How Amazon DataSync works
Learn the key concepts and terminology related to Amazon DataSync transfers, including how data gets transferred from on-premises and cloud locations.
DataSync transfer architecture
The following diagrams show how and where DataSync commonly transfers storage data. For a full list of DataSync supported storage systems and services, see Where can I transfer my data with Amazon DataSync?
Topics
Transferring between on-premises storage and Amazon
The following diagram shows a high-level overview of DataSync transferring files between self-managed, on-premises storage systems and Amazon Web Services services.
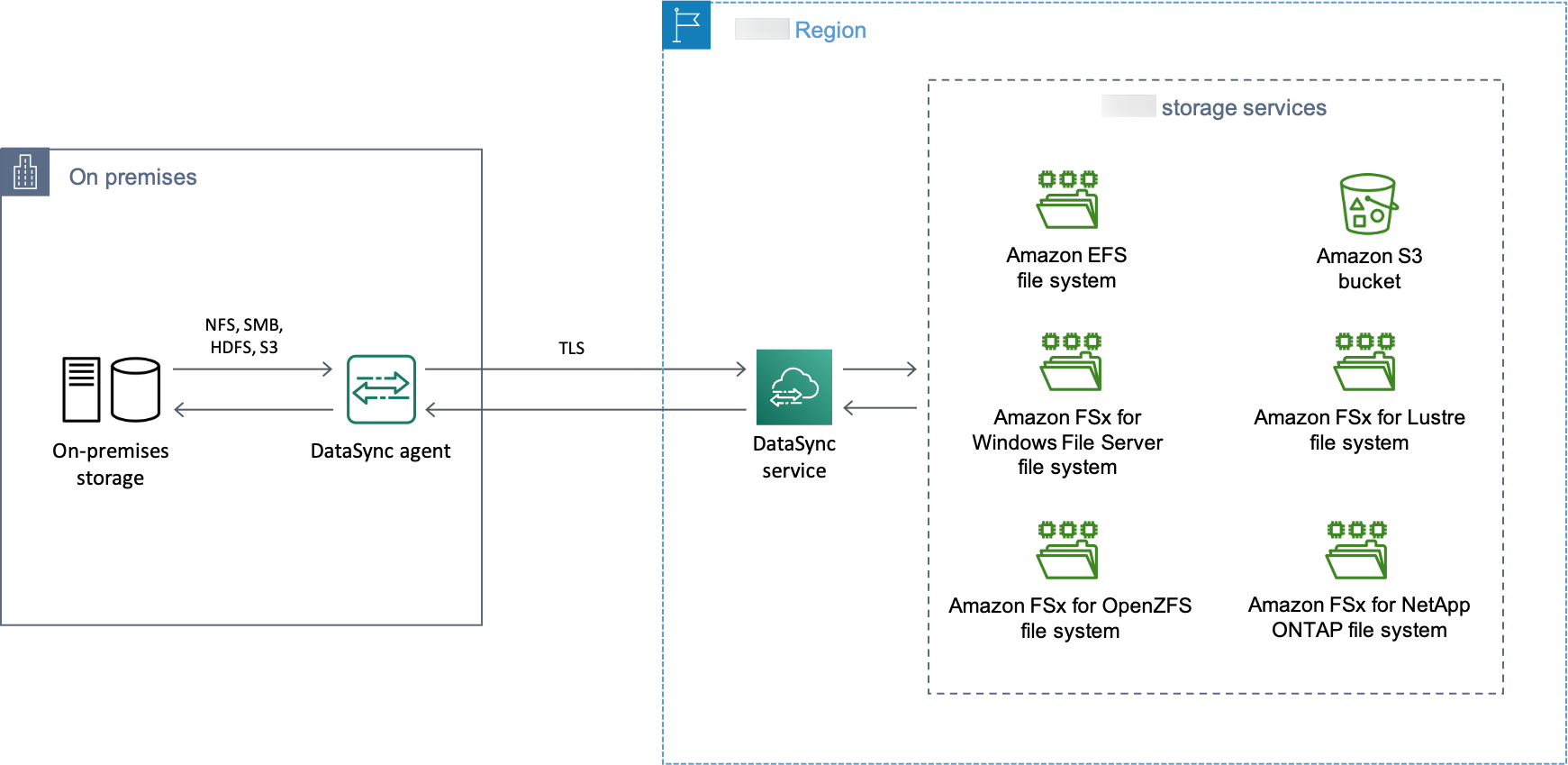
The diagram illustrates a common DataSync use case:
-
A DataSync agent copying data from an on-premises storage system.
-
Data moving into Amazon, encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS).
-
DataSync copying data to a supported Amazon storage service.
Transferring between Amazon storage services
The following diagram shows a high-level overview of DataSync transferring files between Amazon Web Services services in the same Amazon Web Services account.
