Sharing a data lake using Lake Formation tag-based access control and named resources
This tutorial demonstrates how you can configure Amazon Lake Formation to securely share data stored within a data lake with multiple companies, organizations, or business units, without having to copy the entire database. There are two options to share your databases and tables with another Amazon Web Services account by using Lake Formation cross-account access control:
Lake Formation tag-based access control (recommended)
Lake Formation tag-based access control is an authorization strategy that defines permissions based on attributes. In Lake Formation, these attributes are called LF-Tags. For more details, refer to Managing a data lake using Lake Formation tag-based access control.
Lake Formation named resources
The Lake Formation named resource method is an authorization strategy that defines permissions for resources. Resources include databases, tables, and columns. Data lake administrators can assign and revoke permissions on Lake Formation resources. For more details, refer to Cross-account data sharing in Lake Formation.
We recommend using named resources if the data lake administrator prefers granting permissions explicitly to individual resources. When you use the named resource method to grant Lake Formation permissions on a Data Catalog resource to an external account, Lake Formation uses Amazon Resource Access Manager (Amazon RAM) to share the resource.
Topics
Intended audience
This tutorial is intended for data stewards, data engineers, and data analysts. When it comes to sharing Data Catalog tables from Amazon Glue and administering permission in Lake Formation, data stewards within the producing accounts have functional ownership based on the functions they support, and can grant access to various consumers, external organizations, and accounts. The following table lists the roles that are used in this tutorial:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| DataLakeAdminProducer | The data lake admin IAM user has the following access:
|
| DataLakeAdminConsumer |
The data lake admin IAM user has the following access:
|
| DataAnalyst | The DataAnalyst user has the following access:
|
Configure Lake Formation Data Catalog settings in the producer account
Before you start this tutorial, you must have an Amazon Web Services account that you can use to sign in as an administrative user with correct permissions. For more information, see Complete initial Amazon configuration tasks.
The tutorial assumes that you are familiar with IAM. For information about IAM, see the IAM User Guide
Configure Lake Formation Data Catalog settings in the producer account
Note
In this tutorial, the account that has the source table is called the producer account, and the account that needs access to the source table is called a consumer account.
Lake Formation provides its own permission management model. To maintain backward compatibility
with the IAM permission model, the Super permission is granted to the group
IAMAllowedPrincipals on all existing Amazon Glue Data Catalog resources by default. Also,
Use only IAM access control settings are enabled for new Data Catalog
resources. This tutorial uses fine grained access control using Lake Formation permissions and use
IAM policies for coarse grained access control. See Methods for fine-grained access control for
details. Therefore, before you use an Amazon CloudFormation template for a quick setup, you need to
change Lake Formation Data Catalog settings in the producer account.
Important
This setting affects all newly created databases and tables, so we strongly recommend completing this tutorial in a non-production account or in a new account. Also, if you are
using a shared account (such as your company’s development account), make sure it does not affect others resources. If you prefer to keep the default security settings, you must
complete an extra step when sharing resources to other accounts, in which you revoke the default Super permission from IAMAllowedPrincipals on
the database or table. We discuss the details later in this tutorial.
To configure Lake Formation Data Catalog settings in the producer account, complete the following steps:
Sign into the Amazon Web Services Management Console using the producer account as an admin user, or as a user with Lake Formation
PutDataLakeSettingsAPI permission.-
On the Lake Formation console, in the navigation pane, under Data Catalog, choose Settings.
-
Deselect Use only IAM access control for new databases and Use only IAM access control for new tables in new databases
Choose Save.
