Using Elastic Beanstalk with other Amazon services
The topics in this section describe the many ways you can use additional Amazon services with your Elastic Beanstalk application. To implement your application's environments, Elastic Beanstalk manages resources of other Amazon services or uses their functionality. In addition, Elastic Beanstalk integrates with Amazon services that it doesn't use directly as part of your environments.
Topics
Architectural overview
The following diagram illustrates an example architecture of Elastic Beanstalk across multiple Availability Zones working with other Amazon products such as Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS).
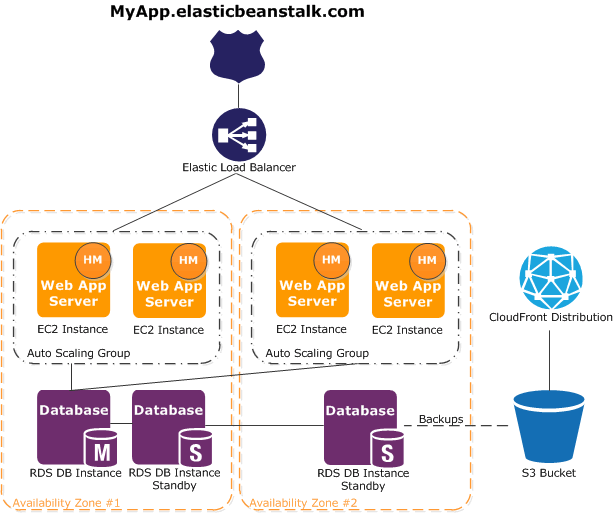
To plan for fault-tolerance, it is advisable to have N+1 Amazon EC2 instances and spread your instances across multiple Availability Zones. In the unlikely
case that one Availability Zone goes down, you will still have your other Amazon EC2 instances running in another Availability Zone. You can adjust Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to
allow for a minimum number of instances as well as multiple Availability Zones. For instructions on how to do this, see Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling your Elastic Beanstalk environment instances. For more information about building fault-tolerant applications, go
to Building Fault-Tolerant Applications on Amazon
The following sections discuss in more detail integration with Amazon CloudFront, Amazon CloudWatch, Amazon DynamoDB Amazon ElastiCache, Amazon RDS, Amazon Route 53, Amazon Simple Storage Service, Amazon VPC , and IAM.