Azure DevOps connections
Connections allow you to authorize and establish configurations that associate your third-party provider with your Amazon resources. To associate your third-party repository as a source for your pipeline, you use a connection.
Note
Instead of creating or using an existing connection in your account, you can use a shared connection between another Amazon Web Services account. See Use a connection shared with another account.
Note
The CodePipeline action for connections is not available in the China (Beijing) and China (Ningxia) Regions. To reference other available actions, see Product and service integrations with CodePipeline.
To add an Azure DevOps source action in CodePipeline, you can choose either to:
-
Use the CodePipeline console Create pipeline wizard or Edit action page to choose the Azure DevOps provider option. See Create a connection to Bitbucket Cloud (console) to add the action. The console helps you create a connections resource.
-
Use the CLI to add the action configuration for the
CreateSourceConnectionaction with theAzure DevOpsprovider as follows:-
To create your connections resources, see Create a connection to Azure DevOps (CLI) to create a connections resource with the CLI.
-
Use the
CreateSourceConnectionexample action configuration in CodeStarSourceConnection for Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub, GitHub Enterprise Server, GitLab.com, and GitLab self-managed actions to add your action as shown in Create a pipeline (CLI).
-
Note
You can also create a connection using the Developer Tools console under Settings. See Create a Connection.
Before you begin:
-
You must have created an account with the provider of the third-party repository, such as Azure DevOps
-
You must have already created a third-party code repository, such as an Azure DevOps repository.
Note
Azure DevOps connections only provide access to repositories owned by the Azure DevOps account that was used to create the connection.
To install the connection, you must have Administer permissions for the Azure account.
Create a connection to Azure DevOps (console)
Use these steps to use the CodePipeline console to add a connections action for your Azure DevOps repository.
Step 1: Create or edit your pipeline
To create or edit your pipeline
-
Sign in to the CodePipeline console.
-
Choose one of the following.
-
Choose to create a pipeline. Follow the steps in Create a Pipeline to complete the first screen and choose Next. On the Source page, under Source Provider, choose Azure DevOps.
-
Choose to edit an existing pipeline. Choose Edit, and then choose Edit stage. Choose to add or edit your source action. On the Edit action page, under Action name, enter the name for your action. In Action provider, choose Azure DevOps.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Under Connection, if you have not already created a connection to your provider, choose Connect to Azure DevOps. Proceed to Step 2: Create a Connection to Azure DevOps.
-
Under Connection, if you have already created a connection to your provider, choose the connection. Proceed to Step 3: Save the Source Action for Your Connection.
-
Step 2: Create a connection to Azure DevOps
To create a connection to Azure DevOps
-
To create a connection to an Azure DevOps repository, under Select a provider, choose Azure DevOps. In Connection name, enter the name for the connection that you want to create. Choose Connect to Azure DevOps, and proceed to Step 2.
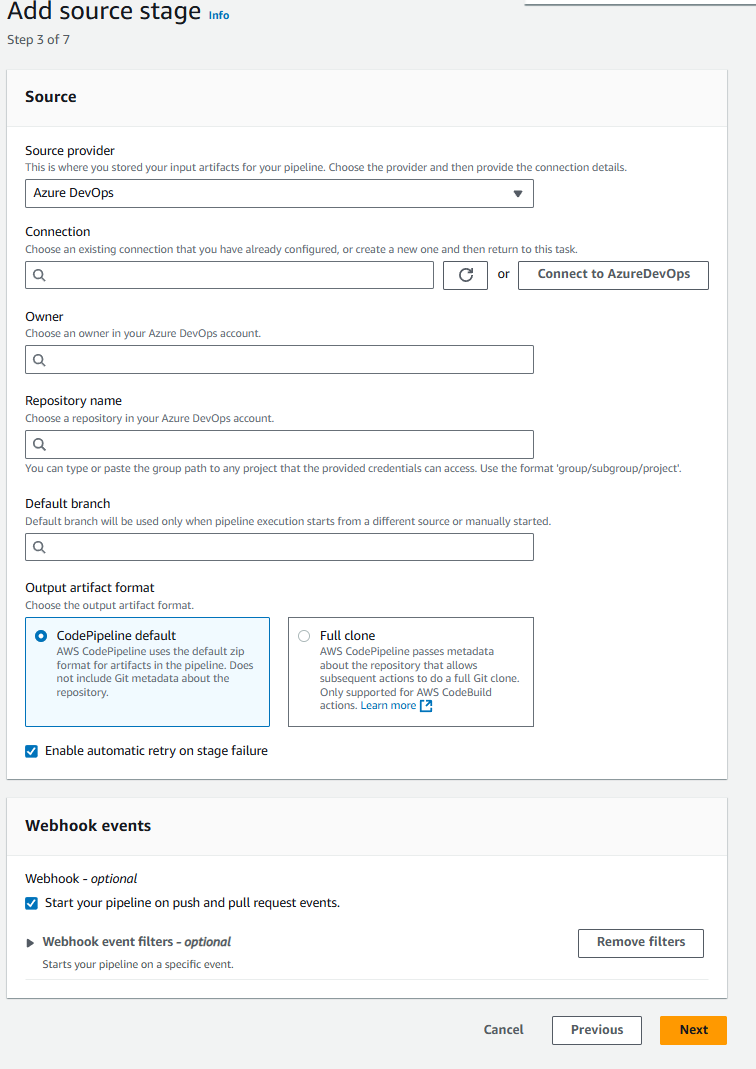
-
On the Connect to Azure DevOps settings page, your connection name displays.
