Working with Amazon DMS Serverless
Amazon DMS Serverless is a feature that provides automatic provisioning, scaling, built-in high availability, and a pay-for-use billing model, to increase operations agility and optimize your costs. The Serverless feature eliminates replication instance management tasks like capacity estimation, provisioning, cost optimization, and managing replication engine versions and patching.
With Amazon DMS Serverless, similar to the current functionality of Amazon DMS (referred to in this document as Amazon DMS Standard), you create source and target connections using endpoints. After you create your source and target endpoints, you create a replication configuration, which includes configuration settings for the given replication. You can manage the replications by starting, stopping, modifying, or deleting them. Each replication has settings that you can configure according to the requirements of your database migration. You specify these settings using either a JSON file or the Amazon DMS section of the Amazon Web Services Management Console. For more information about replication settings, see Working with Amazon DMS endpoints. After starting the replication, Amazon DMS serverless connects to the source database and collects the database metadata to analyze the replication workload. Using this metadata, Amazon DMS computes and provisions the required capacity and starts the data replication.
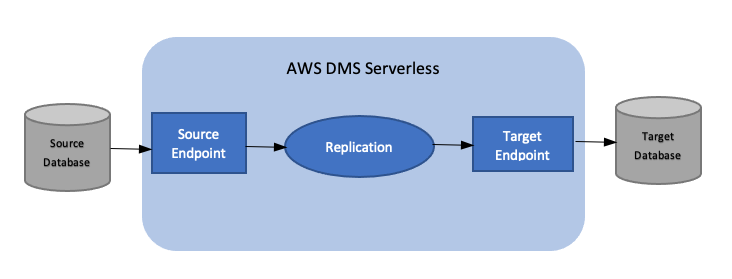
The following diagram shows the Amazon DMS Serverless replication process.
Note
The current engine version for Amazon DMS Serverless is 3.5.4
View the following topics to discover more details about Amazon DMS Serverless.