• Amazon Systems Manager Change Manager is no longer open to new customers. Existing customers can continue to use the service as normal. For more information, see Amazon Systems Manager Change Manager availability change.
• The Amazon Systems Manager CloudWatch Dashboard will no longer be available after April 30, 2026. Customers can continue to use Amazon CloudWatch console to view, create, and manage their Amazon CloudWatch dashboards, just as they do today. For more information, see Amazon CloudWatch Dashboard documentation.
Understanding targets and rate controls in State Manager associations
This topic describes State Manager features that help you deploy an association to dozens or hundreds of nodes while controlling the number of nodes that run the association at the scheduled time. State Manager is a tool in Amazon Systems Manager.
Using targets
When you create a State Manager association, you choose which nodes to configure with the association in the Targets section of the Systems Manager console, as shown here.
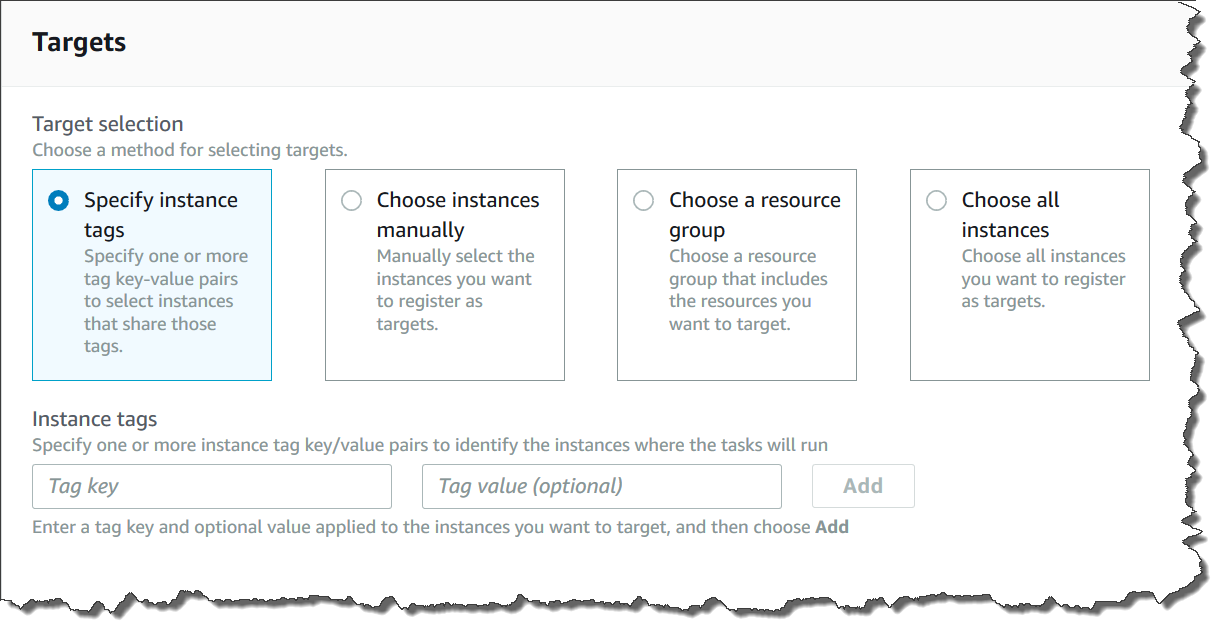
If you create an association by using a command line tool such as the
Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI), then you specify the targets parameter.
Targeting nodes allows you to configure tens, hundreds, or thousands of nodes
with an association without having to specify or choose individual node IDs.
Each managed node can be targeted by a maximum of 20 associations.
State Manager includes the following target options when creating an association.
Specify tags
Use this option to specify a tag key and (optionally) a tag value assigned to your nodes. When you run the request, the system locates and attempts to create the association on all nodes that match the specified tag key and value. If you specified multiple tag values, the association targets any node with at least one of those tag values. When the system initially creates the association, it runs the association. After this initial run, the system runs the association according to the schedule you specified.
If you create new nodes and assign the specified tag key and value to those nodes, the system automatically applies the association, runs it immediately, and then runs it according to the schedule. This applies when the association uses a Command or Policy document and doesn't apply if the association uses an Automation runbook. If you delete the specified tags from a node, the system no longer runs the association on those nodes.
Note
If you use Automation runbooks with State Manager and the tagging limitation prevents you from achieving a specific goal, consider using Automation runbooks with Amazon EventBridge. For more information, see Run automations based on EventBridge events. For more information about using runbooks with State Manager, see Scheduling automations with State Manager associations.
As a best practice, we recommend using tags when creating associations that use a Command or Policy document. We also recommend using tags when creating associations to run Auto Scaling groups. For more information, see Running Auto Scaling groups with associations.
Note
Note the following information.
-
When creating an association in the Amazon Web Services Management Console that targets nodes by using tags, you can specify only one tag key for an automation association and five tag keys for a command association. All tag keys specified in the association must be currently assigned to the node. If they aren't, State Manager fails to target the node for an association.
-
If you want to use the console and you want to target your nodes by using more than one tag key for an automation association and five tag keys for a command association, assign the tag keys to an Amazon Resource Groups group and add the nodes to it. You can then choose the Resource Group option in the Targets list when you create the State Manager association.
