Overloading Global Secondary Indexes in DynamoDB
Although Amazon DynamoDB has a default quota of 20 global secondary indexes per table, in practice, you can index across far more than 20 data fields. As opposed to a table in a relational database management system (RDBMS), in which the schema is uniform, a table in DynamoDB can hold many different kinds of data items at one time. In addition, the same attribute in different items can contain entirely different kinds of information.
Consider the following example of a DynamoDB table layout that saves a variety of different kinds of data.
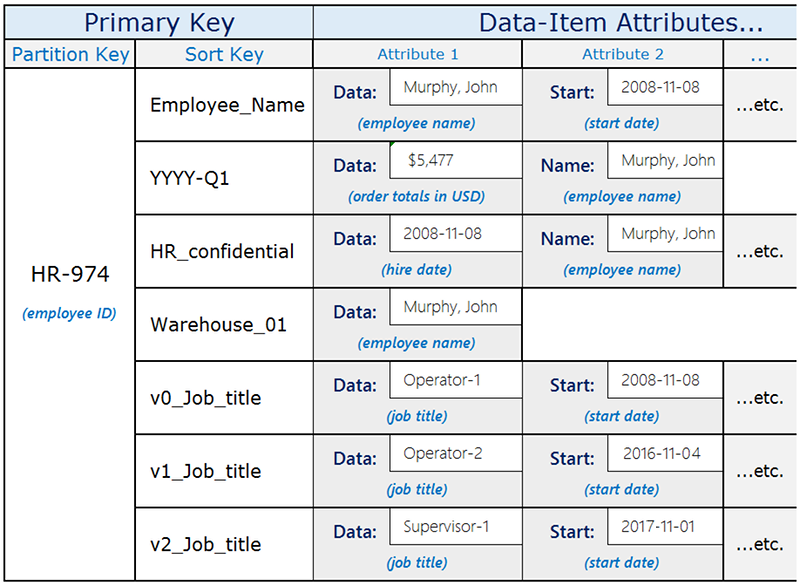
The Data attribute, which is common to all the items, has different content
depending on its parent item. If you create a global secondary index for the table that uses the
table's sort key as its partition key and the Data attribute as its sort key, you
can make a variety of different queries using that single global secondary index. These queries
might include the following:
Look up an employee by name in the global secondary index, using
Employee_Nameas the partition key value and the employee's name (for exampleMurphy, John) as the sort key value.Use the global secondary index to find all employees working in a particular warehouse by searching on a warehouse ID (such as
Warehouse_01).Get a list of recent hires, querying the global secondary index on
HR_confidentialas a partition key value and using a range of dates in the sort key value.