Monitoring features
This topic provides reference information about monitoring and performance management for Microsoft SQL Server and Amazon Aurora MySQL databases. You can learn about the different monitoring capabilities and tools available for each database system, including SQL Server’s dynamic management views and integration with Amazon CloudWatch and Performance Insights.
| Feature compatibility | Amazon SCT / Amazon DMS automation level | Amazon SCT action code index | Key differences |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
N/A |
Use Amazon CloudWatch service. For more information, see Monitoring metrics in an Amazon RDS instance in the Amazon Relational Database Service User Guide. |
SQL Server Usage
Monitoring server performance and behavior is a critical aspect of maintaining service quality and includes ad-hoc data collection, ongoing data collection, root cause analysis, preventative actions, and reactive actions. SQL Server provides an array of interfaces to monitor and collect server data.
SQL Server 2017 introduces several new dynamic management views:
-
sys.dm_db_log_statsexposes summary level attributes and information on transaction log files, helpful for monitoring transaction log health. -
sys.dm_tran_version_store_space_usagetracks version store usage for each database, useful for proactively planningtempdbsizing based on the version store usage for each database. -
sys.dm_db_log_infoexposes VLF information to monitor, alert, and avert potential transaction log issues. -
sys.dm_db_stats_histogramis a new dynamic management view for examining statistics. -
sys.dm_os_host_infoprovides operating system information for both Windows and Linux.
SQL Server 2019 adds new configuration parameter, LIGHTWEIGHT_QUERY_PROFILING. It turns on or turns off the lightweight query profiling infrastructure. The lightweight query profiling infrastructure (LWP) provides query performance data more efficiently than standard profiling mechanisms and is enabled by default. For more information, see Query Profiling Infrastructure
Windows Operating System Level Tools
You can use the Windows Scheduler to trigger run of script files such as CMD, PowerShell, and so on to collect, store, and process performance data.
System Monitor is a graphical tool for measuring and recording performance of SQL Server and other Windows-related metrics using the Windows Management Interface (WMI) performance objects.
Note
Performance objects can also be accessed directly from T-SQL using the SQL Server Operating System Related DMVs. For a full list of the DMVs, see SQL Server Operating System Related Dynamic Management Views (Transact-SQL)
Performance counters exist for real-time measurements such as CPU Utilization and for aggregated history such as average active transactions. For a full list of the object hierarchy, see: Use SQL Server Objects
SQL Server Extended Events
SQL Server latest tracing framework provides very lightweight and robust event collection and storage. SQL Server Management Studio features the New Session Wizard and New Session graphic user interfaces for managing and analyzing captured data. SQL Server Extended Events consists of the following items:
-
SQL Server Extended Events Package is a logical container for Extended Events objects.
-
SQL Server Extended Events Targets are consumers of events. Targets include Event File, which writes data to the file Ring Buffer for retention in memory, or for processing aggregates such as Event Counters and Histograms.
-
SQL Server Extended Events Engine is a collection of services and tools that comprise the framework.
-
SQL Server Extended Events Sessions are logical containers mapped many-to-many with packages, events, and filters.
The following example creates a session that logs lock escalations and lock timeouts to a file.
CREATE EVENT SESSION Locking_Demo ON SERVER ADD EVENT sqlserver.lock_escalation, ADD EVENT sqlserver.lock_timeout ADD TARGET package0.etw_classic_sync_target (SET default_etw_session_logfile_path = N'C:\ExtendedEvents\Locking\Demo_20180502.etl') WITH (MAX_MEMORY=8MB, MAX_EVENT_SIZE=8MB); GO
SQL Server Tracing Framework and the SQL Server Profiler Tool
The SQL Server trace framework is the predecessor to the Extended Events framework and remains popular among database administrators. The lighter and more flexible Extended Events Framework is recommended for development of new monitoring functionality. For more information, see SQL Server Profiler
SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) provides several monitoring extensions:
-
SQL Server Activity Monitor is an in-process, real-time, basic high-level information graphical tool.
-
Query Graphical Show Plan provides easy exploration of estimated and actual query run plans.
-
Query Live Statistics displays query run progress in real time.
-
Replication Monitor presents a publisher-focused view or distributor-focused view of all replication activity. For more information, see Overview of the Replication Monitor Interface
in the SQL Server documentation. -
Log Shipping Monitor displays the status of any log shipping activity whose status is available from the server instance to which you are connected. For more information, see View the Log Shipping Report (SQL Server Management Studio)
in the SQL Server documentation. -
Standard Performance Reports is set of reports that show the most important performance metrics such as change history, memory usage, activity, transactions, HA, and more.
T-SQL
From the T-SQL interface, SQL Server provides many system stored procedures, system views, and functions for monitoring data.
System stored procedures such as sp_who and sp_lock provide real-time information. The sp_monitor procedure provides aggregated data.
