SAML session initiation in Amazon Cognito user pools
Amazon Cognito supports service provider-initiated (SP-initiated) single sign-on (SSO)
and IdP-initiated SSO. As a best security practice, implement SP-initiated SSO in
your user pool. Section 5.1.2 of the SAML V2.0 Technical Overview
For some enterprise use cases, access to internal applications starts at a bookmark on a dashboard hosted by the enterprise IdP. When a user selects a bookmark, the IdP generates a SAML response and sends it to the SP to authenticate the user with the application.
You can configure a SAML IdP in your user pool to support IdP-initiated SSO. When you support IdP-initiated authentication, Amazon Cognito can't verify that it has solicited the SAML response that it receives because Amazon Cognito doesn't initiate authentication with a SAML request. In SP-initiated SSO, Amazon Cognito sets state parameters that validate a SAML response against the original request. With SP-initiated sign-in you can also guard against cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
Implement SP-initated SAML sign-in
As a best practice, implement service-provider-initiated (SP-initiated) sign-in to your user pool. Amazon Cognito initiates your user's session and redirects them to your IdP. With this method, you have the greatest control over who presents sign-in requests. You can also permit IdP-initiated sign-in under certain conditions.
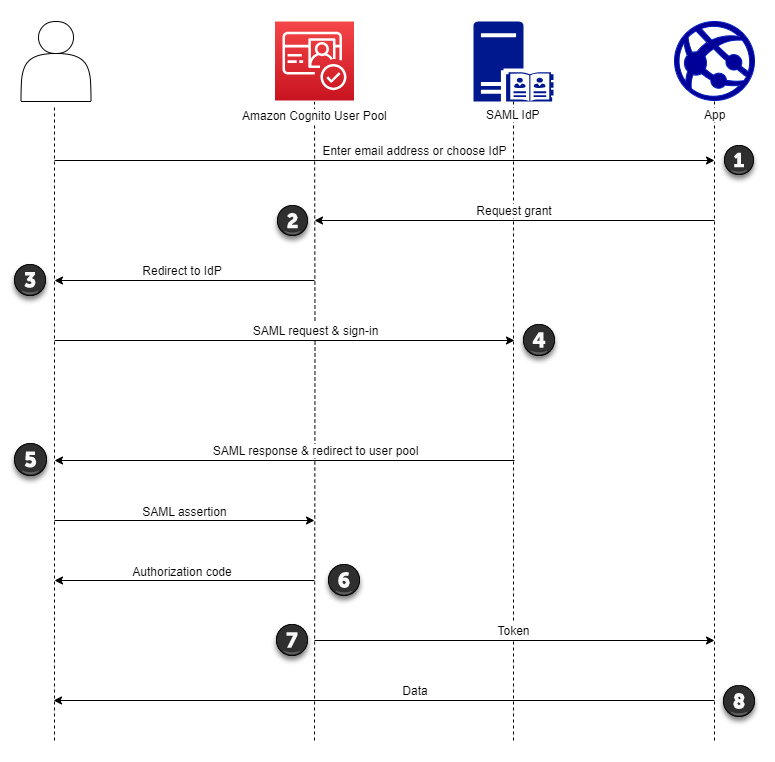
The following process shows how users complete SP-initiated sign in to your user pool through a SAML provider.
-
Your user enters their email address at a sign-in page. To determine your user’s redirect to their IdP, you can collect their email address in a custom-built application or invoke managed login in web view.
You can configure your managed login pages to display a list of IdPs or to prompt for an email address and match it to the identifier of your SAML IdP. To prompt for an email address, edit your managed login branding style and in Foundation, locate Authentication behavior and under Provider display, set Display style to Domain search input.
-
Your app invokes your user pool redirect endpoint and requests a session with the client ID that corresponds to the app and the IdP ID that corresponds to the user.
-
Amazon Cognito redirects your user to the IdP with a SAML request, optionally signed, in an
AuthnRequestelement. -
The IdP authenticates the user interactively, or with a remembered session in a browser cookie.
-
The IdP redirects your user to your user pool SAML response endpoint with the optionally-encrypted SAML assertion in their POST payload.
Note
Amazon Cognito cancels sessions that don't receive a response within 5 minutes, and redirects the user to managed login. When your user experiences this outcome, they receive a
Something went wrongerror message. -
After it verifies the SAML assertion and maps user attributes from the claims in the response, Amazon Cognito internally creates or updates the user's profile in the user pool. Typically, your user pool returns an authorization code to your user's browser session.
-
Your user presents their authorization code to your app, which exchanges the code for JSON web tokens (JWTs).
-
Your app accepts and processes your user's ID token as authentication, generates authorized requests to resources with their access token, and stores their refresh token.
When a user authenticates and receives an authorization code grant, the user
pool returns ID, access, and refresh tokens. The ID token is a authentication
object for OIDC-based identity management. The access token is an authorization
object with OAuth 2.0
You can also choose the duration of refresh tokens. After a user's refresh token expires, they must sign in again. If they authenticated through a SAML IdP, your users' session duration is set by the expiration of their tokens, not the expiration of their session with their IdP. Your app must store each user's refresh token and renew their session when it expires. Managed login maintains user sessions in a browser cookie that's valid for 1 hour.
