Overview of blueprints in Amazon Glue
Note
The blueprints feature is currently unavailable in the following Regions in the Amazon Glue console: Asia Pacific (Jakarta) and Middle East (UAE).
Amazon Glue blueprints provide a way to create and share Amazon Glue workflows. When there is a complex ETL process that could be used for similar use cases, rather than creating an Amazon Glue workflow for each use case, you can create a single blueprint.
The blueprint specifies the jobs and crawlers to include in a workflow, and specifies parameters that the workflow user supplies when they run the blueprint to create a workflow. The use of parameters enables a single blueprint to generate workflows for the various similar use cases. For more information about workflows, see Overview of workflows in Amazon Glue.
The following are example use cases for blueprints:
-
You want to partition an existing dataset. The input parameters to the blueprint are Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) source and target paths and a list of partition columns.
-
You want to snapshot an Amazon DynamoDB table into a SQL data store like Amazon Redshift. The input parameters to the blueprint are the DynamoDB table name and an Amazon Glue connection, which designates an Amazon Redshift cluster and destination database.
-
You want to convert CSV data in multiple Amazon S3 paths to Parquet. You want the Amazon Glue workflow to include a separate crawler and job for each path. The input parameters are the destination database in the Amazon Glue Data Catalog and a comma-delimited list of Amazon S3 paths. Note that in this case, the number of crawlers and jobs that the workflow creates is variable.
Blueprint components
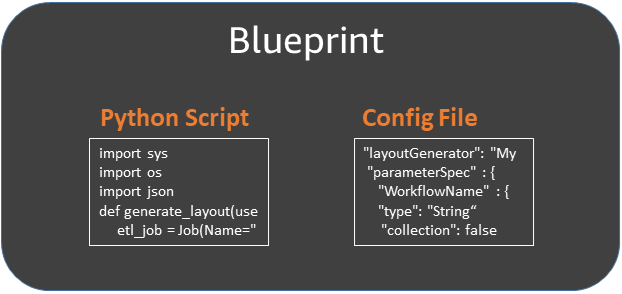
A blueprint is a ZIP archive that contains the following components:
-
A Python layout generator script
Contains a function that specifies the workflow layout—the crawlers and jobs to create for the workflow, the job and crawler properties, and the dependencies between the jobs and crawlers. The function accepts blueprint parameters and returns a workflow structure (JSON object) that Amazon Glue uses to generate the workflow. Because you use a Python script to generate the workflow, you can add your own logic that is suitable for your use cases.
-
A configuration file
Specifies the fully qualified name of the Python function that generates the workflow layout. Also specifies the names, data types, and other properties of all blueprint parameters used by the script.
-
(Optional) ETL scripts and supporting files
As an advanced use case, you can parameterize the location of the ETL scripts that your jobs use. You can include job script files in the ZIP archive and specify a blueprint parameter for an Amazon S3 location where the scripts are to be copied to. The layout generator script can copy the ETL scripts to the designated location and specify that location as the job script location property. You can also include any libraries or other supporting files, provided that your script handles them.
Blueprint runs
When you create a workflow from a blueprint, Amazon Glue runs the blueprint, which starts an asynchronous process to create the workflow and the jobs, crawlers, and triggers that the workflow encapsulates. Amazon Glue uses the blueprint run to orchestrate the creation of the workflow and its components. You view the status of the creation process by viewing the blueprint run status. The blueprint run also stores the values that you supplied for the blueprint parameters.
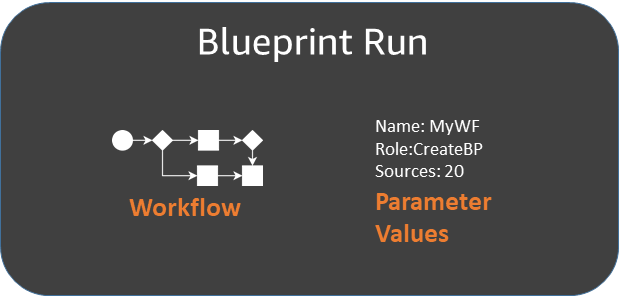
You can view blueprint runs using the Amazon Glue console or Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI). When viewing or troubleshooting a workflow, you can always return to the blueprint run to view the blueprint parameter values that were used to create the workflow.
Lifecycle of a blueprint
blueprints are developed, tested, registered with Amazon Glue, and run to create workflows. There are typically three personas involved in the blueprint lifecycle.
| Persona | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Amazon Glue developer |
|
| Amazon Glue administrator |
|
| Data analyst |
|