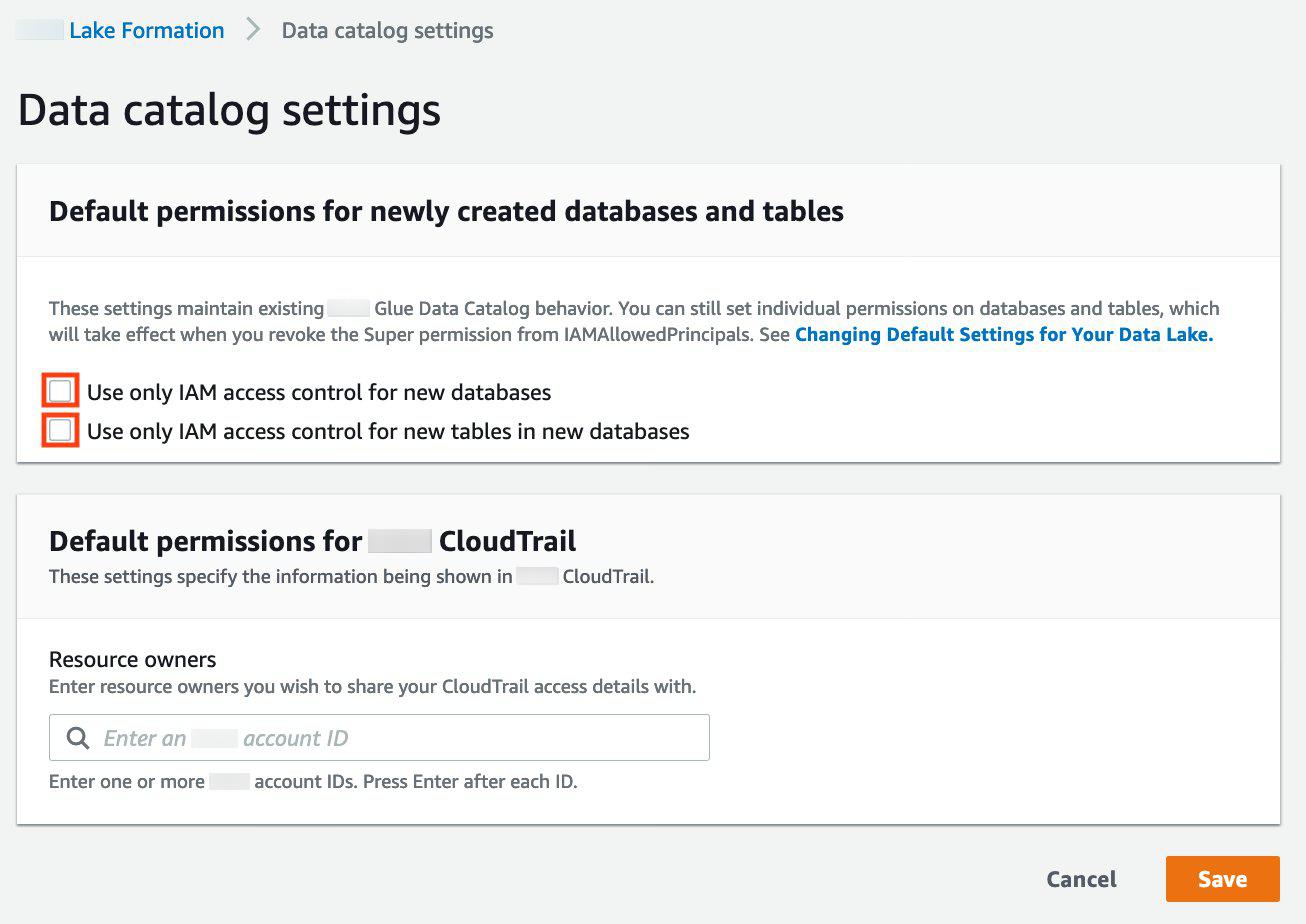
Additionally, you can remove
CREATE_DATABASEpermissions forIAMAllowedPrincipalsunder Administrative roles and tasks, Database creators. Only then, you can govern who can create a new database through Lake Formation permissions.
Step 1: Provision your resources using Amazon CloudFormation templates
The CloudFormation template for the producer account generates the following resources:
An Amazon S3 bucket to serve as the data lake.
A Lambda function (for Lambda-backed Amazon CloudFormation custom resources). We use the function to copy sample data files from the public Amazon S3 bucket to your Amazon S3 bucket.
IAM users and policies: DataLakeAdminProducer.
The appropriate Lake Formation settings and permissions including:
Defining the Lake Formation data lake administrator in the producer account
Registering an Amazon S3 bucket as the Lake Formation data lake location (producer account)
An Amazon Glue Data Catalog database, table, and partition. Since there are two options for sharing resources across Amazon Web Services accounts, this template creates two separate sets of database and table.
The Amazon CloudFormation template for the consumer account generates the following resources:
IAM users and policies:
DataLakeAdminConsumer
DataAnalyst
-
An Amazon Glue Data Catalog database. This database is for creating resource links to shared resources.
Create your resources in the producer account
Sign into the Amazon CloudFormation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/cloudformation
in the US East (N. Virginia) region. Choose Launch Stack
. -
Choose Next.