Under Azure DevOps apps, choose an app installation or choose Install a new app to create one.
Note
You only install the app once for each Azure DevOps account. If you have already installed the connector app, choose it and move to the last step in this section.
-
If the login page for Microsoft displays, log in with your credentials and then choose to continue.
-
On the app installation page, a message shows that the connector app is trying to connect to your Azure DevOps account.
Choose Grant access.
-
On the connection page, the connection ID for your new installation is displayed. Choose Connect. The created connection displays in the connections list.
Step 3: Save your Azure DevOps source action
Use these steps on the wizard or Edit action page to save your source action with your connection information.
To complete and save your source action with your connection
-
In Repository name, choose the name of your third-party repository.
-
Under Pipeline triggers you can add triggers if your action is anCodeConnections action. To configure the pipeline trigger configuration and to optionally filter with triggers, see more details in Add trigger with code push or pull request event types.
-
In Output artifact format, you must choose the format for your artifacts.
-
To store output artifacts from the Azure DevOps action using the default method, choose CodePipeline default. The action accesses the files from the repository and stores the artifacts in a ZIP file in the pipeline artifact store.
-
To store a JSON file that contains a URL reference to the repository so that downstream actions can perform Git commands directly, choose Full clone. This option can only be used by CodeBuild downstream actions.
If you choose this option, you will need to update the permissions for your CodeBuild project service role as shown in Add CodeBuild GitClone permissions for connections to Bitbucket, GitHub, GitHub Enterprise Server, or GitLab.com.
-
-
Choose Next on the wizard or Save on the Edit action page.
Create a connection to Azure DevOps (CLI)
You can use the Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI) to create a connection.
To do this, use the create-connection command.
Important
A connection created through the Amazon CLI or Amazon CloudFormation is in PENDING
status by default. After you create a connection with the CLI or Amazon CloudFormation, use the
console to edit the connection to make its status AVAILABLE.
To create a connection
-
Open a terminal (Linux, OS X, or Unix) or command prompt (Windows). Use the Amazon CLI to run the create-connection command, specifying the
--provider-typeand--connection-namefor your connection. In this example, the third-party provider name isAzureDevOpsand the specified connection name isMyConnection.aws codeconnections create-connection --provider-type AzureDevOps --connection-name MyConnectionIf successful, this command returns the connection ARN information similar to the following.
{ "ConnectionArn": "arn:aws:codeconnections:us-west-2:account_id:connection/aEXAMPLE-8aad-4d5d-8878-dfcab0bc441f" } -
Use the console to complete the connection. For more information, see Update a pending connection.
-
The pipeline defaults to detect changes on code push to the connection source repository. To configure the pipeline trigger configuration for manual release or for Git tags, do one of the following:
-
To configure the pipeline trigger configuration to start with a manual release only, add the following line to the configuration:
"DetectChanges": "false", -
To configure the pipeline trigger configuration to filter with triggers, see more details in Add trigger with code push or pull request event types. For example, the following adds Git tags to the pipeline level of the pipeline JSON definition. In this example,
release-v0andrelease-v1are the Git tags to include, andrelease-v2is the Git tag to exclude."triggers": [ { "providerType": "CodeStarSourceConnection", "gitConfiguration": { "sourceActionName": "Source", "push": [ { "tags": { "includes": [ "release-v0", "release-v1" ], "excludes": [ "release-v2" ] } } ] } } ]
-