Services or capabilities described in Amazon Web Services documentation might vary by Region. To see the differences applicable to the China Regions,
see Getting Started with Amazon Web Services in China
(PDF).
Granting data lake permissions using the
LF-TBAC method
You can grant the DESCRIBE and ASSOCIATE Lake Formation permissions on
LF-Tags to principals so that they can view the LF-Tags and assign them to Data Catalog resources
(databases, tables, views, and columns). When LF-Tags are assigned to Data Catalog resources, you can use
the Lake Formation tag-based access control (LF-TBAC) method to secure those resources. For more information, see
Lake Formation tag-based access control.
At first, only the data lake administrator can grant these permissions. If the data lake
administrator grants these permissions with the grant option, other principals can grant them.
The DESCRIBE and ASSOCIATE permissions are explained in Lake Formation tag-based access control best
practices and considerations.
You can grant the DESCRIBE and ASSOCIATE permissions on a LF-Tag
to an external Amazon account. A data lake administrator in that account can then grant those
permissions to other principals in the account. Principals to whom the data lake administrator
in the external account grants the ASSOCIATE permission can then assign LF-Tags
to Data Catalog resources that you shared with their account.
When granting to an external account, you must include the grant option.
You can grant permissions on LF-Tags by using the Amazon Lake Formation console, the API, or the
Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI).
The following steps are not needed for S3 Tables catalogs. You can use
LF-Tags to grant permissions on existing S3 Tables catalogs without deleting and
recreating them.
Enabling LF-Tags support for existing federated catalogs that uses Lake Formation permissions
Follow these steps, if you have existing federated catalogs that are using Lake Formation
permissions, such as Amazon Redshift or Amazon DynamoDB catalogs that were created before
LF-Tags support was available for federated catalogs.
-
Delete the existing catalog – Call the deleteCatalog API operation to remove the existing federated catalog that uses Lake Formation permissions.
-
Create a new federated catalog – Create a new catalog and point the new catalog to your existing namespace/datashare.
Use a new name for the catalog – This process updates your pre-existing
federated catalogs to support LF-Tag functionality. If you want to use the
same catalog name, contact Amazon support team for assistance.
Granting Data Catalog permissions
Use the Lake Formation console or Amazon CLI to grant
Lake Formation permissions on Data Catalog databases, tables, views, and columns using the Lake Formation tag-based access control (LF-TBAC) method.
- Console
-
The following steps explain how to grant permissions by using the Lake Formation tag-based access
control (LF-TBAC) method and the Grant data lake permissions page on the Lake Formation
console. The page is divided into the following sections:
-
Principals – The users, roles, and Amazon Web Services accounts to
grant permissions to.
-
LF-Tags or catalog resources – The databases,
tables, or resource links to grant permissions on.
-
Permissions – The Lake Formation permissions to grant.
-
Open the Grant data lake permissions page.
Open the Amazon Lake Formation console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/lakeformation/, and sign in as a
data lake administrator or as a user who has been granted Lake Formation permissions on
Data Catalog resources through LF-TBAC with the grant option.
In the navigation pane, under Permissions, choose Data lake permissions. Then
choose Grant.
-
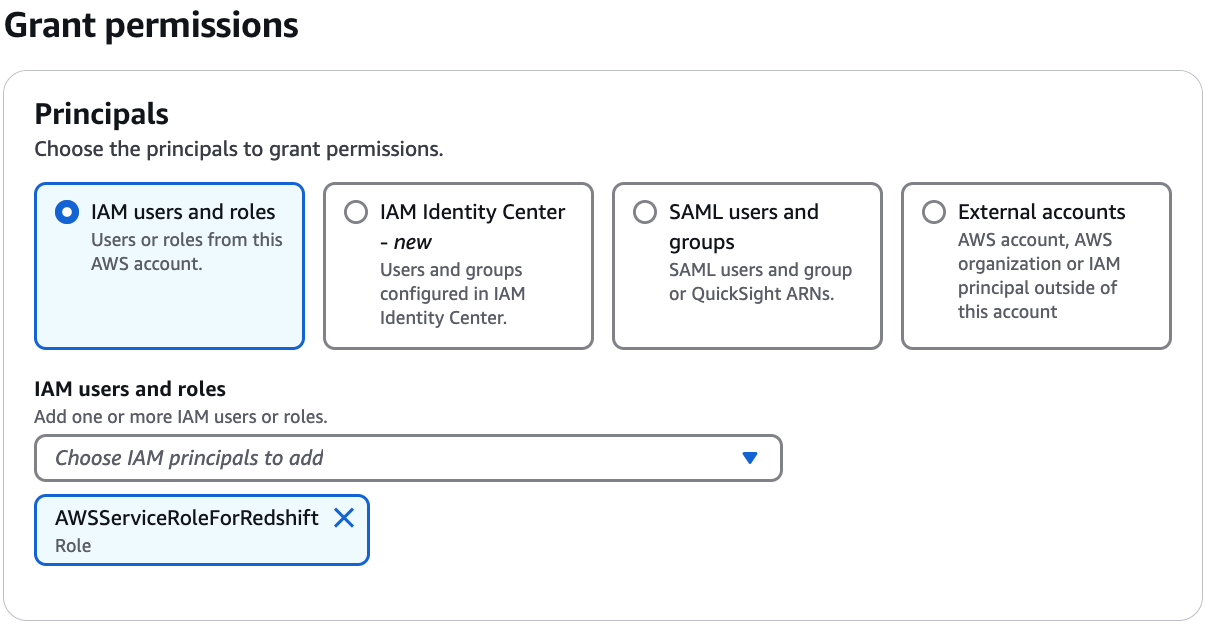
Specify the principals.