For Stack name, enter a stack name, such as
stack-producer.-
In the User Configuration section, enter user name and password for
ProducerDatalakeAdminUserNameandProducerDatalakeAdminUserPassword. -
For DataLakeBucketName, enter the name of your data lake bucket. This name needs to be globally unique.
-
For DatabaseName and TableName, leave the default values.
-
Choose Next.
-
On the next page, choose Next.
Review the details on the final page and select I acknowledge that Amazon CloudFormation might create IAM resources.
Choose Create.
The stack creation can take up to one minute.
Create your resources in the consumer account
Sign into the Amazon CloudFormation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/cloudformation
in the US East (N. Virginia) region. Choose Launch Stack
. -
Choose Next.
For Stack name, enter a stack name, such as
stack-consumer.-
In the User Configuration section, enter user name and password for
ConsumerDatalakeAdminUserNameandConsumerDatalakeAdminUserPassword. For
DataAnalystUserNameandDataAnalystUserPassword, enter the user name and password you want for the data analyst IAM user.-
For DataLakeBucketName, enter the name of your data lake bucket. This name needs to be globally unique.
-
For DatabaseName, leave the default values.
For
AthenaQueryResultS3BucketName, enter the name of the Amazon S3 bucket that stores Amazon Athena query results. If you don’t have one, create an Amazon S3 bucket. -
Choose Next.
-
On the next page, choose Next.
Review the details on the final page and select I acknowledge that Amazon CloudFormation might create IAM resources.
Choose Create.
The stack creation can take up to one minutes.
Note
After completing the tutorial, delete the stack in Amazon CloudFormation to avoid incurring charges. Verify that the resources are successfully deleted in the event status for the stack.
Step 2: Lake Formation cross-account sharing prerequisites
Before sharing resources with Lake Formation, there are prerequisites for both the tag-based access control method and named resource method.
Complete tag-based access control cross-account data sharing prerequisites
-
For more information on cross-account data sharing requirements, see the Prerequisites section in the Cross-account data sharing chapter.
To share Data Catalog resources with version 3 or above of the Cross account version settings, the grantor requires to have the IAM permissions defined in the Amazon managed policy
AWSLakeFormationCrossAccountManagerin your account.If you are using version 1 or version 2 of the Cross account version settings, before you can use the tag-based access control method to grant cross-account access to resources, you must add the following
JSONpermissions object to the Data Catalog resource policy in the producer account. This gives the consumer account permission to access the Data Catalog whenglue:EvaluatedByLakeFormationTagsis true. Also, this condition becomes true for resources on which you granted permission using Lake Formation permission tags to the consumer’s account. This policy is required for every Amazon Web Services account to which you are granting permissions.The following policy must be within a
Statementelement. We discuss the full IAM policy in the next section.{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "glue:*" ], "Principal": { "AWS": [ "consumer-account-id" ] }, "Resource": [ "arn:aws:glue:region:account-id:table/*", "arn:aws:glue:region:account-id:database/*", "arn:aws:glue:region:account-id:catalog" ], "Condition": { "Bool": { "glue:EvaluatedByLakeFormationTags": true } } }
Complete named resource method cross-account sharing prerequisites
-
If there is no Data Catalog resource policy in your account, the Lake Formation cross-account grants that you make proceed as usual. However, if a Data Catalog resource policy exists, you must add the following statement to it to permit your cross-account grants to succeed if they’re made with the named resource method. If you plan to use only the named resource method, or only the tag-based access control method, you can skip this step. In this tutorial, we evaluate both methods, and we need to add the following policy.
The following policy must be within a
Statementelement. We discuss the full IAM policy in the next section.{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "glue:ShareResource" ], "Principal": { "Service":"ram.amazonaws.com" }, "Resource": [ "arn:aws:glue:region:account-id:table/*/*", "arn:aws:glue:region:account-id:database/*", "arn:aws:glue:region:account-id:catalog" ] } Next, add the Amazon Glue Data Catalog resource policy using the Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI).
If you grant cross-account permissions by using both the tag-based access control method and named resource method, you must set the
EnableHybridargument to ‘true’ when adding the preceding policies. Because this option is not currently supported on the console, and you must use theglue:PutResourcePolicyAPI and Amazon CLI.First, create a policy document (such as policy.json) and add the preceding two policies. Replace
consumer-account-idwith theaccount IDof the Amazon Web Services account receiving the grant,regionwith the Region of the Data Catalog containing the databases and tables that you are granting permissions on, andaccount-idwith the producer Amazon Web Services account ID.Enter the following Amazon CLI command. Replace
glue-resource-policywith the correct values (such as file://policy.json).aws glue put-resource-policy --policy-in-jsonglue-resource-policy--enable-hybrid TRUEFor more information, see put-resource-policy.