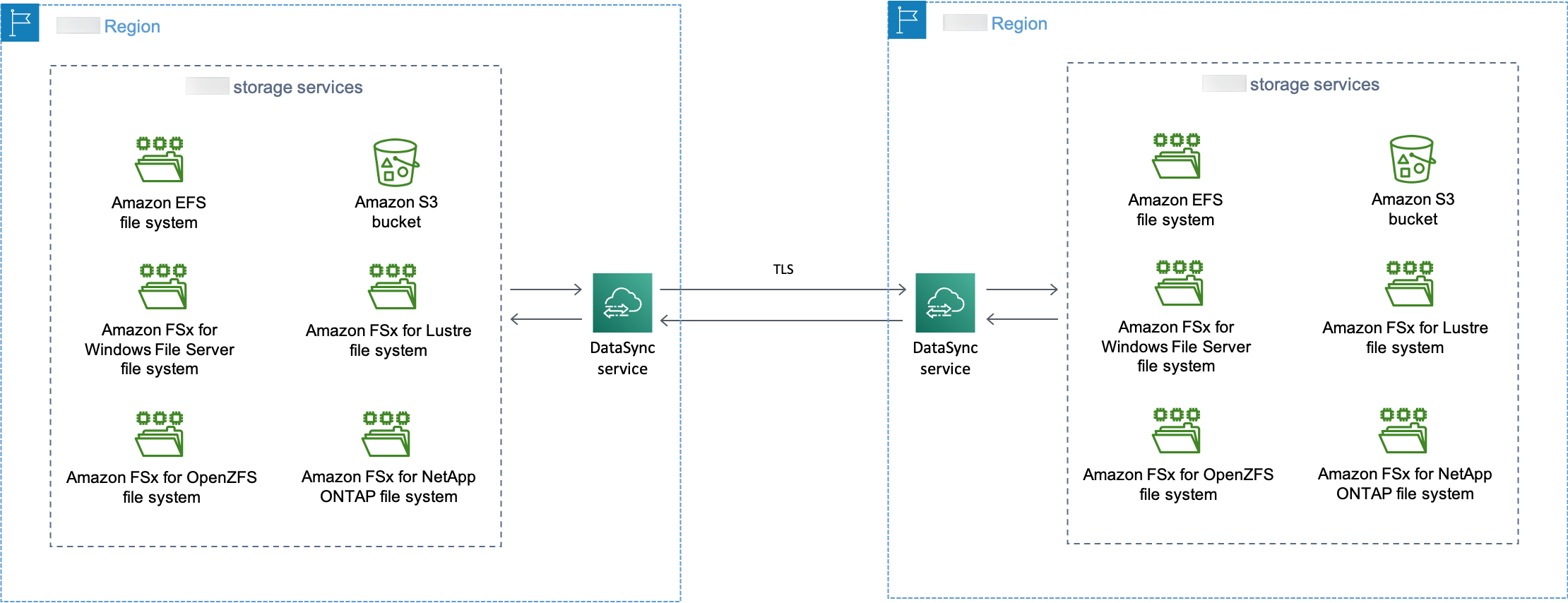
The diagram illustrates a common DataSync use case:
-
DataSync copying data from a supported Amazon storage service.
-
Data moving across Amazon Web Services Regions, encrypted using TLS.
-
DataSync copying data to a supported Amazon storage service.
When transferring between Amazon storage services in the same account (whether in the same Amazon Web Services Region or across Amazon Web Services Regions in the same partition), no agent is required. Your data remains in the Amazon network and doesn't traverse the public internet.
Important
You pay for data transferred between Amazon Web Services Regions. This is billed as data
transfer OUT from your source Region to your destination Region. For more
information, see Data transfer
pricing
Transferring between Amazon storage services and storage systems in other clouds
With DataSync, you can transfer data between other cloud storage systems and Amazon Web Services services. In this context, cloud storage systems can include:
-
Self-managed storage systems, such as an NFS file server in your virtual private cloud (VPC) within Amazon.
DataSync can copy data to and from other clouds with or without using an agent. For more information about when to use an agent, see Do I need an Amazon DataSync agent?.
Concepts and terminology
Familiarize yourself with DataSync transfer features.
Agent
An agent is a virtual machine (VM) appliance that DataSync uses to read from and write to storage during a transfer. DataSync provides two types of agents, with one handling Basic mode tasks and another handling Enhanced mode tasks. For more information about choosing an agent for your use case, see Choosing an agent for your task mode.
You can deploy an agent in your storage environment on VMware ESXi, Linux Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), Nutanix AHV (using the KVM agent image), or Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisors. For storage in a virtual private cloud (VPC) in Amazon, you can deploy an agent as an Amazon EC2 instance.