In the Principals section, choose a principal type and then
specify principals to grant permissions to.
- IAM users and roles
-
Choose one or more users or roles from the IAM users and
roles list.
- IAM Identity Center
-
Choose one or more users or from the Users and
groups list.
- SAML users and groups
-
For SAML and Quick Suite users and groups,
enter one or more Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) for users or groups federated
through SAML, or ARNs for Quick Suite users or groups. Press Enter
after each ARN.
For information about how to construct the ARNs, see Lake Formation grant and revoke Amazon CLI commands.
Lake Formation integration with Quick Suite is supported for
Quick Suite Enterprise Edition only.
- External accounts
-
For Amazon Web Services accounts, Amazon organization, or
IAM principal enter one or more valid
Amazon Web Services account IDs, organization IDs, organizational unit IDs, or ARN for the
IAM user or role. Press Enter after each ID.
An organization ID consists of "o-" followed
by 10 to 32 lower-case letters or digits.
An organizational unit ID starts with "ou-" followed by 4 to 32 lowercase letters or digits (the ID of the root that contains the OU).
This string is followed by a second "-" dash and 8 to 32 additional lowercase letters or digits.
-
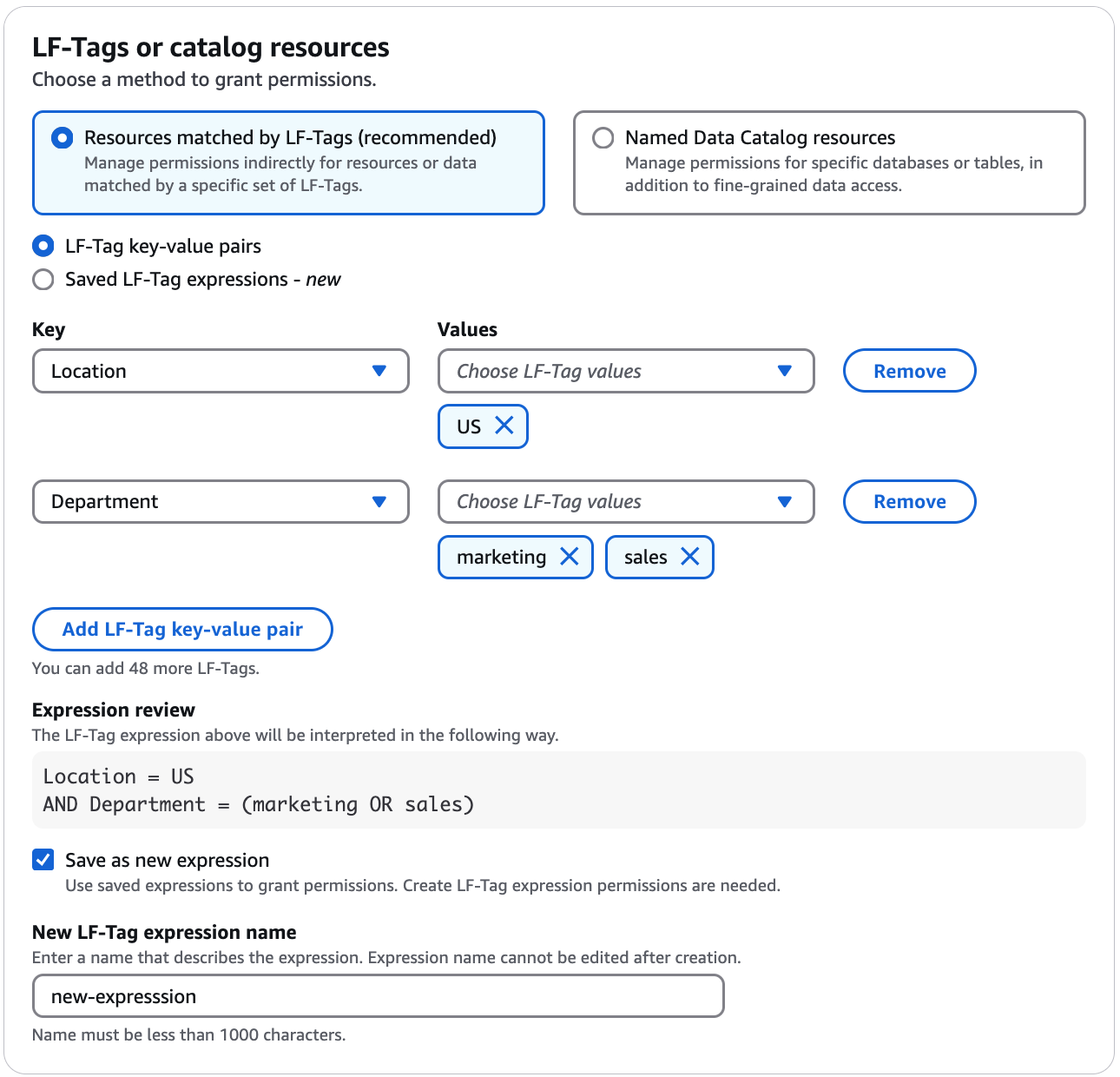
Ensure that the Resources matched by LF-Tags option
is chosen. Choose LF-Tag key-value pairs or Saved LF-Tag expressions.