Step 3: Implement cross-account sharing using the tag-based access control method
In this section, we walk you through the following high-level steps:
-
Define an LF-Tag.
-
Assign the LF-Tag to the target resource.
-
Grant LF-Tag permissions to the consumer account.
-
Grant data permissions to the consumer account.
Optionally, revoke permissions for
IAMAllowedPrincipalson the database, tables, and columns.Create a resource link to the shared table.
Create an LF-Tag and assign it to the target database.
Grant LF-Tag data permissions to the consumer account.
Define an LF-Tag
Note
If you are signed in to your producer account, sign out before completing the following steps.
Sign into the producer account as the data lake administrator at https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
. Use the producer account number, IAM user name (the default is DatalakeAdminProducer), and password that you specified during Amazon CloudFormation stack creation.On the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
), in the navigation pane, under Permissions, choose LF-Tags and Permissions. Choose Add LF-Tag.
Assign the LF-Tag to the target resource
Assign the LF-Tag to the target resource and grant data permissions to another account
As a data lake administrator, you can attach tags to resources. If you plan to use a separate role, you may have to grant describe and attach permissions to the separate role.
In the navigation pane, under Data Catalog, select Databases.
Select the target database
(lakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_tbac)and on the Actions menu, choose Edit LF-Tags.For this tutorial, you assign an LF-Tag to a database, but you can also assign LF-Tags to tables and columns.
Choose Assign new LF-Tag.
Add the key
Confidentialityand valuepublic.Choose Save.
Grant LF-Tag permission to the consumer account
Still in the producer account, grant permissions to the consumer account to access the LF-Tag.
In the navigation pane, under Permissions, choose LF-Tags and permissions.
Choose the LF-Tags tab, and choose the key and values of the LF-Tag that is being shared with the consumer account (key
Confidentialityand valuepublic).Choose Grant permissions.
For Permission type, choose LF-Tag key-value pair permissions.
For Principals, choose External accounts.
Enter the target Amazon Web Services account ID.
Amazon Web Services accounts within the same organization appear automatically. Otherwise, you have to manually enter the Amazon Web Services account ID.
Under Permissions, select Describe.
This is the permissions given to the consumer account. Grantable permissions are permissions that the consumer account can grant to other principals.
Choose Grant.
At this point, the consumer data lake administrator should be able to find the policy tag being shared via the consumer account Lake Formation console, under Permissions, LF-Tags and permissions.
Grant data permission to the consumer account
We will now provide data access to the consumer account by specifying an LF-Tag expression and granting the consumer account access to any table or database that matches the expression..
In the navigation pane, under Permissions,Data lake permissions, choose Grant.
For Principals, choose External accounts, and enter the target Amazon Web Services account ID.
For LF-Tags or catalog resources, choose the key and values of the LF-Tag that is being shared with the consumer account (key
Confidentialityand valuepublic).For Permissions, under Resources matched by LF-Tags (recommended) choose Add LF-Tag.
Select the key and value of the tag that is being shared with the consumer account (key
Confidentialityand valuepublic).For Database permissions, select Describe under Database permissions to grant access permissions at the database level.
The consumer data lake administrator should be able to find the policy tag being shared via the consumer account on the Lake Formation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
, under Permissions, Administrative roles and tasks, LF-Tags. Select Describe under Grantable permissions so the consumer account can grant database-level permissions to its users.
For Table and column permissions, select Select and Describe under Table permissions.
Select Select and Describe under Grantable permissions.
Choose Grant.
Revoke permission for IAMAllowedPrincipals on the database, tables, and columns (Optional).
At the very beginning of this tutorial, you changed the Lake Formation Data Catalog settings. If you skipped that part, this step is required. If you changed your Lake Formation Data Catalog settings, you can skip this step.
In this step, we need to revoke the default Super permission
from IAMAllowedPrincipals on the database or table. See Step 4: Switch your data stores to the
Lake Formation permissions model for details.
