Replicating TIBCO EMS architecture with Amazon MQ
Amazon MQ provides a variety of broker configurations, various instance sizes for different workloads, and broker options such as single instance, single instance mesh, active/standby instance or active/standby mesh for high availabilty and message durability. To learn more about supported broker options, see Amazon MQ Broker Architecture.
In this section, we replicate the architecture of the TIBCO EMS system shown in the previous section with Amazon MQ while keeping the same configuration.
Note
If you wish to use a single region, you can simply
deploy your Amazon MQ brokers in one region with the active/standby configuration. You
can also optimize the performance of your Amazon MQ brokers by taking advantage of
the Apache ActiveMQ optimization settings
The following diagram illustrates Amazon MQ configured across two regions with a linear connection between two active/standby brokers:
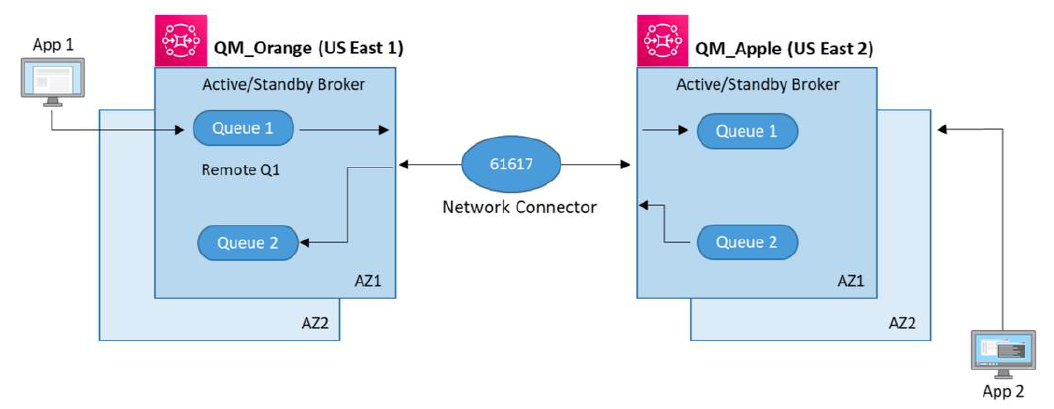
For App 1 to communicate with App 2:
-
Client applications can use a transport connector and put messages onto a Queue or publish to a Topic.
-
Brokers connect to each other over a network connector either in one direction or both directions in cases where request-reply messaging is required.
-
Queues and users can be created and managed in the Amazon Console. To learn more, see Amazon MQ Basic Elements.
Note
-
A Global Topic with the same name has to be created on other EMS Servers for forwarding messages to the Topic on those EMS Servers. In Amazon MQ, a global topic is not required. Once 2 brokers are connected using a network connector, they begin to share all queues/topics, and their data.
-
In Amazon MQ, a routed queue as implemented by a TIBCO EMS server is not required.
-
A network bridge from a topic to a queue can be used in TIBCO EMS architecture to avoid the naming issue with routed queues and to provide multi-hop capability between EMS servers using a Topic. In Amazon MQ, queue names are consistent and all topic/queue messages are shared among a Networks of Brokers.
-
Currently, Amazon MQ only supports JMS 1.1. Applications written for JMS 2.0 can be migrated to Amazon MQ using the Qpid
JMS library, which uses AMQP instead of the default, higher-performing Openwire protocol. For more details, refer to the Amazon MQ workshop .