storage throughput value for the green database. This setting is visible only if you choose General Purpose SSD (gp3) for the storage type. This value applies only to the green primary DB instance, not green replicas. For more information, see gp3 storage (recommended). |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|
| Storage type |
The storage type for the green database. The following storage types are supported:
This value applies only to the green primary DB instance, not green replicas. For more information, see Amazon RDS storage types. |
CLI option:
RDS API parameter:
|