Before revoking permission for IAMAllowedPrincipals, make sure that you
granted existing IAM principals with necessary permission through Lake Formation. This includes three
steps:
Add IAM permission to the target IAM user or role with the Lake Formation
GetDataAccessaction (with IAM policy).Grant the target IAM user or role with Lake Formation data permissions (alter, select, and so on).
Then, revoke permissions for
IAMAllowedPrincipals. Otherwise, after revoking permissions forIAMAllowedPrincipals, existing IAM principals may no longer be able to access the target database or Data Catalog.Revoking Super permission for
IAMAllowedPrincipalsis required when you want to apply the Lake Formation permission model (instead of the IAM policy model) to manage user access within a single account or among multiple accounts using the Lake Formation permission model. You do not have to revoke permission ofIAMAllowedPrincipalsfor other tables where you want to keep the traditional IAM policy model.At this point, the consumer account data lake administrator should be able to find the database and table being shared via the consumer account on the Lake Formation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
, under Data Catalog, databases. If not, confirm if the following are properly configured: The correct policy tag and values are assigned to the target databases and tables.
The correct tag permission and data permission are assigned to the consumer account.
Revoke the default super permission from
IAMAllowedPrincipalson the database or table.
Create a resource link to the shared table
When a resource is shared between accounts, and the shared resources are not put in the consumer accounts’ Data Catalog. To make them available, and query the underlying data of a shared table using services like Athena, we need to create a resource link to the shared table. A resource link is a Data Catalog object that is a link to a local or shared database or table. For details, see Creating resource links. By creating a resource link, you can:
Assign a different name to a database or table that aligns with your Data Catalog resource naming policies.
Use services such as Athena and Redshift Spectrum to query shared databases or tables.
To create a resource link, complete the following steps:
If you are signed into your consumer account, sign out.
Sign in as the consumer account data lake administrator. Use the consumer account ID, IAM user name (default DatalakeAdminConsumer) and password that you specified during Amazon CloudFormation stack creation.
On the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
), in the navigation pane, under Data Catalog, Databases, choose the shared database lakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_tbac.If you don’t see the database, revisit the previous steps to see if everything is properly configured.
Choose View Tables.
Choose the shared table
amazon_reviews_table_tbac.On the Actions menu, choose Create resource link.
For Resource link name, enter a name (for this tutorial,
amazon_reviews_table_tbac_resource_link).Under Database, select the database that the resource link is created in (for this post, the Amazon CloudFormationn stack created the database
lakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_consumer).Choose Create.
The resource link appears under Data catalog, Tables.
Create an LF-tag and assign it to the target database
Lake Formation tags reside in the same Data Catalog as the resources. This means that tags created in the producer account are not available to use when granting access to the resource links in the consumer account. You need to create a separate set of LF-tags in the consumer account to use LF tag-based access control when sharing the resource links in the consumer account.
Define the LF-tag in the consumer account. For this tutorial, we use key
Divisionand valuessales,marketing, andanalyst.Assign the LF-tag key
Divisionand valueanalystto the databaselakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_consumer, where the resource link is created.
Grant LF-tag data permission to the consumer
As a final step, grant LF-tag data permission to the consumer.
In the navigation pane, under Permissions, Data lake permissions, choose Grant.
For Principals, choose IAM users and roles, and choose the user
DataAnalyst.For LF-tags or catalog resources, choose Resources matched by LF-Tags (recommended).
Choose key Division and value analyst.
For Database permissions, select Describe under Database permissions.
For Table and column permissions, select Select and Describe under Table permissions.
Choose Grant.
Repeat these steps for user
DataAnalyst, where the LF-Tag key isConfidentialityand value ispublic.At this point, the data analyst user in the consumer account should be able to find the database and resource link, and query the shared table via the Athena console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/athena/
. If not, confirm if the following are properly configured: The resource link is created for the shared table
You granted the user access to the LF-Tag shared by the producer account
You granted the user access to the LF-Tag associated to the resource link and database that the resource link is created in
Check if you assigned the correct LF-Tag to the resource link, and to the database that the resource link is created in
Step 4: Implement the named resource method
To use the named resource method, we walk you through the following high-level steps:
Optionally, revoke permission for
IAMAllowedPrincipalson the database, tables, and columns.Grant data permission to the consumer account.
Accept a resource share from Amazon Resource Access Manager.
Create a resource link for the shared table.
Grant data permission for the shared table to the consumer.
Grant data permission for the resource link to the consumer.