-
If you choose the LF-Tag key-value pairs option, choose the keys and values.
If you choose more than one value, you are creating a LF-Tag expression with an
OR operator. This means that if any of the LF-Tag values match a
LF-Tag assigned to a Data Catalog resource, you are granted permissions on the
resource.
-
(Optional) Choose Add LF-Tag key-value pair again to specify another
LF-Tag.
If you specify more than one LF-Tag, you are creating a LF-Tag expression with an
AND operator. The principal is granted permissions on a Data Catalog
resource only if the resource was assigned a matching LF-Tag for each LF-Tag
in the LF-Tag expression.
-
Choose Save as a new expression option to reuse the expression.
You need Create LF-Tag expression to save expressions.
For more information about LF-Tag expressions, see Managing LF-Tag expressions for metadata access
control.
-
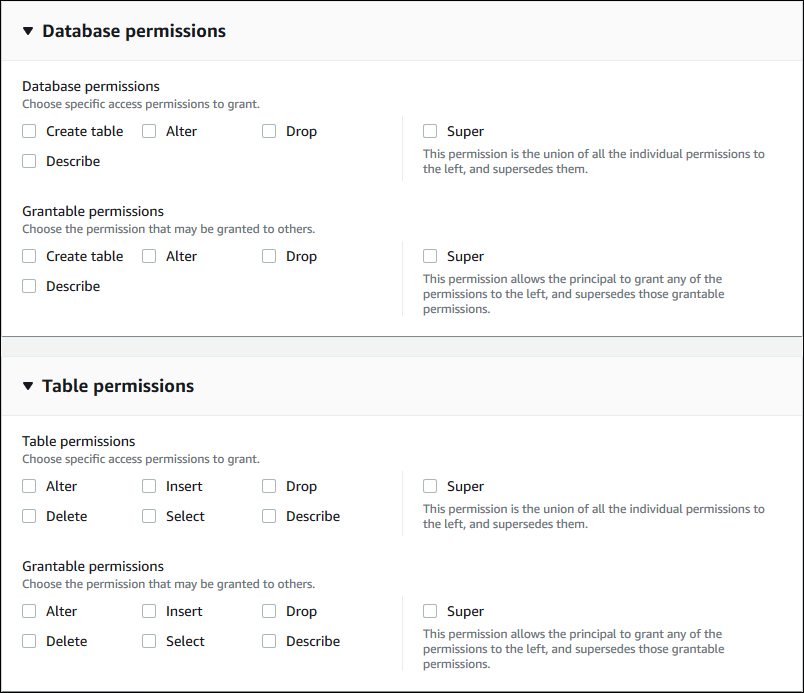
Specify the permissions.
Specify the permissions that you want to grant the principal on matching Data Catalog
resources. Matching resources are those resources that were assigned LF-Tags that
match one of the LF-Tag expressions granted to the principal.
You can specify the permissions to grant on matching databases, matching tables,
and matching views.
Under Database permissions, select the database
permissions to grant to the principal on matching databases.
Under Table permissions, select the table or view permissions
to grant to the principal on matching tables and views.
You can also choose Select, Describe, and Drop permissions from the Table permissions to apply on views.
-
Choose Grant.
- Amazon CLI
-
You can use the Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI) and the Lake Formation tag-based access control (LF-TBAC) method to
grant Lake Formation permissions on Data Catalog databases, tables, and columns.
Granting data lake permissions using the
Amazon CLI and the LF-TBAC method