Built in functions such as @@CONNECTIONS, @@IO_BUSY, @@TOTAL_ERRORS, and others provide high level server information.
A rich set of System Dynamic Management functions and views are provided for monitoring almost every aspect of the server. These functions reside in the sys schema and are prefixed with dm_string. For more information, see System Dynamic Management Views
Trace Flags
You can set trace flags to log events. For example, set trace flag 1204 to log deadlock information. For more information, see DBCC TRACEON - Trace Flags (Transact-SQL)
SQL Server Query Store
Query Store is a database-level framework supporting automatic collection of queries, run plans, and run time statistics. This data is stored in system tables. You can use this data to diagnose performance issues, understand patterns, and understand trends. It can also be set to automatically revert plans when a performance regression is detected.
For more information, see Monitoring performance by using the Query Store
MySQL Usage
The native features for monitoring MySQL databases such as innodb logging and the performance schema are turned off for Aurora MySQL. Most third-party tools that rely on these features can’t be used. Some vendors provide monitoring services specifically for Aurora MySQL.
However, Amazon RDS provides a very rich monitoring infrastructure for Aurora MySQL clusters and instances with the native Amazon CloudWatch service.
These services are improved frequently.
Amazon RDS Performance Insights, an advanced database performance monitoring feature that makes it easy to diagnose and solve performance challenges on Amazon RDS databases, now supports additional counter metrics on Amazon RDS for MySQL and Amazon Aurora MySQL-Compatible Edition (Aurora MySQL). With counter metrics, you can customize the Performance Insights dashboard to include up to 10 additional graphs that show a selection from dozens of operating system and database performance metrics. Counter metrics provide additional information that can be correlated with the database load chart to help identify performance issues and analyze performance. For more information, see Performance Insights
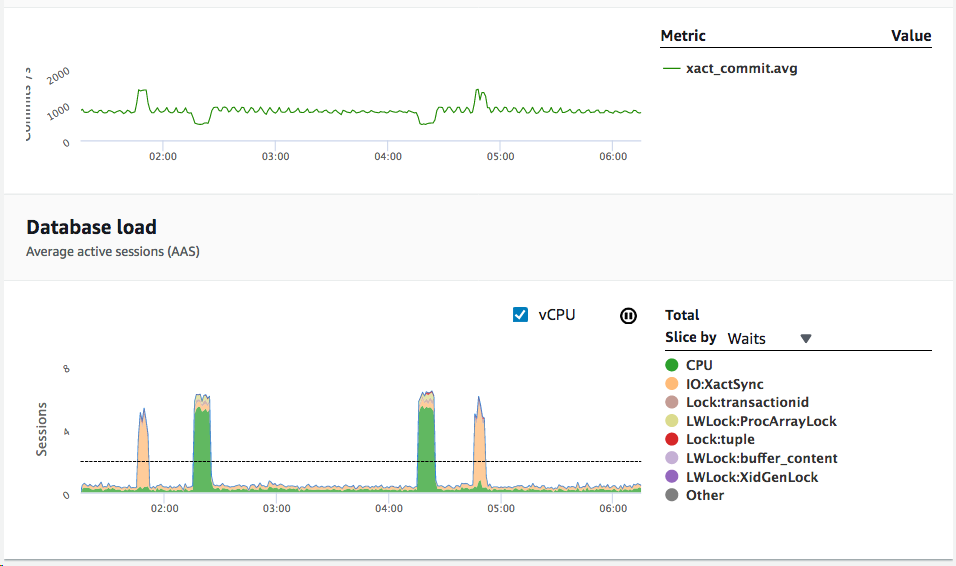
To turn on Performance Insight for your instance, use the step-by-step walkthrough. For more information, see Turning Performance Insights on and off in the Amazon Relational Database Service User Guide.
When the Performance Schema is turned on for Aurora MySQL, Performance Insights provides more detailed information. For example, Performance Insights displays DB load categorized by detailed wait events. When Performance Schema is turned off, Performance Insights displays DB load categorized by the list state of the MySQL process.
The Performance Schema stores many useful metrics that will help you analyze and solve performance related issues.
You have the following options for enabling the Performance Schema:
-
Allow Performance Insights to manage required parameters automatically. When you create an Aurora MySQL DB instance with Performance Insights enabled, Performance Schema is turned on automatically. In this case, Performance Insights automatically manages your parameters.
Note
In this scenario, Performance Insights changes schema-related parameters on the DB instance. These changes aren’t visible in the parameter group associated with the DB instance. However, these changes are visible in the output of the
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLEScommand. -
Set the required parameters yourself. For Performance Insights to list wait events, you must set all parameters as shown in the following table.
| Parameter name | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
1 (the Source column has the value engine-default) |
|
|
ON |
|
|
|
|
|
ON |
|
|
ON |
For more information, see Server Options and Performance Schema Quick Start