To get started, see Do I need an Amazon DataSync agent?
Location
A location describes where you're copying data from or to. Each DataSync transfer (also known as a task) has a source and destination location. For more information, see Where can I transfer my data with Amazon DataSync?
Task
A task describes a DataSync transfer. It identifies a source and destination location along with details about how to copy data between those locations. You also can specify how a task handles metadata, deleted files, and permissions.
Task execution
A task execution is an individual run of a DataSync transfer task. There are several phases involved in a task execution. For more information, see Task execution statuses.
How DataSync transfers files, objects, and directories
During a task execution, DataSync prepares, transfers, and verifies your data. How DataSync performs these actions depends on how you configure your DataSync task options, such as the task mode. Basic mode tasks prepare, transfer, and verify your data sequentially, while Enhanced mode tasks do these in parallel.
Topics
How DataSync prepares your data transfer
DataSync by default prepares your transfer by examining your source and destination locations to determine what to transfer. This is done by scanning the contents and metadata of both locations to identify differences between the two.
Note
If you configure your task to transfer all data, there's no preparation. When you start your task, DataSync immediately transfers everything from your source to your destination without comparing locations.
How DataSync prepares your transfer also depends on your task mode:
| Enhanced mode preparation | Basic mode preparation |
|---|---|
|
DataSync prepares objects as they're found at the source location. Preparation continues throughout the task execution until there are no more objects listed at the source. Unlike Basic mode, DataSync can prepare virtually unlimited numbers of objects with each task execution. |
Preparation can take just minutes, a few hours, or even longer depending on the number of files, objects, or directories in both locations and the performance of your storage. The items that DataSync inventories in your source and destination count towards your task quotas. These quotas aren't based on the number of items that DataSync transfers during each task execution. |
DataSync might skip some files, objects, and directories during preparation. The reasons for this can depend on several factors, such as how you configure your task and storage system permissions. Here are some examples:
-
There's a file that exists in your source and destination locations. The file in the source hasn't been modified since the previous task execution. Since you're only transferring data that has changed, DataSync doesn't transfer that file next time you run your task.
-
An object that exists in both of your locations changes in your source. When you run your task, DataSync skips this object in your destination because your task doesn't overwrite data in the destination.
-
DataSync skips an object in your source location that's using an archival storage class and isn't restored. You must restore an archived object for DataSync to read it.
-
DataSync skips a file, object, or directory in your source location because it can't read it. If this happens and isn't expected, check your storage's access permissions and make sure that DataSync can read what was skipped.
How DataSync transfers your data
DataSync copies your data (including metadata) from the source to the destination based on your task options. For example, you can specify what metadata gets copied, exclude certain files, and limit how much bandwidth DataSync uses, among other options.
How DataSync transfers your data also depends on your task mode:
| Enhanced mode transferring | Basic mode transferring |
|---|---|
|
DataSync transfers each object as soon as it's prepared. |
Once DataSync prepares all of your data, the transfer begins. |
DataSync might skip some items during the transfer. If you configure your task to transfer all data, this can happen with an object in your source location that's using an archival storage class and isn't restored.
How DataSync verifies your data's integrity
DataSync always performs integrity checks on your data during a transfer. At the end of a transfer, DataSync can also perform additional checks on just the transferred data or the entire dataset in both locations. For more information, see Configuring how Amazon DataSync verifies data integrity.
When checking data integrity, DataSync calculates and compares the checksum and
metadata of the files, objects, or directories in your locations. If DataSync notices
differences between locations, verification fails with an error. For example, you
might see errors such as Checksum failure, Metadata
failure, Files were added, or Files were
removed.
How verification works depends on your task mode and whether you configure DataSync to verify data integrity at the end of your transfer.
| Enhanced mode verification | Basic mode verification |
|---|---|
|
DataSync verifies each object as it's transferred to your destination. With Enhanced mode, DataSync verifies only transferred data. |
At the end of your transfer, DataSync verifies the integrity of your data. Depending on how you configure data verification, this can take a significant amount of time for large datasets. |
How DataSync works with open and locked files
Keep in mind the following when trying to transfer files that are open (in use) or locked:
-
In general, DataSync can transfer open files without any limitations.
-
If a file is open and being written to during a transfer, DataSync can detect this kind of inconsistency during the transfer task's verification phase. To get the latest version of the file, you must run the task again.
-
If a file is locked and the server prevents DataSync from opening it, DataSync skips the file during the transfer and logs an error.
-
DataSync can't lock or unlock files.
Recurring transfer options
In addition to one-time transfers, DataSync can transfer data on a recurring basis. Some of the options for these situations include:
-
Scheduling when your task executes.
-
Transferring only the data that's changed since the previous task execution.
-
Deleting data in the destination location that's no longer present in the source.