Implement IdP-initiated SAML sign-in
When you configure your identity provider for IdP-initiated SAML 2.0 sign-in,
you can present SAML assertions to the saml2/idpresponse endpoint
in your user pool domain without the need to initiate the session at the Authorize endpoint. A
user pool with this configuration accepts IdP-initiated SAML assertions from a
user pool external identity provider that the requested app client
supports.
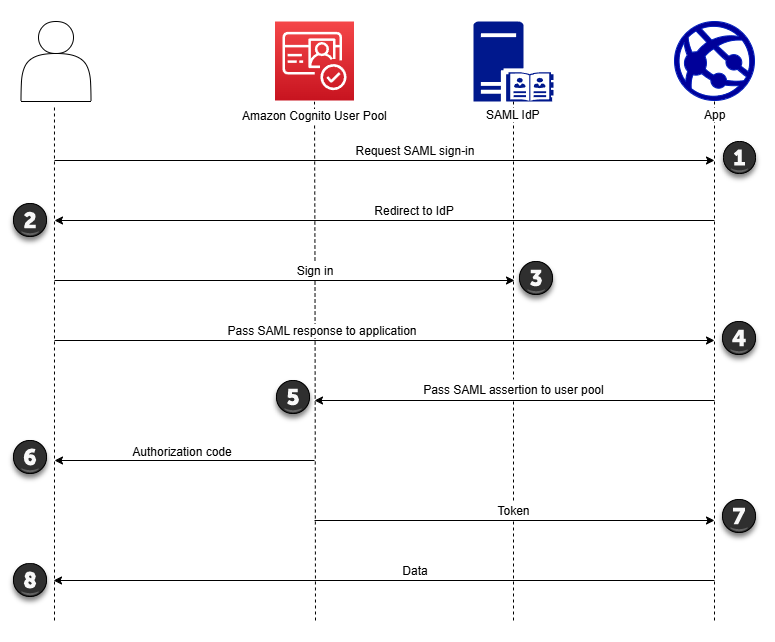
-
A user requests SAML sign-in with your application.
-
Your application invokes a browser or redirects the user to the sign-in page for their SAML provider.
-
The IdP authenticates the user interactively, or with a remembered session in a browser cookie.
-
The IdP redirects your user to your application with the SAML assertion, or response, in their POST body.
-
Your application adds the SAML assertion to the POST body of a request to your user pool
saml2/idpresponseendpoint. -
Amazon Cognito issues an authorization code to your user.
-
Your user presents their authorization code to your app, which exchanges the code for JSON web tokens (JWTs).
-
Your application accepts and processes your user's ID token as authentication, generates authorized requests to resources with their access token, and stores their refresh token.
The following steps describe the overall process to configure and sign in with an IdP-initiated SAML 2.0 provider.
-
Create or designate a user pool and app client.
-
Create a SAML 2.0 IdP in your user pool.
-
Configure your IdP to support IdP initiation. IdP-initiated SAML introduces security considerations that other SSO providers aren’t subject to. Because of this, you can’t add non-SAML IdPs, including the user pool itself, to any app client that uses a SAML provider with IdP-initiated sign-in.
-
Associate your IdP-initiated SAML provider with an app client in your user pool.
-
Direct your user to the sign-in page for your SAML IdP and retrieve a SAML assertion.
-
Direct your user to your user pool
saml2/idpresponseendpoint with their SAML assertion. -
Receive JSON web tokens (JWTs).
To accept unsolicited SAML assertions in your user pool, you must consider its effect on your app security. Request spoofing and CSRF attempts are likely when you accept IdP-initiated requests. Although your user pool can't verify an IdP-initiated sign-in session, Amazon Cognito validates your request parameters and SAML assertions.
Additionally, your SAML assertion must not contain an
InResponseTo claim and must have been issued within the
previous 6 minutes.
You must submit requests with IdP-initiated SAML to your
/saml2/idpresponse. For SP-initiated and managed login
authorization requests, you must provide parameters that identify your requested
app client, scopes, redirect URI, and other details as query string parameters
in HTTP GET requests. For IdP-initiated SAML assertions, however,
the details of your request must be formatted as a RelayState
parameter in the body of an HTTP POST request. The request body
must also contain your SAML assertion as a SAMLResponse
parameter.
The following is an example request and response for an IdP-initiated SAML provider.
POST /saml2/idpresponse HTTP/1.1 User-Agent:USER_AGENTAccept: */* Host:example.auth.us-east-1.amazoncognito.comContent-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded SAMLResponse=[Base64-encoded SAML assertion]&RelayState=identity_provider%3DMySAMLIdP%26client_id%3D1example23456789%26redirect_uri%3Dhttps%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%26response_type%3Dcode%26scope%3Demail%2Bopenid%2BphoneHTTP/1.1 302 Found Date: Wed, 06 Dec 2023 00:15:29 GMT Content-Length: 0 x-amz-cognito-request-id: 8aba6eb5-fb54-4bc6-9368-c3878434f0fb Location:https://www.example.com?code=[Authorization code]