Revoke permission for IAMAllowedPrincipals on the database, tables, and columns (Optional)
-
At the very beginning of this tutorial, we changed Lake Formation Data Catalog settings. If you skipped that part, this step is required. For instructions, see the optional step in the previous section.
Grant data permission to the consumer account
-
Note
If you’re signed in to producer account as another user, sign out first.
Sign into the Lake Formation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
using the producer account data lake administrator using the Amazon Web Services account ID, IAM user name (default is DatalakeAdminProducer), and password specified during Amazon CloudFormation stack creation. On the Permissions page, under Data lake Permissions choose Grant.
Under Principals, choose External accounts, and enter one or more Amazon Web Services account IDs or Amazon organizations IDs. For more information see: Amazon Organizations
. Organizations that the producer account belongs to and Amazon Web Services accounts within the same organization appear automatically. Otherwise, manually enter the account ID or organization ID.
For LF-Tags or catalog resources, choose
Named data catalog resources.Under Databases, choose the database
lakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_named_resource.Choose Add LF-Tag.
Under Tables, choose All tables.
For Table column permissions¸ choose Select, and Describe under Table permissions.
SelectSelect and Describe, under Grantable Permissions.
Optionally, for Data permissions, choose Simple column-based access if column-level permission management is required.
Choose Grant.
If you have not revoked permission for IAMAllowedPrincipals, you get a Grant permissions failed error.
At this point, you should see the target table being shared via Amazon RAM with the consumer account under Permissions, Data permissions.
Accept a resource share from Amazon RAM
Note
This step is required only for Amazon Web Services account-based sharing, not for organization-based sharing.
Sign into the Amazon console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/connect/
using the consumer account data lake administrator using the IAM user name (default is DatalakeAdminConsumer) and password specified during Amazon CloudFormation stack creation. On the Amazon RAM console, in the navigation pane, under Shared with me, Resource shares, choose the shared Lake Formation resource. The Status should be Pending.
Choose Action and Grant.
Confirm the resource details, and choose Accept resource share.
At this point, the consumer account data lake administrator should be able to find the shared resource on the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
) under Data Catalog, Databases.
Create a resource link for the shared table
Follow the instructions in Step 3: Implement cross-account sharing using the tag-based access control method (step 6) to create a resource link for a shared table. Name the resource link
amazon_reviews_table_named_resource_resource_link. Create the resource link in the databaselakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_consumer.
Grant data permission for the shared table to the consumer
To grant data permission for the shared table to the consumer, complete the following steps:
On the Lake Formationconsole (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
), under Permissions, Data lake permissions, choose Grant. For Principals, choose IAM users and roles, and choose the user
DataAnalyst.For LF-Tags or catalog resources, choose Named data catalog resources.
Under Databases, choose the database
lakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_named_resource. If you don’t see the database on the drop-down list, choose Load more.Under Tables, choose the table
amazon_reviews_table_named_resource.For Table and column permissions, select Select and Describe under Table permissions.
Choose Grant.
Grant data permission for the resource link to the consumer
In addition to granting the data lake user permission to access the shared table, you also need to grant the data lake user permission to access the resource link.
On the Lake Formation console (https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
), under Permissions, Data lake permissions, choose Grant. For Principals, choose IAM users and roles, and choose the user
DataAnalyst.For LF-Tags or catalog resources, choose Named data catalog resources.
Under Databases, choose the database
lakeformation_tutorial_cross_account_database_consumer. If you don’t see the database on the drop-down list, choose Load more.Under Tables, choose the table
amazon_reviews_table_named_resource_resource_link.For Resource link permissions, select Describe under Resource link permissions.
Choose Grant.
At this point, the data analyst user in the consumer account should be able to find the database and resource link, and query the shared table via the Athena console.
If not, confirm if the following are properly configured:
The resource link is created for the shared table
You granted the user access to the table shared by the producer account
You granted the user access to the resource link and database for which the resource link is created
Step 5: Clean up Amazon resources
To prevent unwanted charges to your Amazon Web Services account, you can delete the Amazon resources that you used for this tutorial.
-
Sign into Lake Formation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
using the producer account and delete or change the following: Amazon Resource Access Manager resource share
Lake Formation tags
Amazon CloudFormation stack
Lake Formation settings
Amazon Glue Data Catalog
Sign into Lake Formation console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/lakeformation/
using the consumer account and delete or change the following: Lake Formation tags
Amazon CloudFormation stack