-
You can specify a maximum of five tag keys by using the Amazon CLI. If you use the Amazon CLI, all tag keys specified in the
create-associationcommand must be currently assigned to the node. If they aren't, State Manager fails to target the node for an association.
Choose nodes manually
Use this option to manually select the nodes where you want to create the association. The Instances pane displays all Systems Manager managed nodes in the current Amazon Web Services account and Amazon Web Services Region. You can manually select as many nodes as you want. When the system initially creates the association, it runs the association. After this initial run, the system runs the association according to the schedule you specified.
Note
If a managed node you expect to see isn't listed, see Troubleshooting managed node availability for troubleshooting tips.
Choose a resource group
Use this option to create an association on all nodes returned by an Amazon Resource Groups tag-based or Amazon CloudFormation stack-based query.
Below are details about targeting resource groups for an association.
-
If you add new nodes to a group, the system automatically maps the nodes to the association that targets the resource group. The system applies the association to the nodes when it discovers the change. After this initial run, the system runs the association according to the schedule you specified.
-
If you create an association that targets a resource group and the
AWS::SSM::ManagedInstanceresource type was specified for that group, then by design, the association runs on both Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances and non-EC2 nodes in a hybrid and multicloud environment.The converse is also true. If you create an association that targets a resource group and the
AWS::EC2::Instanceresource type was specified for that group, then by design, the association runs on both non-EC2 nodes in a hybrid and multicloud environment and (Amazon EC2) instances. -
If you create an association that targets a resource group, the resource group must not have more than five tag keys assigned to it or more than five values specified for any one tag key. If either of these conditions applies to the tags and keys assigned to your resource group, the association fails to run and returns an
InvalidTargeterror. -
If you create an association that targets a resource group using tags, you can't choose the (empty value) option for the tag value.
-
If you delete a resource group, all instances in that group no longer run the association. As a best practice, delete associations targeting the group.
-
At most you can target a single resource group for an association. Multiple or nested groups aren't supported.
-
After you create an association, State Manager periodically updates the association with information about resources in the Resource Group. If you add new resources to a Resource Group, the schedule for when the system applies the association to the new resources depends on several factors. You can determine the status of the association in the State Manager page of the Systems Manager console.
Warning
An Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) user, group, or role with permission to create an association that targets a resource group of Amazon EC2 instances automatically has root-level control of all instances in the group. Only trusted administrators should be permitted to create associations.
For more information about Resource Groups, see What Is Amazon Resource Groups? in the Amazon Resource Groups User Guide.
Choose all nodes
Use this option to target all nodes in the current Amazon Web Services account and Amazon Web Services Region. When you run the request, the system locates and attempts to create the association on all nodes in the current Amazon Web Services account and Amazon Web Services Region. When the system initially creates the association, it runs the association. After this initial run, the system runs the association according to the schedule you specified. If you create new nodes, the system automatically applies the association, runs it immediately, and then runs it according to the schedule.
Using rate controls
You can control the execution of an association on your nodes by specifying a concurrency value and an error threshold. The concurrency value specifies how many nodes can run the association simultaneously. An error threshold specifies how many association executions can fail before Systems Manager sends a command to each node configured with that association to stop running the association. The command stops the association from running until the next scheduled execution. The concurrency and error threshold features are collectively called rate controls.

Concurrency
Concurrency helps to limit the impact on your nodes by allowing you to specify that only a certain number of nodes can process an association at one time. You can specify either an absolute number of nodes, for example 20, or a percentage of the target set of nodes, for example 10%.
State Manager concurrency has the following restrictions and limitations:
-
If you choose to create an association by using targets, but you don't specify a concurrency value, then State Manager automatically enforces a maximum concurrency of 50 nodes.
-
If new nodes that match the target criteria come online while an association that uses concurrency is running, then the new nodes run the association if the concurrency value isn't exceeded. If the concurrency value is exceeded, then the nodes are ignored during the current association execution interval. The nodes run the association during the next scheduled interval while conforming to the concurrency requirements.
-
If you update an association that uses concurrency, and one or more nodes are processing that association when it's updated, then any node that is running the association is allowed to complete. Those associations that haven't started are stopped. After running associations complete, all target nodes immediately run the association again because it was updated. When the association runs again, the concurrency value is enforced.
Error thresholds
An error threshold specifies how many association executions are allowed to fail before Systems Manager sends a command to each node configured with that association. The command stops the association from running until the next scheduled execution. You can specify either an absolute number of errors, for example 10, or a percentage of the target set, for example 10%.
If you specify an absolute number of three errors, for example, State Manager sends the stop command when the fourth error is returned. If you specify 0, then State Manager sends the stop command after the first error result is returned.
If you specify an error threshold of 10% for 50 associations, then State Manager sends the stop command when the sixth error is returned. Associations that are already running when an error threshold is reached are allowed to complete, but some of these associations might fail. To ensure that there aren't more errors than the number specified for the error threshold, set the Concurrency value to 1 so that associations proceed one at a time.
State Manager error thresholds have the following restrictions and limitations:
-
Error thresholds are enforced for the current interval.
-
Information about each error, including step-level details, is recorded in the association history.
-
If you choose to create an association by using targets, but you don't specify an error threshold, then State Manager automatically enforces a threshold of 100% failures.